Authoritarian leaders exert strict control and expect obedience, often leading to reduced team morale and creativity. Humble leaders, by embracing vulnerability and valuing others' input, foster collaboration and trust within their teams. This inclusive approach enhances innovation and long-term organizational success.
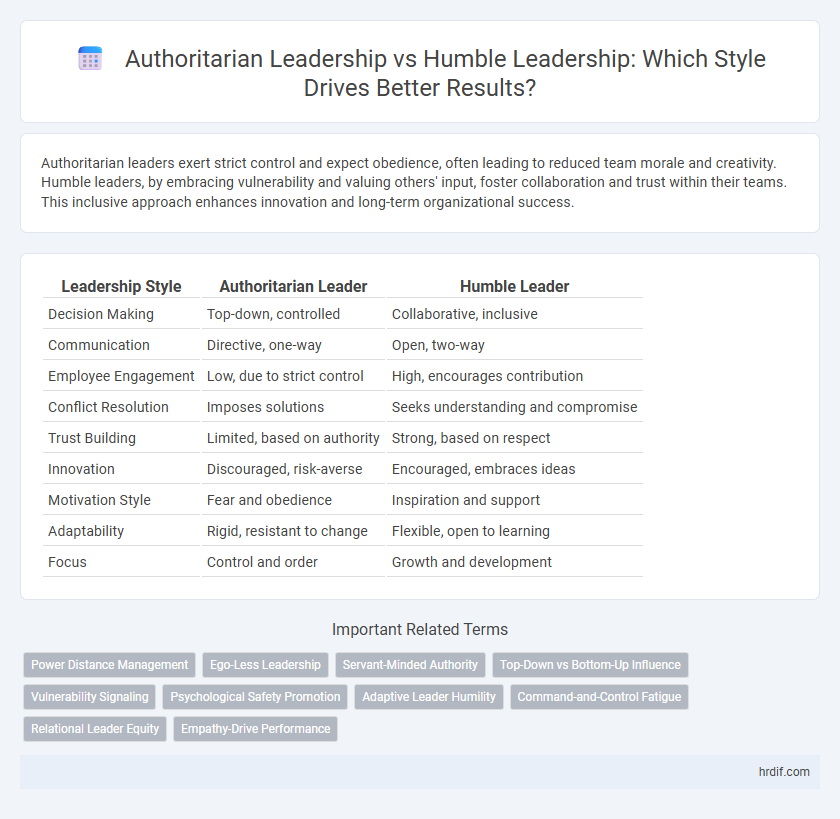
Table of Comparison
| Leadership Style | Authoritarian Leader | Humble Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Top-down, controlled | Collaborative, inclusive |
| Communication | Directive, one-way | Open, two-way |
| Employee Engagement | Low, due to strict control | High, encourages contribution |
| Conflict Resolution | Imposes solutions | Seeks understanding and compromise |
| Trust Building | Limited, based on authority | Strong, based on respect |
| Innovation | Discouraged, risk-averse | Encouraged, embraces ideas |
| Motivation Style | Fear and obedience | Inspiration and support |
| Adaptability | Rigid, resistant to change | Flexible, open to learning |
| Focus | Control and order | Growth and development |
Defining Authoritarian and Humble Leadership Styles
Authoritarian leadership is characterized by centralized decision-making, strict control, and clear directives that demand compliance, often limiting team input. In contrast, humble leadership emphasizes empathy, openness to feedback, and shared authority, fostering collaboration and personal growth within the team. These distinct styles impact organizational culture and employee engagement differently, where authoritarianism can ensure order but reduce morale, while humility promotes trust and innovation.
Core Characteristics of Authoritarian Leaders
Authoritarian leaders exhibit core characteristics such as centralized decision-making, strict control, and clear hierarchical structures, often prioritizing obedience and discipline over collaboration. Their leadership style emphasizes unilateral authority and a top-down approach, which can lead to efficient execution but may stifle creativity and employee engagement. Understanding these traits is essential for distinguishing authoritarian leadership from more inclusive and humble leadership approaches that value openness and shared responsibility.
Essential Traits of Humble Leaders
Humble leaders demonstrate essential traits such as active listening, empathy, and a willingness to admit mistakes, fostering trust and collaboration within teams. Unlike authoritarian leaders who rely on control and command, humble leaders prioritize inclusivity and empower others to contribute their ideas and expertise. This approach enhances team morale, innovation, and long-term organizational success.
Decision-Making: Top-Down vs Collaborative Approaches
Authoritarian leaders rely on top-down decision-making, enforcing directives with minimal input from team members, which can lead to quick but less flexible outcomes. Humble leaders prioritize collaborative approaches, encouraging diverse perspectives and fostering collective problem-solving to enhance decision quality and team engagement. This contrast significantly impacts organizational culture, where authoritarian styles may suppress innovation and humble leadership promotes adaptability and shared responsibility.
Impact on Team Morale and Motivation
Authoritarian leaders often diminish team morale by imposing strict control and limiting employee autonomy, which can lead to decreased motivation and higher turnover rates. In contrast, humble leaders foster an inclusive environment that encourages collaboration and values individual contributions, resulting in increased employee engagement and sustained motivation. Studies from the Harvard Business Review indicate teams led by humble leaders exhibit 20% higher productivity and report greater job satisfaction.
Productivity and Performance Outcomes
Authoritarian leaders often drive short-term productivity through strict control and clear directives, but this can stifle creativity and long-term performance. Humble leaders foster collaboration and trust, enhancing employee engagement and sustained innovation that boosts overall organizational effectiveness. Research indicates teams led by humble leaders demonstrate higher adaptability and consistent performance improvements compared to authoritarian-led groups.
Adaptability in Dynamic Work Environments
Authoritarian leaders often struggle with adaptability in dynamic work environments due to their rigid decision-making styles and resistance to input from team members. In contrast, humble leaders embrace flexibility by encouraging collaboration, actively seeking feedback, and adjusting strategies based on evolving circumstances. This adaptability enhances team resilience and drives innovation in rapidly changing industries.
Conflict Resolution Strategies
Authoritarian leaders often rely on top-down decision-making and enforce strict rules to resolve conflicts quickly but may suppress team input, potentially escalating tensions. Humble leaders prioritize empathetic listening and collaborative problem-solving, fostering trust and mutual understanding that lead to sustainable conflict resolution. Effective leadership blends decisive action with openness to diverse perspectives to maintain harmony and drive team cohesion.
Employee Retention and Loyalty
Authoritarian leaders often experience higher employee turnover due to rigid control and limited autonomy, which stifles motivation and loyalty. In contrast, humble leaders foster trust and open communication, leading to increased employee retention and stronger organizational commitment. Studies show that organizations with humble leadership enjoy up to 30% higher employee loyalty and reduced turnover rates.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style for Organizational Success
Authoritarian leaders enforce strict control and clear directives, optimizing decision-making speed in crisis-driven environments. Humble leaders foster collaboration and emphasize emotional intelligence, improving team engagement and long-term innovation. Selecting the appropriate leadership style aligns organizational needs with cultural context, driving sustainable success.
Related Important Terms
Power Distance Management
Authoritarian leaders maintain high power distance by centralizing authority and enforcing strict control, often limiting open communication and subordinate autonomy; in contrast, humble leaders reduce power distance by promoting inclusive decision-making, encouraging feedback, and fostering a collaborative organizational culture. Effective power distance management in leadership directly influences employee engagement, innovation, and organizational adaptability.
Ego-Less Leadership
Ego-less leadership emphasizes humility and self-awareness, contrasting sharply with authoritarian leaders who prioritize control and ego-driven decision-making; this approach fosters collaboration, trust, and long-term organizational success. By minimizing personal ego, humble leaders create inclusive environments where diverse perspectives thrive, enhancing innovation and employee engagement.
Servant-Minded Authority
An authoritarian leader exerts control through directive power, while a humble leader practices servant-minded authority by prioritizing the growth and well-being of their team members. Servant leadership fosters trust, collaboration, and empowerment, leading to sustainable organizational success and stronger employee engagement.
Top-Down vs Bottom-Up Influence
Authoritarian leaders exert top-down influence through centralized decision-making, often limiting team input and innovation, which can stifle engagement and adaptability. Humble leaders embrace bottom-up influence by encouraging collaboration and valuing diverse perspectives, fostering a culture of trust, empowerment, and responsive problem-solving.
Vulnerability Signaling
Authoritarian leaders often conceal vulnerability to maintain control, which can hinder trust and openness, whereas humble leaders signal vulnerability to foster psychological safety and promote authentic team collaboration. This vulnerability signaling enhances emotional intelligence and resilience, driving stronger organizational commitment and adaptive problem-solving.
Psychological Safety Promotion
Authoritarian leaders often hinder psychological safety by enforcing rigid control and discouraging open communication, leading to reduced team creativity and trust. Humble leaders promote psychological safety by valuing input, admitting mistakes, and fostering an inclusive environment that enhances collaboration and employee well-being.
Adaptive Leader Humility
Adaptive leader humility enhances leadership effectiveness by balancing confidence with openness to feedback, fostering collaboration and innovation in dynamic environments. Unlike authoritarian leaders who rely on control and command, humble leaders embrace flexibility and continuous learning, driving sustainable team growth and resilience.
Command-and-Control Fatigue
Authoritarian leaders often trigger command-and-control fatigue by enforcing strict control and limiting autonomy, which drains employee motivation and stifles creativity. Humble leaders, conversely, foster empowerment and open communication, reducing fatigue and enhancing engagement and innovation in teams.
Relational Leader Equity
Authoritarian leaders often centralize decision-making, which can hinder relational leader equity by limiting collaboration and trust within teams, whereas humble leaders foster inclusivity and mutual respect, enhancing equity through open communication and shared power. Emphasizing empathy and active listening, humble leadership strengthens relational ties and promotes an equitable organizational culture.
Empathy-Drive Performance
Authoritarian leaders often rely on strict control and unilateral decision-making, which can stifle empathy and reduce team morale, whereas humble leaders foster an environment of trust and active listening, enhancing empathetic understanding that drives higher performance. Empathy-driven leadership promotes collaboration, emotional intelligence, and motivation, leading to sustained success and improved employee engagement.
Authoritarian Leader vs Humble Leader for Leadership. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com