Employers who hire full-time staff maintain direct control over employee management, benefits, and long-term commitment, ensuring consistent alignment with company culture and goals. Fractional employers, often used for part-time or project-based roles, provide flexibility and cost-efficiency by engaging specialized talent without the obligations of full-time employment. Choosing between these options depends on the organization's need for control, scalability, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
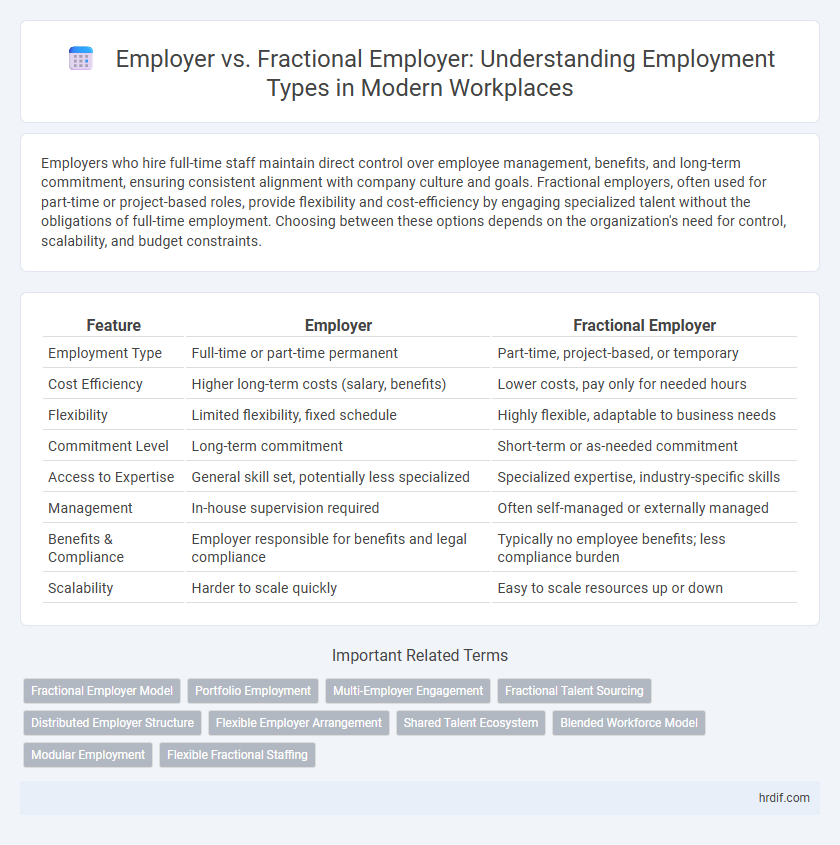
| Feature | Employer | Fractional Employer |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Type | Full-time or part-time permanent | Part-time, project-based, or temporary |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher long-term costs (salary, benefits) | Lower costs, pay only for needed hours |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, fixed schedule | Highly flexible, adaptable to business needs |
| Commitment Level | Long-term commitment | Short-term or as-needed commitment |
| Access to Expertise | General skill set, potentially less specialized | Specialized expertise, industry-specific skills |
| Management | In-house supervision required | Often self-managed or externally managed |
| Benefits & Compliance | Employer responsible for benefits and legal compliance | Typically no employee benefits; less compliance burden |
| Scalability | Harder to scale quickly | Easy to scale resources up or down |
Understanding the Employer Model in Today’s Workforce
The traditional employer model involves a direct and ongoing employment relationship where the employer manages all aspects of job roles, benefits, and compliance. Fractional employers provide specialized, part-time leadership or expertise, allowing businesses to access high-level skills without committing to full-time hires. This flexible approach helps companies optimize talent acquisition while reducing overhead and adapting rapidly to changing workforce demands.
What is a Fractional Employer?
A fractional employer is a company or individual that provides partial employment services, managing specific functions such as payroll, benefits, or human resources for a fraction of the workforce. Unlike traditional employers who handle all employment responsibilities internally, fractional employers allow businesses to outsource certain employment duties, reducing overhead and improving flexibility. This model is particularly beneficial for startups or small businesses seeking expert HR management without the cost of full-time staff.
Key Differences Between Traditional Employers and Fractional Employers
Traditional employers typically offer full-time, permanent positions with comprehensive benefits and direct management of employee roles, while fractional employers provide part-time, specialized expertise on a contractual basis without long-term commitments. Fractional employment allows businesses to access high-level skills flexibly and cost-effectively, often benefiting startups and SMEs seeking strategic input without expanding full payroll obligations. Key differences include employment duration, financial commitments, control over work processes, and the scope of employee benefits.
Pros and Cons of Being a Traditional Employer
Being a traditional employer offers direct control over hiring, employee management, and company culture, enabling tailored workforce development and consistent alignment with business goals. However, this model involves higher fixed costs such as salaries, benefits, payroll taxes, and administrative overhead, along with compliance risks related to labor laws and regulations. Traditional employers face challenges in scaling quickly and managing fluctuating workloads compared to fractional employers, who provide flexible staffing solutions.
Advantages and Challenges of the Fractional Employer Approach
The fractional employer approach allows businesses to access specialized talent on a part-time basis, reducing overhead costs and increasing flexibility in workforce management. This model facilitates rapid scaling and skill diversification without the long-term commitment or benefits administration typical of traditional employment. Challenges include potential misalignment of company culture, limited availability of fractional employees, and complexities in coordinating work across multiple clients.
When Should You Consider a Fractional Employer Arrangement?
A fractional employer arrangement is ideal when a company needs specialized talent for specific projects without the commitment of full-time hiring, offering flexibility and cost efficiency. This approach benefits startups and small businesses requiring expert skills on a part-time basis to scale operations gradually. Choosing fractional employment allows access to experienced professionals while managing payroll expenses and reducing long-term employment risks.
Legal and Compliance Factors: Employer vs Fractional Employer
An Employer holds full legal responsibility for employee compliance with labor laws, tax withholding, benefits administration, and workplace safety regulations. Fractional Employers, often third-party or part-time staffing providers, share or delegate these legal obligations, which can complicate liability and compliance enforcement depending on contract terms and jurisdictional employment laws. Ensuring clear agreements and understanding state and federal employment regulations is critical for both parties to mitigate risks related to worker classification and regulatory compliance.
Impact on Employee Experience and Talent Acquisition
Choosing between a traditional employer and a fractional employer significantly impacts employee experience and talent acquisition strategies. Traditional employers often offer greater job stability, comprehensive benefits, and direct career development opportunities, fostering long-term employee engagement and loyalty. Fractional employers provide flexibility and specialized roles that attract high-caliber talent seeking project-based or part-time work but may challenge sustained employee retention and consistent company culture.
Cost and Resource Implications of Both Employment Types
Employers opting for full-time hiring face higher fixed costs including salaries, benefits, and long-term commitments, while fractional employers reduce expenses by contracting specialized talent only when needed, avoiding overhead like health insurance and retirement plans. Fractional employment offers flexible resource allocation, enabling companies to scale expertise based on project demands without incurring the continuous cost of full-time staff. Traditional employers bear recruitment and training costs, whereas fractional arrangements minimize these investments, enhancing cost efficiency and operational agility.
Choosing the Right Employment Model for Your Business Needs
Selecting the right employment model hinges on your business's operational scale and flexibility requirements. Traditional employers offer full-time control and stability, ideal for long-term projects and consistent workforce management. Fractional employers reduce overhead by providing specialized talent on a part-time basis, perfect for startups or businesses needing expert skills without the full-time commitment.
Related Important Terms
Fractional Employer Model
The Fractional Employer model offers businesses flexible workforce management by hiring employees for specific projects or limited hours, reducing overhead costs and improving resource allocation compared to traditional full-time employment. This approach enhances talent acquisition efficiency and promotes scalability for companies adapting to fluctuating market demands.
Portfolio Employment
Portfolio employment blends full-time roles with fractional employer arrangements, allowing professionals to diversify their work across multiple organizations simultaneously. This model offers employers flexible staffing solutions and access to specialized skills on demand, enhancing productivity and reducing long-term employment costs.
Multi-Employer Engagement
Multi-employer engagement enables businesses to leverage fractional employers who provide specialized skills across multiple organizations without the overhead of full-time employment, enhancing flexibility and cost efficiency. Traditional employers typically manage single-entity workforces, whereas fractional employers facilitate distributed talent pools to support dynamic project demands across various employers simultaneously.
Fractional Talent Sourcing
Fractional employer models offer businesses flexible talent sourcing by enabling access to specialized professionals on a part-time or project basis, reducing costs compared to traditional full-time employment. Utilizing fractional talent sourcing allows organizations to scale expertise efficiently without the long-term commitment and overhead associated with standard employer-employee relationships.
Distributed Employer Structure
A Distributed Employer Structure leverages fractional employers to allocate specific job roles across multiple specialized providers, enhancing flexibility and cost-efficiency compared to traditional single-employer models. This approach enables organizations to tap into diverse talent pools globally while maintaining compliance with local employment regulations and minimizing administrative overhead.
Flexible Employer Arrangement
Flexible employer arrangements offer businesses the ability to engage talent as either a traditional employer or a fractional employer, optimizing workforce management for scalability and cost efficiency. Fractional employment allows access to specialized skills on a part-time basis without the full commitments of a traditional employer, enhancing flexibility and operational agility.
Shared Talent Ecosystem
A traditional employer directly manages full-time employees, bearing all responsibilities for benefits, payroll, and compliance, whereas a fractional employer leverages the Shared Talent Ecosystem to allocate expert talent on a part-time or project basis, optimizing cost-efficiency and flexibility. This model enables businesses to access specialized skills without the overhead of permanent hires, fostering agility within dynamic workforce demands.
Blended Workforce Model
A blended workforce model integrates traditional full-time employees with fractional employers, enabling businesses to optimize resource allocation and reduce operational costs while maintaining flexibility. Fractional employers offer specialized expertise on a part-time basis, complementing the stability and consistency provided by full-time employers in dynamic work environments.
Modular Employment
Modular employment offers a flexible alternative to traditional employer arrangements by allowing businesses to engage fractional employers who provide specialized services on a project or part-time basis, optimizing workforce costs and scalability. This approach enables companies to tailor employment relationships to specific needs, improving operational efficiency while maintaining compliance with labor regulations.
Flexible Fractional Staffing
Flexible fractional staffing allows employers to engage highly skilled professionals on a part-time or project basis, optimizing labor costs and enhancing workforce agility. Compared to traditional full-time employment, this model provides employers with scalable talent solutions that adapt to fluctuating business needs without long-term commitments.
Employer vs Fractional Employer for employment type. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com