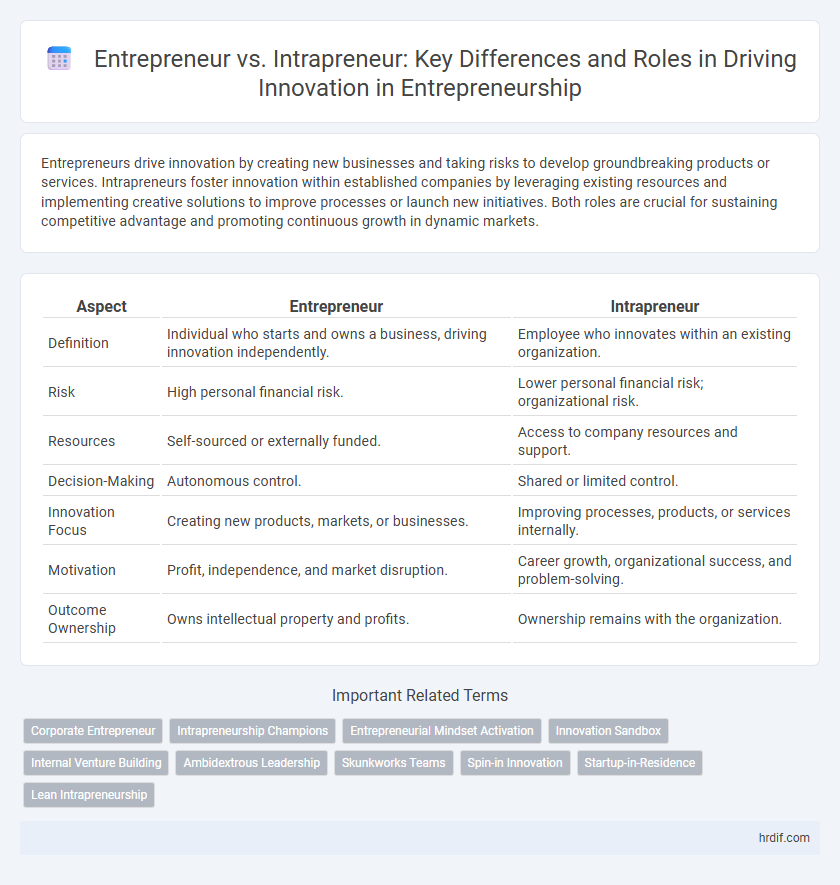
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new businesses and taking risks to develop groundbreaking products or services. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within established companies by leveraging existing resources and implementing creative solutions to improve processes or launch new initiatives. Both roles are crucial for sustaining competitive advantage and promoting continuous growth in dynamic markets.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and owns a business, driving innovation independently. | Employee who innovates within an existing organization. |
| Risk | High personal financial risk. | Lower personal financial risk; organizational risk. |
| Resources | Self-sourced or externally funded. | Access to company resources and support. |
| Decision-Making | Autonomous control. | Shared or limited control. |
| Innovation Focus | Creating new products, markets, or businesses. | Improving processes, products, or services internally. |
| Motivation | Profit, independence, and market disruption. | Career growth, organizational success, and problem-solving. |
| Outcome Ownership | Owns intellectual property and profits. | Ownership remains with the organization. |
Defining Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs are individuals who create and lead new ventures by taking financial risks to develop innovative products or services independently. Intrapreneurs operate within an existing organization, using entrepreneurial skills to innovate, improve processes, and drive growth from inside the company. Both roles are crucial for fostering innovation, with entrepreneurs focusing on market disruption and intrapreneurs enhancing competitive advantage through internal innovation.
Core Differences: Ownership and Risk
Entrepreneurs assume full ownership and financial risk, driving innovation through founding new ventures and making autonomous decisions that directly impact business outcomes. Intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging company resources while bearing limited personal financial risk and focusing on advancing internal projects. The core difference lies in the level of ownership and risk exposure, which influences decision-making power and motivation in driving innovation.
Innovation Drivers: Structure vs. Freedom
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by leveraging freedom and flexibility to explore novel ideas outside traditional frameworks, fostering disruptive breakthroughs through risk-taking and creative autonomy. Intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations by utilizing structured resources, defined processes, and organizational support to implement incremental improvements and scalable innovations. The balance between entrepreneurial freedom and intrapreneurial structure shapes innovation outcomes, with entrepreneurs excelling in radical innovation and intrapreneurs optimizing existing systems for sustained growth.
Resource Allocation: Corporate vs. Independent
Entrepreneurs independently control resource allocation, enabling agile investment in innovative ideas without organizational constraints, fostering rapid product development and market entry. Intrapreneurs operate within corporate frameworks, balancing resource use with company goals and existing priorities, which may limit flexibility but ensures alignment with broader strategic objectives. Efficient resource management is critical as entrepreneurs face funding challenges, while intrapreneurs benefit from established infrastructures yet must navigate internal approval processes.
Impact on Organizational Culture
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by introducing disruptive ideas and fostering a risk-taking culture that challenges traditional organizational norms. Intrapreneurs enhance organizational culture by leveraging existing resources to implement innovative solutions, promoting collaboration and agility within established frameworks. Both roles are crucial for sustaining a dynamic and adaptable business environment that cultivates continuous growth and competitive advantage.
Motivations and Rewards
Entrepreneurs are primarily motivated by autonomy, financial gain, and the potential to disrupt markets, driving them to innovate independently with high-risk, high-reward outcomes. Intrapreneurs, motivated by organizational support and resource access, focus on innovation within existing companies, aiming for product development and process improvement with lower personal financial risk. Rewards for entrepreneurs often include equity ownership and market leadership, while intrapreneurs gain career advancement, recognition, and influence within corporate structures.
Case Studies: Successful Innovations
Case studies highlight how entrepreneurs like Elon Musk revolutionized electric vehicles with Tesla, while intrapreneurs such as Google's Paul Buchheit innovated Gmail within an existing corporate structure. Entrepreneur-driven innovations often stem from personal vision and risk-taking, whereas intrapreneurs leverage company resources to execute groundbreaking projects. Both approaches demonstrate significant innovation outcomes, emphasizing the diverse pathways to commercial and technological breakthroughs.
Challenges Faced by Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs face challenges such as securing funding, managing business risks, and establishing market presence, which often require high levels of autonomy and resourcefulness. Intrapreneurs encounter obstacles like navigating corporate bureaucracy, aligning innovation with company goals, and limited decision-making authority within established organizational structures. Both roles demand resilience and creativity, but entrepreneurs operate in uncertain external markets while intrapreneurs innovate within the constraints of existing company systems.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Career
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new businesses with high risk and autonomy, while intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations, leveraging existing resources and networks to implement change. Choosing the right path depends on your risk tolerance, desire for independence, and access to capital or organizational support. Understanding these factors helps determine whether launching a startup or leading innovation projects inside a company aligns better with your career goals.
The Future of Innovation: Blending Both Roles
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by launching new ventures with high risk and autonomy, while intrapreneurs innovate within established organizations leveraging existing resources and market access. Blending these roles accelerates future innovation, enabling companies to scale breakthrough ideas rapidly while maintaining agility and entrepreneurial spirit. Organizations fostering intrapreneurship alongside external entrepreneurship create ecosystems that drive sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Related Important Terms
Corporate Entrepreneur
Corporate entrepreneurs drive innovation within established organizations by leveraging internal resources and market knowledge to develop disruptive products and services. Unlike traditional entrepreneurs who assume full risk, corporate entrepreneurs balance innovation with company goals, fostering a culture that accelerates competitive advantage and sustainable growth.
Intrapreneurship Champions
Intrapreneurship champions drive organizational innovation by leveraging internal resources and fostering a culture that encourages risk-taking and creative problem-solving within established companies. These individuals act as entrepreneurial leaders who navigate corporate structures to launch new projects, accelerate product development, and enhance competitive advantage without the need to start an independent business.
Entrepreneurial Mindset Activation
Entrepreneurial mindset activation drives both entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs to innovate by embracing risk, creativity, and proactive problem-solving within dynamic environments. Entrepreneurs leverage this mindset to create new ventures, while intrapreneurs apply it internally to disrupt and advance existing organizations, fostering transformative innovation.
Innovation Sandbox
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by independently launching startups within Innovation Sandboxes, leveraging flexible regulatory environments to test and scale disruptive ideas rapidly. Intrapreneurs catalyze innovation inside established companies by using Innovation Sandboxes to experiment with new products or business models while minimizing organizational risks.
Internal Venture Building
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new businesses externally, while intrapreneurs foster internal venture building within existing organizations, leveraging company resources to develop innovative products and services. Internal venture building enables intrapreneurs to accelerate innovation cycles, reduce market risks, and align new initiatives with corporate strategy for sustainable growth.
Ambidextrous Leadership
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures and taking risks, while intrapreneurs foster innovation within existing organizations by leveraging resources and navigating corporate structures; ambidextrous leadership balances exploration and exploitation to maximize both entrepreneurial and intrapreneurial potential. Effective ambidextrous leaders cultivate a culture that supports creative risk-taking alongside efficient operational management, enabling sustained innovation and competitive advantage.
Skunkworks Teams
Skunkworks teams, often spearheaded by intrapreneurs within established companies, drive breakthrough innovations by operating with startup-like autonomy and agility. These specialized groups leverage entrepreneurial thinking while utilizing corporate resources to accelerate product development and disruptive solutions.
Spin-in Innovation
Spin-in innovation leverages intrapreneurs who drive entrepreneurial initiatives within established organizations, accelerating product development by integrating external startup ideas and internal resources. This approach contrasts with entrepreneurs who independently create new ventures, as spin-in innovation maximizes corporate assets to foster market disruption and competitive advantage.
Startup-in-Residence
Entrepreneurs driving innovation within Startup-in-Residence programs leverage agility and risk-taking to develop disruptive solutions, while intrapreneurs foster innovation by applying entrepreneurial skills inside established organizations to scale ideas efficiently. Both roles complement each other by blending startup creativity with corporate resources, accelerating innovation cycles and market impact.
Lean Intrapreneurship
Lean Intrapreneurship drives innovation within established companies by encouraging employees to act like entrepreneurs, applying lean startup principles to rapidly test ideas and minimize risks. Unlike entrepreneurs who build ventures from scratch, lean intrapreneurs leverage existing resources and market insights to develop scalable solutions that align with corporate goals.
Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur for innovation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com