Choosing between franchise ownership and bootstrapping significantly impacts funding strategies for entrepreneurship pet businesses. Franchise owners benefit from established brand support and financing options but often face higher initial investment requirements and ongoing fees. Bootstrappers rely on personal savings and organic growth, allowing greater control and lower upfront costs but requiring disciplined financial management and slower scaling.
Table of Comparison
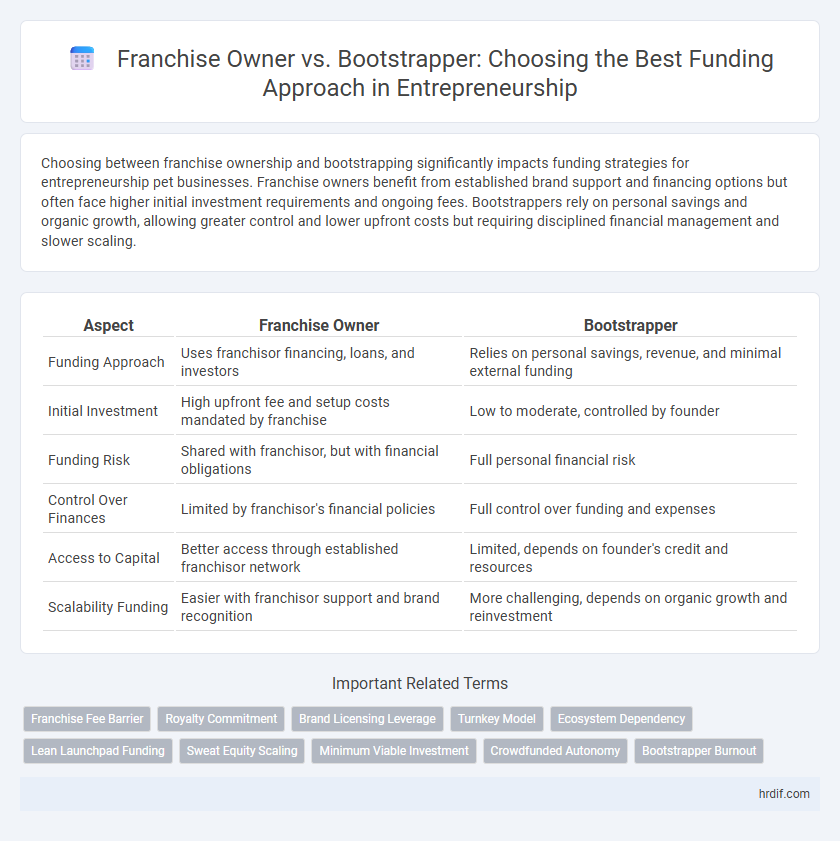
| Aspect | Franchise Owner | Bootstrapper |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Approach | Uses franchisor financing, loans, and investors | Relies on personal savings, revenue, and minimal external funding |
| Initial Investment | High upfront fee and setup costs mandated by franchise | Low to moderate, controlled by founder |
| Funding Risk | Shared with franchisor, but with financial obligations | Full personal financial risk |
| Control Over Finances | Limited by franchisor's financial policies | Full control over funding and expenses |
| Access to Capital | Better access through established franchisor network | Limited, depends on founder's credit and resources |
| Scalability Funding | Easier with franchisor support and brand recognition | More challenging, depends on organic growth and reinvestment |
Introduction: Franchise Owner vs Bootstrapper Funding
Franchise owners typically secure funding through loans, franchisor financing programs, or investors, leveraging the established brand and proven business model to attract capital. Bootstrappers rely primarily on personal savings, revenue reinvestment, and minimal external funding to maintain full control and reduce financial risk. Understanding these distinct funding approaches is crucial for entrepreneurs when evaluating scalability, resource allocation, and long-term financial strategy.
Defining the Franchise Funding Model
The franchise funding model typically involves securing capital through franchisor support, loans, or investors, enabling entrepreneurs to leverage established brand recognition and operational frameworks. Franchise owners benefit from structured financial guidance, fixed startup costs, and access to collective marketing funds, reducing investment risks compared to independent startups. This model contrasts with bootstrapping, where entrepreneurs rely primarily on personal savings and organic revenue growth, often facing higher financial uncertainty and limited external funding sources.
The Bootstrapper’s Approach to Financing
Bootstrappers primarily rely on personal savings, revenue from early sales, and tight cost control to finance their ventures, avoiding external funding sources to maintain full ownership and decision-making authority. This self-reliant approach fosters financial discipline and encourages innovative, resource-efficient strategies for growth. Unlike franchise owners who often access established funding channels and support systems, bootstrappers develop sustainable business models through organic growth and reinvestment.
Initial Investment: Costs and Considerations
Franchise owners face higher initial investments due to franchise fees, mandatory equipment, and marketing contributions, providing a structured business model with built-in brand recognition and support. Bootstrappers rely on personal savings or small loans, minimizing upfront costs but requiring greater resourcefulness and risk management to build their brand from the ground up. Understanding the balance between these funding approaches is crucial for entrepreneurs assessing capital availability and long-term growth potential.
Access to Capital: Franchise vs. Bootstrap
Franchise owners typically benefit from established brand recognition and proven business models, making it easier to secure startup capital through traditional lenders and franchisor financing programs. Bootstrappers rely predominantly on personal savings, revenue reinvestment, and smaller-scale funding sources, often facing greater challenges in accessing substantial external capital. This contrast in funding approaches significantly impacts the scalability and financial risk management of each entrepreneurial path.
Risk and Reward Profiles in Funding
Franchise owners typically benefit from established brand recognition and proven business models, reducing risk but limiting reward potential due to royalty fees and initial franchise costs. Bootstrappers face higher personal financial risk, relying on minimal external funding while retaining full control and maximizing profits from successful ventures. The funding approach directly influences risk tolerance and reward scale, with franchise ownership offering stability and bootstrapping offering entrepreneurial freedom.
Scalability and Growth Prospects
Franchise owners benefit from established brand recognition and support systems, enabling faster scalability due to access to proven business models and franchisor resources. Bootstrappers rely on personal funds and organic growth strategies, which can limit rapid expansion but offer greater control and flexibility. While franchising offers accelerated growth prospects, bootstrapping fosters sustainable, self-driven development tailored to market demands.
Support Systems: Franchisor vs DIY
Franchise owners benefit from comprehensive support systems provided by the franchisor, including established training programs, marketing resources, and ongoing operational assistance, which facilitate smoother business operations and reduce risks. Bootstrappers rely heavily on DIY methods, leveraging personal networks and self-taught skills to fund and grow their ventures, often facing higher uncertainty and requiring more resourcefulness. The structured support from franchisors contrasts with the independent, flexible approach of bootstrappers, influencing the scalability and operational stability of their businesses.
Long-Term Financial Commitments
Franchise owners often face significant long-term financial commitments, including franchise fees, royalties, and mandatory marketing expenses, which require steady revenue streams to remain viable. Bootstrappers, by contrast, rely on personal savings and reinvested profits, avoiding debt but limiting rapid expansion opportunities. This self-funded approach allows greater control over financial risks and operational decisions without binding obligations to external entities.
Choosing the Right Funding Path for Your Entrepreneurial Journey
Franchise owners often secure funding through established lending channels and franchisor support, benefiting from proven business models and brand recognition. Bootstrappers rely on personal savings, revenue reinvestment, and minimal external financing, maintaining full control but facing slower growth. Selecting the right funding path hinges on risk tolerance, growth goals, and the desire for operational autonomy in the entrepreneurial journey.
Related Important Terms
Franchise Fee Barrier
Franchise owners face a significant initial financial barrier due to high franchise fees, often ranging from $10,000 to $50,000 or more, which can limit access to funding and increase reliance on loans or investors. Bootstrappers avoid these upfront costs by self-funding operations, maintaining full control and equity but assuming higher financial risk and slower growth potential.
Royalty Commitment
Franchise owners often face ongoing royalty commitments, requiring a percentage of revenue to be paid to the franchisor, which can impact cash flow but provide access to established brand support and financing options. Bootstrappers rely on self-funding and minimal external capital, avoiding royalty fees but assuming full financial risk and slower growth potential.
Brand Licensing Leverage
Franchise owners benefit from brand licensing leverage by accessing established brand recognition and support systems, which typically attract easier funding from investors or lenders due to reduced risk perception. Bootstrappers, relying solely on self-funding and organic growth, often face challenges in leveraging brand licensing, limiting their ability to secure external financing and scale rapidly.
Turnkey Model
Franchise owners benefit from proven turnkey models that provide established branding, operational systems, and support, reducing financial risks and facilitating easier access to funding from lenders seeking lower-risk ventures. Bootstrappers rely on personal funds and incremental revenue generation, often facing greater funding challenges due to lack of external validation and standardized business frameworks associated with turnkey franchise models.
Ecosystem Dependency
Franchise owners benefit from a structured ecosystem dependency where franchisors provide essential support, brand recognition, and systematized funding channels, reducing individual risk. Bootstrappers rely heavily on personal networks and organic growth, creating a self-sustained funding approach with limited external ecosystem leverage.
Lean Launchpad Funding
Franchise owners typically secure funding through franchise loans or corporate-backed financing, leveraging established brand credibility for quicker access to capital, while bootstrappers rely on personal savings and lean launchpad funding models that emphasize iterative customer feedback and minimal viable product development to optimize resource allocation. Lean Launchpad funding prioritizes hands-on customer validation and adaptive business models, enabling bootstrappers to minimize financial risk and maximize market fit without traditional venture capital dependencies.
Sweat Equity Scaling
Franchise owners leverage established brand recognition and franchisor support to minimize financial risk, relying on initial franchise fees and ongoing royalties for funding, while bootstrappers focus on sweat equity by reinvesting personal labor and profits to scale operations organically without external capital. Sweat equity scaling allows bootstrappers to maintain full control and equity, fostering sustainable growth through relentless innovation and resourcefulness.
Minimum Viable Investment
Franchise owners benefit from a structured funding model with a clear Minimum Viable Investment (MVI) defined by franchise fees and startup costs that reduce financial uncertainty. Bootstrappers rely on self-funding and lean operations to minimize initial investment, prioritizing agility and organic growth without external capital constraints.
Crowdfunded Autonomy
Franchise owners often rely on established brand backing and traditional financing, while bootstrappers prioritize crowdfunded autonomy by leveraging platforms like Kickstarter and Indiegogo to raise capital without sacrificing equity. This funding approach empowers entrepreneurs to maintain full control over their business direction and fosters direct community engagement.
Bootstrapper Burnout
Franchise owners often secure funding through established systems and external investors, reducing personal financial strain, while bootstrappers rely solely on personal savings and revenue, increasing the risk of burnout due to continuous, high-stress self-funding demands. Bootstrapper burnout frequently results from prolonged financial pressure and limited access to resources, negatively impacting mental health and business sustainability.
Franchise Owner vs Bootstrapper for funding approach. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com