Entrepreneurs drive business innovation by launching new ventures and assuming full responsibility for risks and rewards, while intrapreneurs lead within existing organizations, leveraging company resources to develop new products or processes. Both roles require strong leadership, creativity, and strategic thinking, but entrepreneurs focus on building businesses from the ground up, whereas intrapreneurs innovate internally to push companies forward. Understanding the distinct challenges and opportunities of each approach helps organizations foster effective leadership and sustainable growth.
Table of Comparison
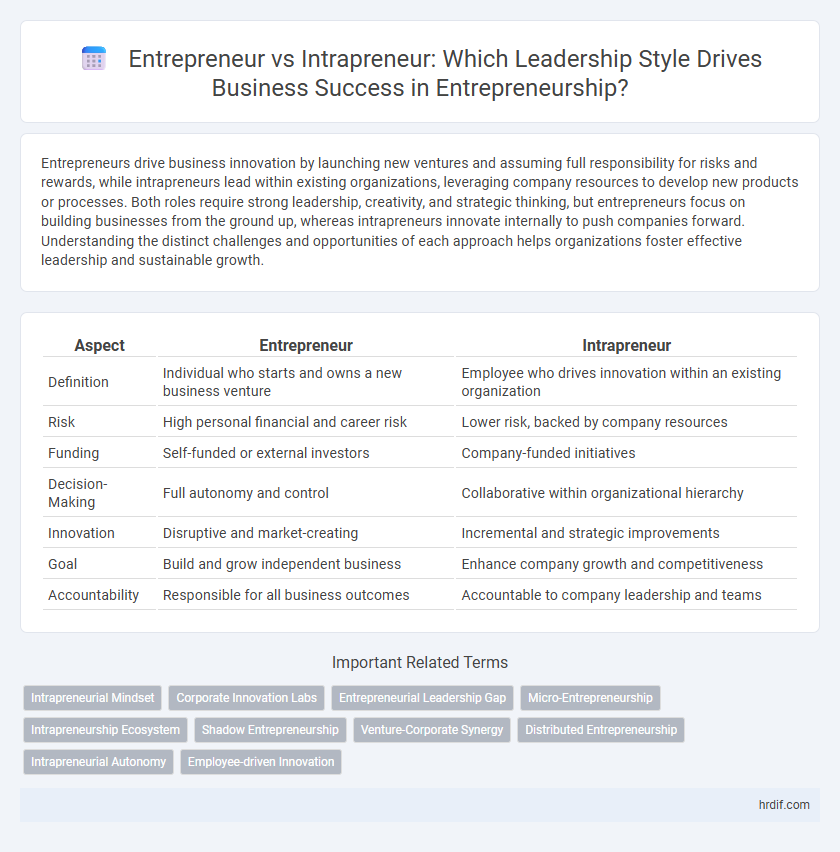
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and owns a new business venture | Employee who drives innovation within an existing organization |
| Risk | High personal financial and career risk | Lower risk, backed by company resources |
| Funding | Self-funded or external investors | Company-funded initiatives |
| Decision-Making | Full autonomy and control | Collaborative within organizational hierarchy |
| Innovation | Disruptive and market-creating | Incremental and strategic improvements |
| Goal | Build and grow independent business | Enhance company growth and competitiveness |
| Accountability | Responsible for all business outcomes | Accountable to company leadership and teams |
Defining Entrepreneurship and Intrapreneurship
Entrepreneurship involves individuals who create, organize, and manage new ventures, assuming full financial risk and innovation responsibility to bring original ideas to market. Intrapreneurship refers to employees within an existing organization who apply entrepreneurial skills to develop new products, services, or processes while leveraging company resources and sharing organizational risks. Both roles drive business leadership by fueling innovation, growth, and competitive advantage, but entrepreneurs operate independently whereas intrapreneurs work inside corporate structures.
Key Traits of Entrepreneurs vs Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs exhibit traits such as risk-taking, innovation, and autonomy, driving new business ventures with a bold vision and resilience. Intrapreneurs demonstrate creativity, adaptability, and proactive problem-solving while operating within established organizations, leveraging existing resources to foster growth. Both roles require leadership, strategic thinking, and a strong drive for results, yet entrepreneurs prioritize market disruption, whereas intrapreneurs focus on internal improvement and scalability.
Leadership Styles: Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur
Entrepreneurs exhibit transformational leadership by driving innovation and taking calculated risks to build new ventures, while intrapreneurs leverage transactional leadership within established organizations to improve processes and foster internal growth. Entrepreneurial leadership emphasizes vision, autonomy, and adaptability, contrasting with intrapreneurs' focus on collaboration, resource optimization, and aligning with corporate strategies. Understanding these distinct leadership styles enhances organizational capacity to cultivate creativity and sustain competitive advantage.
Risk-Taking: Who Takes More?
Entrepreneurs typically assume higher risks by investing personal resources and pursuing disruptive innovations to establish new ventures. Intrapreneurs take calculated risks within the safety of an existing organization, leveraging company assets while aligning with corporate goals. The entrepreneurial risk-taking often drives market breakthroughs, whereas intrapreneurial risk supports incremental growth and internal transformation.
Innovation Approaches in Entrepreneurship and Intrapreneurship
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by launching new ventures that disrupt markets with novel products and business models, leveraging external resources and high risk tolerance. Intrapreneurs foster innovation within established organizations by applying entrepreneurial approaches to develop new ideas, improve processes, and create value, utilizing existing structures and corporate support. Both innovation approaches emphasize creativity, strategic thinking, and proactive problem-solving to achieve business growth and competitive advantage.
Decision-Making Differences in Both Roles
Entrepreneurs drive business leadership by taking high-risk decisions independently, focusing on innovation and market disruption to create new ventures. Intrapreneurs operate within existing organizations, making strategic decisions that align with corporate goals while fostering innovation and minimizing risks. The key difference lies in entrepreneurs' autonomy and risk tolerance versus intrapreneurs' emphasis on leveraging organizational resources and navigating internal structures for decision-making.
Resource Management: Ownership vs Allocation
Entrepreneurs exercise full ownership over resource management, making strategic decisions to allocate capital, talent, and assets to maximize business growth and innovation. Intrapreneurs, operating within established organizations, focus on efficient resource allocation by optimizing existing assets and navigating internal constraints to drive new initiatives. Effective leadership in both roles requires balancing risk and opportunity while leveraging available resources to achieve organizational goals.
Impact on Organizational Growth
Entrepreneurs drive organizational growth by introducing innovative products and disruptive business models, often accelerating market expansion through risk-taking and agile decision-making. Intrapreneurs foster growth by leveraging existing company resources to implement internal innovations that improve efficiency, employee engagement, and competitive advantage. Both roles significantly influence organizational growth, with entrepreneurs catalyzing external market opportunities and intrapreneurs optimizing internal development processes.
Career Pathways: Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur
Entrepreneurs forge their own career paths by creating startups, taking on significant risks to innovate and capture new markets independently. Intrapreneurs, on the other hand, drive innovation within established corporations, leveraging existing resources and organizational support to lead projects and develop new products. Choosing between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship depends on an individual's risk tolerance, desire for autonomy, and preference for structured environments versus self-directed ventures.
Choosing the Right Path for Business Leadership
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures and assuming financial risks, while intrapreneurs leverage resources within existing organizations to innovate and lead change. Selecting the right path for business leadership depends on individual risk tolerance, resource access, and desire for autonomy or structured support. Understanding whether to build a business from scratch or innovate internally impacts strategic decision-making and long-term business growth.
Related Important Terms
Intrapreneurial Mindset
The intrapreneurial mindset drives business innovation by empowering employees to act like entrepreneurs within established companies, fostering creativity, risk-taking, and proactive problem-solving that align with corporate goals. Unlike entrepreneurs who build ventures from scratch, intrapreneurs leverage existing resources and networks to accelerate growth and competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Corporate Innovation Labs
Entrepreneurs drive innovation through independent ventures, while intrapreneurs leverage corporate innovation labs to foster transformative projects within established organizations. Corporate innovation labs provide structured resources and strategic support, accelerating intrapreneurs' ability to implement disruptive ideas and enhance competitive advantage.
Entrepreneurial Leadership Gap
Entrepreneurial leadership gaps often emerge when organizations struggle to cultivate intrapreneurs with the visionary risk-taking capabilities that entrepreneurs naturally possess, hindering innovation and strategic growth. Bridging this gap requires fostering a culture that empowers intrapreneurs to adopt entrepreneurial mindsets, drive transformative initiatives, and lead business ventures with autonomy and agility.
Micro-Entrepreneurship
Micro-entrepreneurs drive business growth by innovating independently and assuming full responsibility for risks and profits, while intrapreneurs leverage internal resources within established companies to foster innovation without personal financial exposure. Effective business leadership in micro-entrepreneurship emphasizes agility, resourcefulness, and direct market engagement, setting it apart from the structured approaches typical of intrapreneurship.
Intrapreneurship Ecosystem
Intrapreneurship ecosystems foster innovation within established organizations by empowering employees to act like entrepreneurs, driving business leadership through internal venture development and resource access. These ecosystems enhance corporate agility and competitive advantage by integrating entrepreneurial mindset with existing company infrastructures and support systems.
Shadow Entrepreneurship
Shadow entrepreneurship refers to employees within an organization who adopt an entrepreneurial mindset, driving innovation and new business initiatives without formal recognition as entrepreneurs. These intrapreneurs leverage company resources and networks to create value while operating under the strategic direction and risk constraints of their employers.
Venture-Corporate Synergy
Entrepreneurs drive innovative startups by creating new markets, while intrapreneurs leverage existing corporate resources to innovate within a company's structure, fostering venture-corporate synergy that accelerates growth and competitive advantage. This strategic collaboration enhances agility and scales disruptive ideas by combining entrepreneurial risk-taking with corporate stability and infrastructure.
Distributed Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs drive innovation by creating new ventures, while intrapreneurs lead transformative projects within established organizations, leveraging internal resources to scale ideas rapidly. Distributed entrepreneurship decentralizes leadership by empowering teams across various locations to initiate and manage business opportunities, enhancing agility and fostering collaborative innovation in complex enterprises.
Intrapreneurial Autonomy
Intrapreneurial autonomy empowers employees to innovate and lead within established organizations, blending entrepreneurial initiative with corporate resources. This autonomy drives agile decision-making and fosters a culture of intrapreneurship, enhancing business leadership from within.
Employee-driven Innovation
Entrepreneurs spearhead business ventures through individual initiative and risk-taking, driving innovation from the outside, while intrapreneurs cultivate employee-driven innovation within existing organizations by leveraging internal resources and fostering a culture of creativity. Empowering intrapreneurs enhances organizational agility, accelerates product development, and sustains competitive advantage through continuous employee-led innovation.
Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur for business leadership. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com