Startup owners often prioritize scaling quickly with external funding and structured teams to grow their ventures rapidly. Indie hackers focus on bootstrapping and maintaining full control, building sustainable businesses with minimal resources. Both approaches offer unique advantages depending on goals, risk tolerance, and desired lifestyle flexibility.
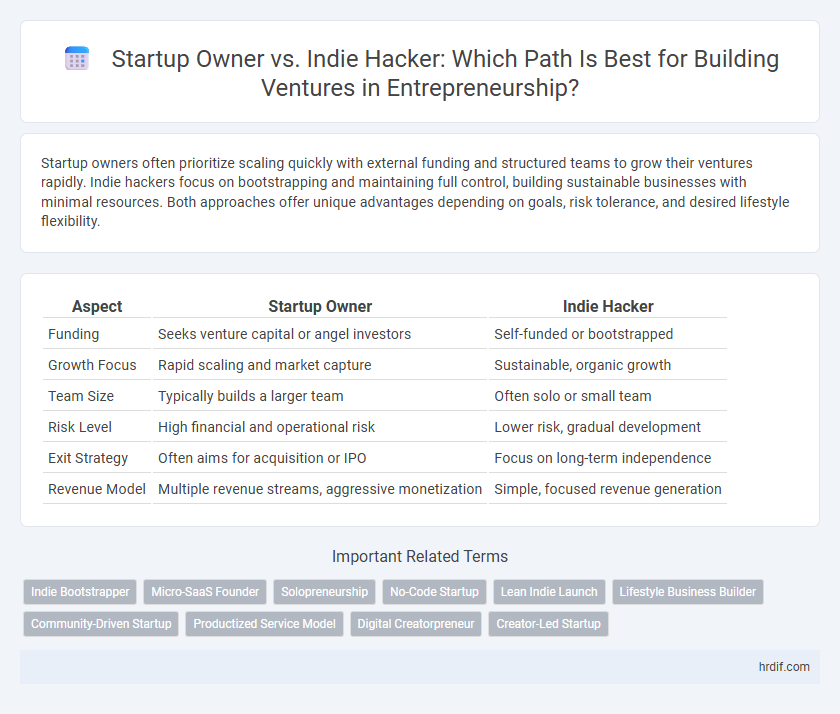
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Startup Owner | Indie Hacker |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Seeks venture capital or angel investors | Self-funded or bootstrapped |
| Growth Focus | Rapid scaling and market capture | Sustainable, organic growth |
| Team Size | Typically builds a larger team | Often solo or small team |
| Risk Level | High financial and operational risk | Lower risk, gradual development |
| Exit Strategy | Often aims for acquisition or IPO | Focus on long-term independence |
| Revenue Model | Multiple revenue streams, aggressive monetization | Simple, focused revenue generation |
Defining Startup Owners and Indie Hackers
Startup owners typically manage ventures aiming for rapid growth through external funding and scaling teams, prioritizing market disruption and large-scale impact. Indie hackers build and grow businesses independently, emphasizing profitability, sustainability, and direct customer relationships without relying on venture capital. Both pathways embody distinct entrepreneurial mindsets shaped by their goals, resource management, and growth strategies within the startup ecosystem.
Core Mindsets: Growth vs. Independence
Startup owners prioritize rapid growth, scalability, and securing external funding to accelerate their ventures, often focusing on market dominance and team expansion. Indie hackers emphasize independence, sustainable profits, and maintaining control by bootstrapping their projects with minimal outside investment. The core mindset for startup owners centers on aggressive growth strategies, while indie hackers value autonomy and steady, organic development.
Funding Approaches: Venture Capital vs. Bootstrapping
Startup owners often pursue venture capital to rapidly scale their businesses, leveraging large financial investments and strategic partnerships to accelerate growth. Indie hackers typically prefer bootstrapping, relying on personal savings and incremental revenue to maintain control and sustainable development without external influence. Funding approaches significantly impact decision-making, equity distribution, and risk tolerance in venture-building strategies.
Risk Appetite and Failure Management
Startup owners typically exhibit a higher risk appetite, often seeking significant external funding to scale rapidly while accepting potential high failure costs. Indie hackers prefer lean, self-funded ventures, embracing smaller, manageable risks with an iterative approach that mitigates failure impact. Effective failure management for startup owners involves strategic pivots and investor relations, whereas indie hackers focus on agile problem-solving and sustainable growth.
Product Development Strategies
Startup owners often emphasize rapid scaling and securing venture capital to accelerate product development and market entry. Indie hackers typically prioritize lean methodologies, iterating quickly with minimal resources to validate product-market fit independently. Both approaches require strategic focus on user feedback and agile development cycles to optimize growth and innovation.
Growth Metrics: Scale vs. Sustainability
Startup owners prioritize rapid growth metrics such as user acquisition rates, market penetration, and funding rounds to scale quickly and capture market share. Indie hackers emphasize sustainable growth by focusing on consistent revenue streams, customer retention, and profitability without heavy reliance on external funding. Evaluating growth metrics through the lens of scale versus sustainability helps founders align their business models with long-term objectives and resource availability.
Team Building and Solo Operations
Startup owners typically prioritize building diverse teams to leverage specialized skills, improve scalability, and attract investors, enabling faster growth and market penetration. Indie hackers often operate solo or with minimal collaboration, capitalizing on agility and low overhead while maintaining complete control over product direction and revenue. Both approaches offer unique advantages: startups excel in resource pooling and risk distribution, whereas indie hackers benefit from streamlined decision-making and independence.
Community and Networking Differences
Startup owners often rely heavily on formal networks including investors, accelerators, and industry events to scale their ventures quickly and secure funding. Indie hackers prioritize building organic communities through online platforms like forums, social media, and niche groups, fostering direct peer-to-peer support and collaboration. The startup ecosystem emphasizes structured networking for growth, while indie hackers focus on community-driven learning and grassroots connections.
Exit Strategies and Longevity
Startup owners often pursue aggressive growth and scalable exit strategies such as acquisitions or IPOs, aiming for rapid valuation increases and external funding rounds. Indie hackers prioritize sustainable, self-funded growth with a focus on long-term profitability and maintaining control, favoring steady cash flow over high-risk exits. Both approaches reflect distinct mindsets around venture longevity and financial independence within the entrepreneurship ecosystem.
Which Path Fits Your Entrepreneurial Goals?
Startup owners often pursue rapid growth and external funding to scale their ventures, aligning with goals of market dominance and large exit potential. Indie hackers prioritize bootstrapping and sustainable income, focusing on control, independence, and steady growth without relying on venture capital. Choosing between these paths depends on your appetite for risk, desire for autonomy, and long-term vision for your entrepreneurial journey.
Related Important Terms
Indie Bootstrapper
Indie hackers prioritize organic growth and lean methodologies, leveraging personal skills and minimal external funding to build sustainable ventures. This bootstrapper approach contrasts with traditional startup owners who often seek significant venture capital and rapid scaling.
Micro-SaaS Founder
Micro-SaaS founders often adopt the indie hacker model, prioritizing lean operations, rapid MVP development, and direct customer feedback over traditional startup scaling strategies. This approach enables micro-SaaS ventures to maintain control, optimize niche markets, and achieve sustainable revenue without extensive external funding.
Solopreneurship
Startup owners typically seek external funding and scalable growth models, prioritizing rapid expansion and team building, whereas indie hackers emphasize bootstrapping, self-reliance, and sustainable, small-scale ventures often managed solo. Solopreneurs following the indie hacker path leverage digital tools and lean methodologies to validate ideas quickly and maintain full control over their businesses.
No-Code Startup
Startup owners leverage no-code tools to rapidly scale ventures through structured teams and external funding, while indie hackers prioritize lean, self-funded projects, emphasizing autonomy and direct user engagement in building sustainable businesses. No-code platforms empower both paths by enabling faster product development and iteration without extensive technical skills, fueling innovation in entrepreneurial ecosystems.
Lean Indie Launch
Startup owners prioritize rapid scaling and external funding to grow their ventures, whereas indie hackers emphasize sustainable, bootstrapped growth through Lean Indie Launch principles centered on customer feedback and iterative development. Lean Indie Launch advocates a minimalist approach that reduces risk by validating ideas early and optimizing resources for maximum product-market fit.
Lifestyle Business Builder
Startup owners often pursue rapid growth by securing venture capital and scaling teams quickly, while indie hackers prioritize sustainable, self-funded lifestyle businesses that emphasize autonomy and steady income. Lifestyle business builders typically value work-life balance and personal freedom over market domination, leveraging lean approaches to create profitable, manageable ventures.
Community-Driven Startup
Community-driven startups emphasize collaboration and shared growth among founders, customers, and contributors, differing from indie hackers who often prioritize solo ventures with minimal external input. Startup owners leverage community feedback to rapidly iterate products and scale operations, resulting in ventures that are more resilient and aligned with user needs.
Productized Service Model
Startup owners leverage the productized service model to scale ventures by standardizing offerings and optimizing client acquisition through targeted marketing funnels, ensuring predictable revenue streams. Indie hackers embrace this model for its low overhead and flexibility, focusing on automating service delivery and utilizing lean growth strategies to maintain independence while validating product-market fit.
Digital Creatorpreneur
Startup owners prioritize scalable growth and external funding to rapidly expand their ventures, while indie hackers emphasize bootstrapping and maintaining full control over product development. Digital creatorpreneurs blend both approaches by leveraging personal brand assets and digital platforms to build sustainable online businesses with minimal reliance on external capital.
Creator-Led Startup
Creator-led startups prioritize product innovation and community engagement, allowing founders to maintain full control without external funding. Indie hackers leverage lean methodologies and bootstrapped growth to quickly validate ideas, whereas traditional startup owners often depend on venture capital and scalable team structures.
Startup Owner vs Indie Hacker for building ventures. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com