Entrepreneurs typically build and manage businesses with teams, aiming for scalable growth and diverse opportunities, while solopreneurs operate independently, handling all aspects of their ventures for greater control and flexibility. Choosing between these career paths depends on one's preference for collaboration versus autonomy, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. Both offer unique advantages in developing leadership, innovation, and financial independence within the entrepreneurial landscape.
Table of Comparison
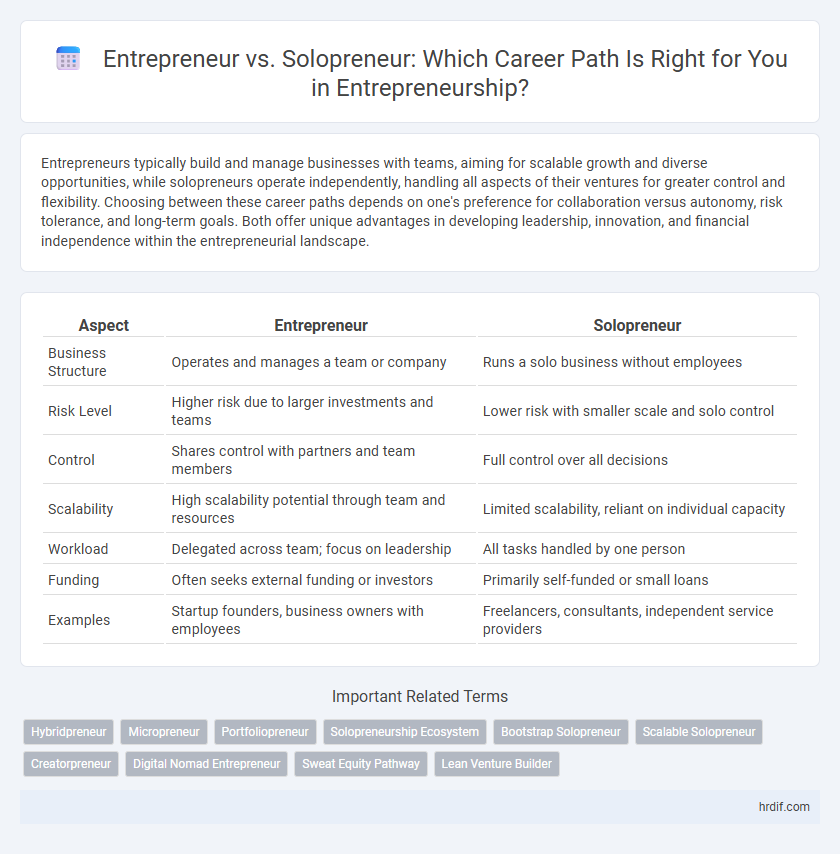
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Solopreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Business Structure | Operates and manages a team or company | Runs a solo business without employees |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to larger investments and teams | Lower risk with smaller scale and solo control |
| Control | Shares control with partners and team members | Full control over all decisions |
| Scalability | High scalability potential through team and resources | Limited scalability, reliant on individual capacity |
| Workload | Delegated across team; focus on leadership | All tasks handled by one person |
| Funding | Often seeks external funding or investors | Primarily self-funded or small loans |
| Examples | Startup founders, business owners with employees | Freelancers, consultants, independent service providers |
Entrepreneurship vs Solopreneurship: Defining the Career Paths
Entrepreneurship involves building and managing scalable businesses with teams, focusing on growth, innovation, and long-term market impact. Solopreneurship centers on independent business ownership where individuals maintain full control, prioritize flexibility, and handle all operational aspects personally. Choosing between these career paths depends on one's goals for autonomy, risk tolerance, resource management, and desired business scale.
Key Differences Between Entrepreneurs and Solopreneurs
Entrepreneurs typically build scalable businesses by assembling teams and seeking external funding to expand operations rapidly, while solopreneurs operate independently, managing all aspects of their business without the intention to scale significantly. Entrepreneurs prioritize creating systems and delegating tasks to leverage growth, whereas solopreneurs focus on personalized service and maintaining direct control over every function. The core difference lies in growth ambitions and operational structure, where entrepreneurs pursue high growth and solopreneurship favors self-sufficiency and lifestyle flexibility.
Pros and Cons of Being an Entrepreneur
Entrepreneurs often build scalable businesses with the potential for large growth and team expansion, allowing them to leverage diverse skills and resources. However, they face significant risks, including higher financial investment, complex management challenges, and the pressure of maintaining investor relationships. Despite these challenges, the entrepreneurial path offers opportunities for substantial wealth creation and market influence compared to the typically smaller scale and more controlled workload of solopreneurs.
Pros and Cons of Being a Solopreneur
Being a solopreneur offers complete control over business decisions and flexibility in managing work-life balance, allowing for faster decision-making and lower operational costs due to the absence of a team. However, solopreneurs face challenges such as limited capacity for scaling, increased risk of burnout, and the pressure to handle all aspects of the business alone without the support network typical in entrepreneurial ventures. While solopreneurship suits individuals seeking autonomy and streamlined operations, it may restrict growth potential compared to entrepreneurs who leverage larger teams and resources.
Skill Sets Required: Entrepreneur vs Solopreneur
Entrepreneurs require a diverse skill set encompassing leadership, strategic planning, financial management, and the ability to build and scale teams. Solopreneurs prioritize specialized skills related to their niche, self-management, and versatile multitasking to handle all operational aspects independently. Mastery of marketing, time management, and technology tools is critical for solopreneurs, while entrepreneurs focus more on delegation and investor relations.
Risk and Reward: Which Career Path Suits You?
Entrepreneurs typically face higher financial risks as they build and scale businesses with multiple employees, but they also stand to gain larger rewards through equity and market expansion. Solopreneurs assume more personal risk since their income depends solely on their individual efforts, yet they enjoy greater control and flexibility without the complexities of managing a team. Choosing between these paths depends on your risk tolerance, desire for autonomy, and long-term career goals in entrepreneurship.
Growth Potential: Teams vs Going Solo
Entrepreneurs leveraging teams often experience accelerated growth potential through diverse skill sets, resource pooling, and scalable operations, enabling larger market reach and increased revenue streams. Solopreneurs maintain complete control and flexibility but face limitations in capacity and scalability, which can constrain long-term expansion opportunities. Choosing between these paths depends on one's appetite for risk, delegation, and vision for business growth.
Financial Considerations for Entrepreneurs and Solopreneurs
Entrepreneurs often face higher financial risks due to the need for substantial investments, employee salaries, and scalable operations, while solopreneurs usually operate with lower overhead costs and minimal initial capital. Access to funding varies significantly; entrepreneurs may secure venture capital or business loans, whereas solopreneurs typically rely on personal savings or small business financing. Profit distribution and cash flow management also differ, with entrepreneurs balancing reinvestment for growth and solopreneurs focusing on immediate income sustainability.
Work-Life Balance: Entrepreneurial vs Solopreneurial Lifestyles
Entrepreneurs often face blurred boundaries between work and personal life due to managing teams and scaling businesses, leading to fluctuating work-life balance. Solopreneurs typically experience greater control over their schedules, allowing for more flexibility but also bearing all responsibilities alone, which can cause stress. Understanding these distinct lifestyle dynamics is crucial for choosing the optimal career path aligned with individual work-life balance preferences.
How to Choose the Right Career Path for You: Entrepreneur or Solopreneur
Evaluating career goals, risk tolerance, and preferred work style helps in choosing between entrepreneur and solopreneur paths. Entrepreneurs typically manage scalable businesses with teams and seek external funding, while solopreneurs maintain full control and operate independently without employees. Prioritizing long-term vision and desired lifestyle ensures alignment with either entrepreneurial growth or solopreneurial autonomy.
Related Important Terms
Hybridpreneur
Hybridpreneurs blend the scalability mindset of entrepreneurs with the autonomy of solopreneurs, leveraging both team collaboration and independent control to optimize business growth and personal freedom. This career path maximizes resource flexibility by combining outsourcing, technology, and strategic partnerships, delivering diversified revenue streams while maintaining hands-on involvement.
Micropreneur
Micropreneurs prioritize sustainable, lifestyle-focused businesses with limited scale, differentiating them from entrepreneurs who often seek rapid growth and solopreneur individuals working entirely alone without support networks. By maintaining a balance between autonomy and manageable operations, micropreneurs optimize personal freedom and steady income, carving a distinct niche in the entrepreneurial landscape.
Portfoliopreneur
A portfoliopreneur diversifies income by managing multiple business ventures simultaneously, unlike traditional entrepreneurs who focus on scaling a single enterprise or solopreneurs who operate solo businesses. This approach mitigates risk and enhances resilience by leveraging various revenue streams across industries.
Solopreneurship Ecosystem
Solopreneurship thrives within a dynamic ecosystem characterized by digital tools, remote work platforms, and niche market opportunities that empower independent professionals to build scalable careers without traditional team structures. This ecosystem fosters agility, personalized branding, and direct client relationships, distinguishing solopreneurs from entrepreneurs who typically manage larger organizations and diversified operations.
Bootstrap Solopreneur
Bootstrap solopreneurs embrace self-funding and streamlined operations to maintain full control over their ventures, often prioritizing sustainable growth without external investment. This career path contrasts with traditional entrepreneurs who typically seek scalable business models and outside capital to expand rapidly.
Scalable Solopreneur
Scalable solopreneurs leverage technology and automation to grow their businesses without traditional team expansion, creating high-impact career paths with sustainable revenue streams. Unlike entrepreneurs who build large organizations, scalable solopreneurs optimize solo operations for market agility and exponential growth potential.
Creatorpreneur
Creatorpreneurs blend entrepreneurial innovation with content creation, leveraging digital platforms to build scalable personal brands and diverse income streams. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs who focus on building large enterprises or solopreneurs who operate independently, creatorpreneurs harness audience engagement and creative capital to drive sustainable career growth.
Digital Nomad Entrepreneur
Digital nomad entrepreneurs leverage technology to build scalable businesses while traveling, prioritizing innovation and team collaboration for growth. Solopreneurs operate independently, focusing on self-sufficiency and niche expertise to maintain flexibility within remote, location-independent careers.
Sweat Equity Pathway
An entrepreneur often builds a scalable business by leveraging sweat equity through team collaboration, while a solopreneur invests personal time and effort solely into self-managed projects with limited external resources. Choosing the sweat equity pathway influences control, growth potential, and risk exposure in entrepreneurship career trajectories.
Lean Venture Builder
Lean Venture Builders prioritize efficient resource allocation and iterative development, enabling entrepreneurs to scale startups through systematic team collaboration, while solopreneurs often focus on independent operations with limited scaling potential. This distinction highlights that entrepreneurs leverage Lean Venture methodologies to optimize market fit and growth, whereas solopreneurs emphasize autonomy and niche specialization in their career paths.
Entrepreneur vs Solopreneur for career paths. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com