Entrepreneurs create value by launching new ventures, assuming risks, and driving innovation independently to fulfill market needs. Intrapreneurs generate value within existing organizations by applying entrepreneurial skills to develop new products or processes that enhance company growth. Both roles leverage creativity and strategic thinking, but entrepreneurs build value from the ground up, while intrapreneurs innovate inside established structures.
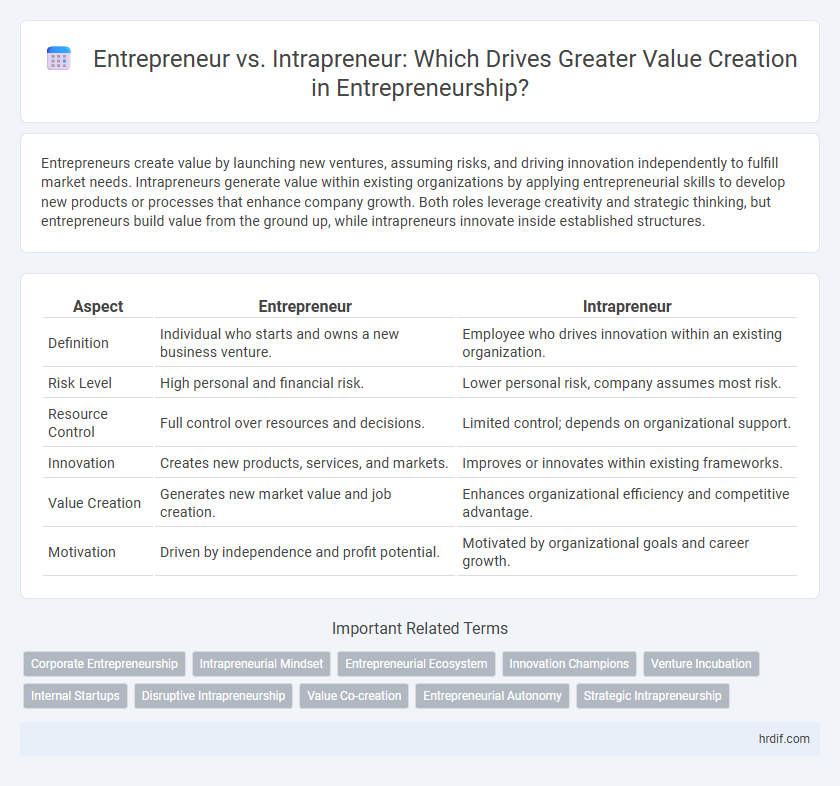
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Entrepreneur | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and owns a new business venture. | Employee who drives innovation within an existing organization. |
| Risk Level | High personal and financial risk. | Lower personal risk, company assumes most risk. |
| Resource Control | Full control over resources and decisions. | Limited control; depends on organizational support. |
| Innovation | Creates new products, services, and markets. | Improves or innovates within existing frameworks. |
| Value Creation | Generates new market value and job creation. | Enhances organizational efficiency and competitive advantage. |
| Motivation | Driven by independence and profit potential. | Motivated by organizational goals and career growth. |
Defining Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs are individuals who create and manage new businesses, assuming financial risks to innovate and generate economic value independently. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, driving innovation and value creation by applying entrepreneurial principles without bearing personal financial risk. Both roles focus on identifying opportunities, but entrepreneurs aim to build standalone ventures, while intrapreneurs transform internal processes and products to enhance corporate growth.
Core Differences in Value Creation
Entrepreneurs drive value creation by taking ownership of new ventures, assuming financial risks, and innovating independently to disrupt markets. Intrapreneurs create value within established organizations by leveraging existing resources, promoting internal innovation, and enhancing processes without direct financial risk. The core difference lies in entrepreneurs building value through market creation, whereas intrapreneurs enhance value through organizational transformation and efficiency.
Innovation Approaches: Startup vs Established Company
Entrepreneurs drive value creation through disruptive innovation by launching startups that prioritize agility, risk-taking, and market disruption, often introducing breakthrough products or services. In contrast, intrapreneurs foster innovation within established companies by leveraging existing resources, processes, and market knowledge to implement incremental improvements and optimize efficiency. Startup innovation emphasizes rapid experimentation and scalability, while established company innovation balances creativity with structured risk management and long-term sustainability.
Risk and Reward: Personal Stakes
Entrepreneurs assume high personal financial and reputational risks with the potential for significant rewards tied directly to their ventures' success, fostering innovation through complete ownership and accountability. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations, leveraging company resources to minimize personal financial risk while contributing to value creation, with rewards often limited to recognition and career advancement. This fundamental difference in risk and reward structures drives diverse approaches to innovation and value creation in entrepreneurial and intrapreneurial settings.
Resource Utilization and Access
Entrepreneurs leverage diverse external resources to innovate and scale new ventures, often securing funding, partnerships, and market access independently. Intrapreneurs maximize internal organizational assets, utilizing existing infrastructure, established networks, and company resources to drive innovation within corporate boundaries. Both roles require strategic resource utilization, but entrepreneurs face higher resource acquisition challenges while intrapreneurs benefit from streamlined access to organizational support.
Impact on Organizational Growth
Entrepreneurs drive organizational growth by introducing innovative products and services that create new market opportunities and revenue streams. Intrapreneurs accelerate growth within existing companies by leveraging internal resources to optimize processes and develop scalable innovations, enhancing operational efficiency. Both roles are critical in fostering sustainable value creation, with entrepreneurs expanding market boundaries while intrapreneurs enhance competitive advantage from within.
Autonomy and Decision-Making Power
Entrepreneurs possess high autonomy and decision-making power, enabling them to identify opportunities and drive innovation independently. Intrapreneurs operate within established organizations but retain significant autonomy to develop new ideas and create value while navigating corporate structures. Both roles leverage autonomy differently to maximize value creation, with entrepreneurs leading external ventures and intrapreneurs fostering internal innovation.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Entrepreneurs and Intrapreneurs
Entrepreneurs like Elon Musk have transformed industries by launching innovative companies such as Tesla and SpaceX, demonstrating significant value creation through risk-taking and market disruption. In contrast, intrapreneurs like Google's Paul Buchheit leveraged organizational resources to create products like Gmail, driving internal innovation and fostering growth within established companies. Case studies reveal that both entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs play critical roles in value creation by applying creativity and strategic thinking to solve market or organizational challenges.
Challenges Faced in Creating Value
Entrepreneurs face challenges such as securing funding, managing market uncertainties, and establishing brand identity to create value in competitive environments. Intrapreneurs encounter obstacles like navigating corporate bureaucracy, limited autonomy, and aligning innovative projects with organizational goals. Both roles require strategic risk management and resource optimization to drive sustained value creation.
Choosing the Right Path: Entrepreneurship or Intrapreneurship
Entrepreneurs drive value creation by launching new ventures that disrupt markets and introduce innovative products or services, leveraging autonomy and risk-taking to maximize impact. Intrapreneurs foster value within established organizations by applying entrepreneurial skills to develop internal projects, optimize processes, and accelerate growth without the risks associated with startup ownership. Choosing between entrepreneurship and intrapreneurship hinges on one's tolerance for risk, desire for independence, and preference for leveraging existing resources versus building ventures from the ground up.
Related Important Terms
Corporate Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs drive value creation by launching independent ventures that disrupt markets, whereas intrapreneurs foster innovation within established organizations through corporate entrepreneurship, leveraging existing resources and networks. Corporate entrepreneurship enables companies to sustain competitive advantage by encouraging intrapreneurs to develop new products, processes, or business models that align with strategic goals.
Intrapreneurial Mindset
The intrapreneurial mindset drives value creation within organizations by fostering innovation, risk-taking, and proactive problem-solving, enabling employees to act like entrepreneurs while leveraging existing company resources. Unlike entrepreneurs who build ventures from scratch, intrapreneurs accelerate growth internally by transforming ideas into impactful projects that align with corporate goals and market demands.
Entrepreneurial Ecosystem
Entrepreneurs drive value creation by launching innovative ventures that disrupt markets within a dynamic entrepreneurial ecosystem, leveraging resources like venture capital, mentorship, and supportive policies. In contrast, intrapreneurs foster value inside established organizations by applying entrepreneurial skills to develop new products or processes, enhancing internal growth and competitiveness within the corporate ecosystem.
Innovation Champions
Entrepreneurs drive value creation by launching innovative startups, leveraging risk-taking and market disruption to develop groundbreaking products and services. Intrapreneurs, acting as innovation champions within established organizations, cultivate internal creativity and streamline processes to generate sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Venture Incubation
Entrepreneurs drive value creation by founding startups and harnessing venture incubation programs to accelerate early-stage business growth through access to funding, mentorship, and market networks. Intrapreneurs create value within established companies by leveraging corporate venture incubation resources to innovate, reduce risk, and scale new products without disrupting existing operations.
Internal Startups
Entrepreneurs drive value creation by launching external startups that introduce innovative products or services to new markets, while intrapreneurs foster internal startups within existing organizations, leveraging company resources to develop novel solutions that enhance operational efficiency and market competitiveness. Internal startups spearheaded by intrapreneurs accelerate corporate growth by embedding entrepreneurial agility into established structures, enabling sustainable value creation without the risks associated with external venture initiation.
Disruptive Intrapreneurship
Disruptive intrapreneurship drives value creation within established companies by fostering innovative projects that challenge existing business models without the risk of starting anew, blending entrepreneurial agility with corporate resources. Entrepreneurs create value through new ventures, while disruptive intrapreneurs generate breakthrough innovations internally, accelerating growth and competitive advantage.
Value Co-creation
Entrepreneurs drive value co-creation by identifying market gaps and launching innovative ventures that engage customers as active partners, fostering collaborative value generation. Intrapreneurs create value within existing organizations by leveraging internal resources and promoting cross-functional teamwork to enhance products and services through shared stakeholder involvement.
Entrepreneurial Autonomy
Entrepreneurs exercise high levels of entrepreneurial autonomy, driving value creation through independent decision-making and innovative risk-taking outside established organizational structures. In contrast, intrapreneurs operate within existing corporations, leveraging internal resources and strategic alignment to create value while navigating organizational constraints.
Strategic Intrapreneurship
Strategic intrapreneurship drives value creation within established companies by leveraging entrepreneurial skills to innovate while aligning with organizational goals; intrapreneurs identify growth opportunities and implement strategic initiatives that enhance competitive advantage. Unlike entrepreneurs who assume full risk in startups, intrapreneurs utilize company resources and networks to create scalable innovations, optimizing value through internal strategic alignment and resource efficiency.
Entrepreneur vs Intrapreneur for value creation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com