A manager primarily directs teams by assigning tasks and monitoring performance to achieve organizational goals, often emphasizing control and efficiency. In contrast, a servant leader prioritizes the growth and well-being of team members, fostering trust and collaboration through empathy and support. This leadership style enhances employee engagement and drives sustainable success by empowering individuals rather than simply managing them.
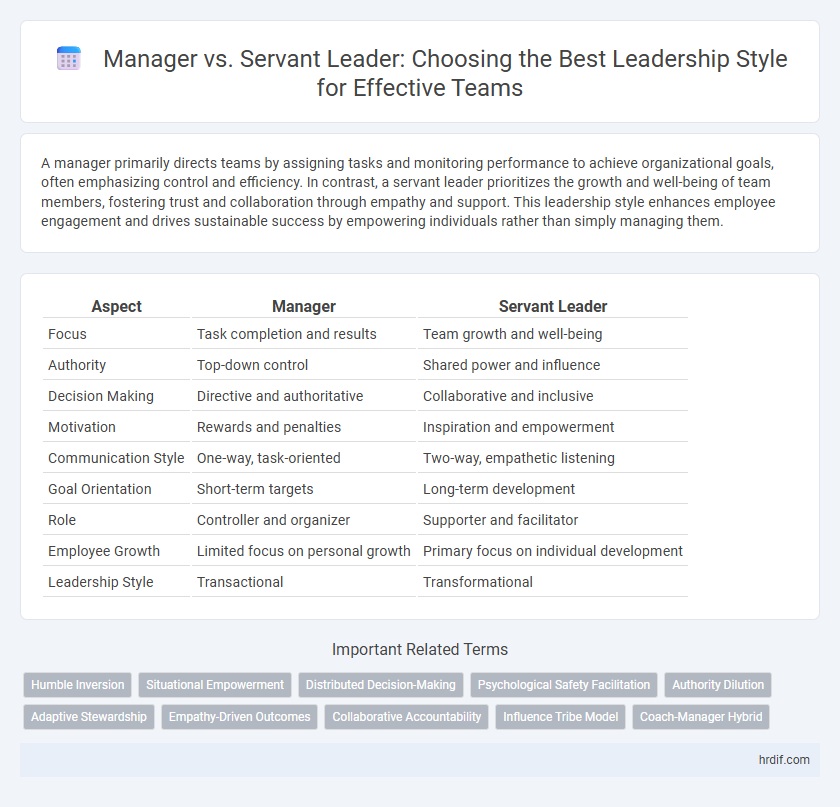
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Manager | Servant Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Task completion and results | Team growth and well-being |
| Authority | Top-down control | Shared power and influence |
| Decision Making | Directive and authoritative | Collaborative and inclusive |
| Motivation | Rewards and penalties | Inspiration and empowerment |
| Communication Style | One-way, task-oriented | Two-way, empathetic listening |
| Goal Orientation | Short-term targets | Long-term development |
| Role | Controller and organizer | Supporter and facilitator |
| Employee Growth | Limited focus on personal growth | Primary focus on individual development |
| Leadership Style | Transactional | Transformational |
Defining Managerial Leadership vs Servant Leadership
Managerial leadership focuses on directing tasks, overseeing performance, and maintaining organizational control through hierarchical authority. Servant leadership prioritizes serving team members' needs, fostering personal growth, and promoting a collaborative environment rooted in empathy and ethical behavior. The fundamental difference lies in the manager's emphasis on achieving objectives through control versus the servant leader's commitment to empowering individuals and cultivating trust.
Key Characteristics of Managers and Servant Leaders
Managers emphasize directive control, task delegation, and performance metrics to achieve organizational goals efficiently. Servant leaders prioritize empathy, active listening, and the growth and well-being of their team members, fostering a collaborative and supportive environment. While managers focus on authority and accountability, servant leaders cultivate trust and empowerment to inspire long-term commitment and innovation.
Core Values: Results vs People-Centric Approaches
Managers prioritize measurable results, emphasizing efficiency, targets, and organizational goals to drive performance. Servant leaders center their approach on people, fostering trust, empathy, and collaboration to cultivate team growth and well-being. Embracing servant leadership aligns core values with employee empowerment, leading to sustainable success through motivated and engaged teams.
Decision-Making: Top-Down vs Collaborative
Managers typically employ a top-down decision-making approach, relying on hierarchical authority to set directives and ensure compliance, which streamlines processes but may limit team input. Servant leaders prioritize collaborative decision-making by actively involving team members in problem-solving, fostering a culture of trust and shared responsibility. This inclusive method enhances creativity and commitment but requires more time and communication to reach consensus.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Motivation
Managers often focus on task completion and maintaining control, which can lead to compliance but may limit intrinsic motivation and employee engagement. Servant leaders prioritize empathy, support, and the growth of their team members, fostering higher levels of trust, motivation, and commitment. Research shows servant leadership correlates with increased job satisfaction, employee retention, and overall organizational performance.
Influence on Team Performance and Productivity
Managers typically exert influence through formal authority and directive control, which can create clear expectations but may limit team autonomy and creativity. Servant leaders prioritize the growth and well-being of team members, fostering trust, collaboration, and higher intrinsic motivation that often results in enhanced performance and sustainable productivity. Research indicates teams led by servant leaders show increased engagement, innovation, and resilience compared to those managed through traditional hierarchical approaches.
Communication Styles: Directive vs Empathetic
Managers typically use a directive communication style, focusing on clear instructions and task-oriented commands to achieve specific goals. Servant leaders employ an empathetic communication style, prioritizing active listening, emotional support, and fostering collaborative relationships to empower their teams. Research shows empathetic communication enhances team trust and engagement, while directive communication ensures efficiency and clarity in task execution.
Building Trust: Authority vs Service
Managerial leadership primarily builds trust through authority, clear expectations, and control, ensuring team members know their roles and responsibilities. Servant leadership fosters trust by prioritizing the needs and growth of team members, emphasizing empathy, active listening, and support. This service-oriented approach often results in deeper relational trust and greater employee engagement compared to the directive nature of managerial authority.
Pros and Cons of Managerial and Servant Leadership
Managerial leadership emphasizes control, task delegation, and organizational efficiency, which drives clear structures and accountability but may limit employee creativity and morale. Servant leadership prioritizes empathy, personal growth, and team well-being, fostering high employee engagement and collaboration, though it can result in slower decision-making and challenges in enforcing discipline. Balancing the directive strengths of managerial leadership with the supportive nature of servant leadership can optimize organizational performance and employee satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style for Your Career
Effective leaders understand the critical differences between manager and servant leader roles to choose the right leadership style for their career. Managers focus on task delegation, performance metrics, and organizational control, while servant leaders prioritize employee growth, empathy, and fostering collaboration. Selecting a leadership style aligned with personal values and team dynamics enhances engagement, productivity, and long-term success.
Related Important Terms
Humble Inversion
Servant leaders practicing humble inversion prioritize the growth and well-being of their team over authority, fostering trust and collaboration by serving rather than commanding. Managers often focus on control and efficiency, whereas humble servant leadership cultivates empowerment and shared purpose, driving sustainable success through empathy and humility.
Situational Empowerment
Managers often rely on authority and control to direct teams, while servant leaders prioritize situational empowerment by actively supporting and adapting to individual team members' needs. Situational empowerment under servant leadership enhances motivation and performance by fostering trust, autonomy, and collaboration in varying contexts.
Distributed Decision-Making
Distributed decision-making thrives under servant leadership, as servant leaders prioritize team empowerment and collective input to enhance accountability and innovation. Managers often centralize decisions, limiting opportunities for diverse perspectives that distributed leadership fosters to improve organizational agility.
Psychological Safety Facilitation
Managers often prioritize task completion and control, which can inhibit open communication and reduce psychological safety, whereas servant leaders actively foster trust and empathy, creating an environment where team members feel safe to express ideas and risks. Servant leadership enhances psychological safety by emphasizing active listening, support, and empowerment, resulting in higher team engagement and innovation.
Authority Dilution
Managerial leadership often centralizes decision-making authority, maintaining clear hierarchical control, whereas servant leadership diffuses power by prioritizing team empowerment and collaboration, resulting in notable authority dilution. This shift promotes shared responsibility and enhances organizational trust but challenges traditional command-and-control dynamics.
Adaptive Stewardship
Adaptive stewardship in leadership emphasizes a servant leader's commitment to empowering teams and fostering growth, contrasting with traditional managers who prioritize task completion and control. This approach cultivates resilience and innovation by adapting to changing environments while prioritizing the well-being and development of team members.
Empathy-Driven Outcomes
Managers prioritize task completion and efficiency through directive control, while servant leaders emphasize empathy-driven outcomes by deeply understanding and addressing team members' needs. Empathy in servant leadership fosters trust and collaboration, leading to sustainable performance and enhanced employee well-being.
Collaborative Accountability
A manager emphasizes hierarchical control and task delegation, whereas a servant leader fosters collaborative accountability by prioritizing team empowerment and shared responsibility. This leadership style cultivates trust and engagement, driving collective success through active participation and mutual support.
Influence Tribe Model
Managers typically rely on positional authority to direct teams, whereas servant leaders prioritize empowering and serving their followers to cultivate trust and collaboration; the Influence Tribe Model emphasizes how servant leadership fosters stronger group cohesion and sustained motivation through relational influence rather than formal power. Embracing the Influence Tribe Model, servant leaders drive organizational success by nurturing authentic connections and enabling others to realize their potential, contrasting with managers who often focus on task execution and hierarchical control.
Coach-Manager Hybrid
A Coach-Manager hybrid leadership style combines the directive, goal-oriented focus of traditional managers with the empathetic, development-centered approach of servant leaders, fostering both accountability and personal growth within teams. This blend enhances employee engagement and performance by balancing clear expectations with supportive coaching to unlock individual potential.
Manager vs Servant Leader for leadership style. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com