Self-employed individuals typically build businesses rooted in a fixed location, prioritizing stability and consistent client relationships, whereas digital nomads leverage technology to work remotely from anywhere, embracing flexibility and travel. Choosing between these lifestyles depends on one's preference for structure versus mobility and the ability to manage work without geographic constraints. Balancing productivity with personal freedom is key for entrepreneurs navigating the self-employed versus digital nomad dynamic.
Table of Comparison
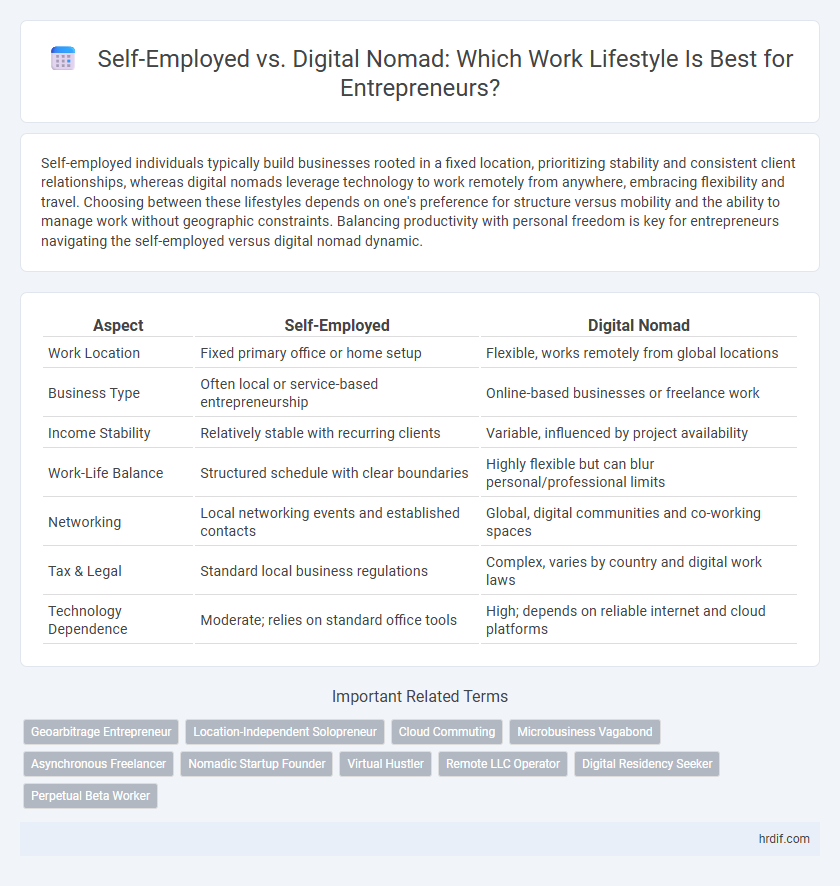
| Aspect | Self-Employed | Digital Nomad |
|---|---|---|
| Work Location | Fixed primary office or home setup | Flexible, works remotely from global locations |
| Business Type | Often local or service-based entrepreneurship | Online-based businesses or freelance work |
| Income Stability | Relatively stable with recurring clients | Variable, influenced by project availability |
| Work-Life Balance | Structured schedule with clear boundaries | Highly flexible but can blur personal/professional limits |
| Networking | Local networking events and established contacts | Global, digital communities and co-working spaces |
| Tax & Legal | Standard local business regulations | Complex, varies by country and digital work laws |
| Technology Dependence | Moderate; relies on standard office tools | High; depends on reliable internet and cloud platforms |
Defining Self-Employment and Digital Nomadism
Self-employment refers to individuals who operate their own businesses or work freelance, maintaining control over their income and work schedule without reliance on traditional employers. Digital nomadism describes a lifestyle where entrepreneurs or remote workers leverage technology to perform their job while traveling or living in various locations, often prioritizing flexibility and geographical independence. Both self-employed individuals and digital nomads share autonomy but differ primarily in mobility and work environment dependence.
Key Differences in Daily Workflow
Self-employed individuals often have structured daily workflows centered around managing client projects, maintaining administrative tasks, and ensuring consistent income streams. Digital nomads prioritize flexibility, frequently adapting their work hours and locations to balance productivity with travel experiences. While self-employed workers may rely on stable routines and local networks, digital nomads leverage technology and remote collaboration tools to sustain their itinerant lifestyles.
Flexibility and Autonomy in Each Lifestyle
Self-employed individuals often enjoy high autonomy by setting their own schedules and making strategic business decisions, which offers significant flexibility in managing work-life balance. Digital nomads leverage technology to work remotely from various global locations, combining flexibility in work environment with the freedom to explore different cultures. Both lifestyles prioritize self-direction, but digital nomads typically experience greater geographical freedom, whereas self-employed entrepreneurs have more control over their business operations.
Financial Stability and Earning Potential
Self-employed entrepreneurs often experience more consistent financial stability due to steady client contracts and predictable income streams, whereas digital nomads face fluctuating earnings influenced by location and market demand. The earning potential for self-employed individuals typically scales with business growth and client acquisition, while digital nomads leverage remote, location-independent opportunities but may encounter irregular revenue. Balancing reliable cash flow and flexible income sources is crucial for both work lifestyles to achieve sustainable financial success.
Location Independence: Pros and Cons
Self-employed individuals maintain control over their business operations but often face challenges tied to a fixed location, such as local market dependencies and limited networking opportunities. Digital nomads embrace location independence, leveraging technology to work from anywhere globally, which fosters cultural exposure and flexibility but can lead to unstable internet access and difficulties in establishing long-term client relationships. Both lifestyles prioritize autonomy, yet location-independent digital nomads must manage logistical complexities that self-employed entrepreneurs rooted in a single location may avoid.
Work-Life Balance Comparisons
Self-employed individuals often enjoy the flexibility to structure their work hours but may face challenges in setting clear boundaries between professional and personal time, impacting their work-life balance. Digital nomads leverage location independence to integrate travel and leisure into their routines, yet they can experience instability due to irregular schedules and varying time zones. Balancing productivity with personal well-being remains a critical challenge in both work lifestyles, influenced by autonomy, routine consistency, and environmental factors.
Necessary Skills and Tools for Success
Successful entrepreneurs who are self-employed must master time management, financial literacy, and client acquisition while utilizing tools like accounting software, project management apps, and CRM systems to streamline operations. Digital nomads require adaptability, strong digital communication skills, and tech-savviness, relying heavily on VPNs, cloud storage, and collaboration platforms to maintain productivity across diverse locations. Both work lifestyles benefit from proficiency in online marketing and resilience, but the digital nomad lifestyle demands a greater focus on cultural awareness and remote work technology.
Community, Networking, and Social Impact
Self-employed entrepreneurs often build strong local communities through face-to-face networking, fostering long-term relationships that can lead to collaborative opportunities and social impact within their geographic area. Digital nomads leverage global online networks and co-working spaces to create diverse, cross-cultural connections, enabling innovative projects with broader social reach. Both lifestyles contribute uniquely to social impact: self-employed individuals grounded in local ecosystems, and digital nomads driving global collaboration and knowledge exchange.
Challenges and Risk Factors
Self-employed individuals often face challenges such as inconsistent income, managing taxes, and maintaining work-life balance under a fixed location. Digital nomads encounter risks including unreliable internet connectivity, legal complexities with visas and work permits, and isolation from professional networks. Both lifestyles require strong self-discipline and adaptability but differ significantly in their operational uncertainties and environmental stressors.
Which Lifestyle Suits Your Career Goals?
Self-employed individuals often build stable businesses with consistent client bases, ideal for those prioritizing long-term financial security and local networking. Digital nomads thrive on flexibility, leveraging remote technology to work from anywhere, suited for careers valuing freedom, travel, and diverse cultural experiences. Choosing between these lifestyles depends on whether career goals emphasize stability and growth or adaptability and global exploration.
Related Important Terms
Geoarbitrage Entrepreneur
Geoarbitrage entrepreneurs maximize income by leveraging lower living costs while working remotely, blending aspects of self-employment with the flexibility of a digital nomad lifestyle. This approach enhances financial freedom and operational efficiency by strategically relocating to cost-effective regions without sacrificing business productivity.
Location-Independent Solopreneur
A location-independent solopreneur thrives by leveraging digital tools to operate a business from anywhere, often adopting a digital nomad lifestyle that prioritizes flexibility over physical office presence. Self-employed individuals may run local businesses requiring a fixed location, while digital nomads focus on scalable online ventures that enable constant travel and remote client engagement.
Cloud Commuting
Self-employed individuals benefit from cloud commuting by accessing business resources and managing clients remotely, ensuring flexibility and control over their work environment. Digital nomads leverage cloud-based tools to maintain productivity while traveling, fostering a dynamic lifestyle that blends work with exploration and continuous connectivity.
Microbusiness Vagabond
Microbusiness Vagabonds blend the autonomy of self-employment with the flexibility of a digital nomad lifestyle, enabling entrepreneurs to operate microbusinesses from anywhere globally while maintaining consistent cash flow and client relationships. This hybrid approach leverages digital tools and remote work opportunities, optimizing productivity and work-life balance without the constraints of a fixed location.
Asynchronous Freelancer
Asynchronous freelancers, often digital nomads, leverage flexible schedules and remote technologies to operate independently without being tethered to traditional offices, contrasting with self-employed individuals who may prioritize stable locations and synchronous work hours. This shift enhances productivity growth and global client reach, redefining contemporary entrepreneurship through location-independent income streams and time-zone agnostic collaboration.
Nomadic Startup Founder
A Nomadic Startup Founder leverages the flexibility of remote work, combining entrepreneurial drive with global mobility to access diverse markets and talent pools. Unlike traditional self-employed individuals tied to a fixed location, they optimize productivity and innovation through location-independent tools and networks, enabling scalable business growth across borders.
Virtual Hustler
Virtual Hustlers blend entrepreneurial drive with location independence, leveraging online platforms to build self-sustaining income streams without traditional office constraints. Their work lifestyle prioritizes flexibility and scalability, distinguishing them from typical self-employed individuals anchored to a fixed location.
Remote LLC Operator
A Remote LLC Operator balances the flexibility of self-employment with the mobility of a digital nomad by managing business operations entirely online, enabling seamless work from any location while maintaining legal and financial structure. This lifestyle maximizes tax advantages and operational control without sacrificing the freedom to travel globally.
Digital Residency Seeker
Digital residency seekers prioritize flexibility and global mobility by leveraging digital nomad lifestyles, using virtual business infrastructure to operate without geographical constraints. This approach contrasts with traditional self-employment, which often ties entrepreneurs to fixed locations and local regulatory environments.
Perpetual Beta Worker
Self-employed individuals often maintain a stable business model focused on local or niche markets, while digital nomads embrace perpetual beta work by continuously adapting to new environments, technologies, and clients globally. This flexible, experimental approach supports innovation and resilience, distinguishing the digital nomad lifestyle as a dynamic alternative to traditional self-employment.
Self-employed vs Digital Nomad for work lifestyle. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com