Employers maintain greater control over workforce engagement by directly managing employee relationships, offering consistent benefits, and fostering long-term loyalty. Gig platforms prioritize flexible, task-based work, often leading to lower engagement and limited commitment from workers. This fundamental difference impacts productivity, job satisfaction, and the overall stability of the workforce.
Table of Comparison
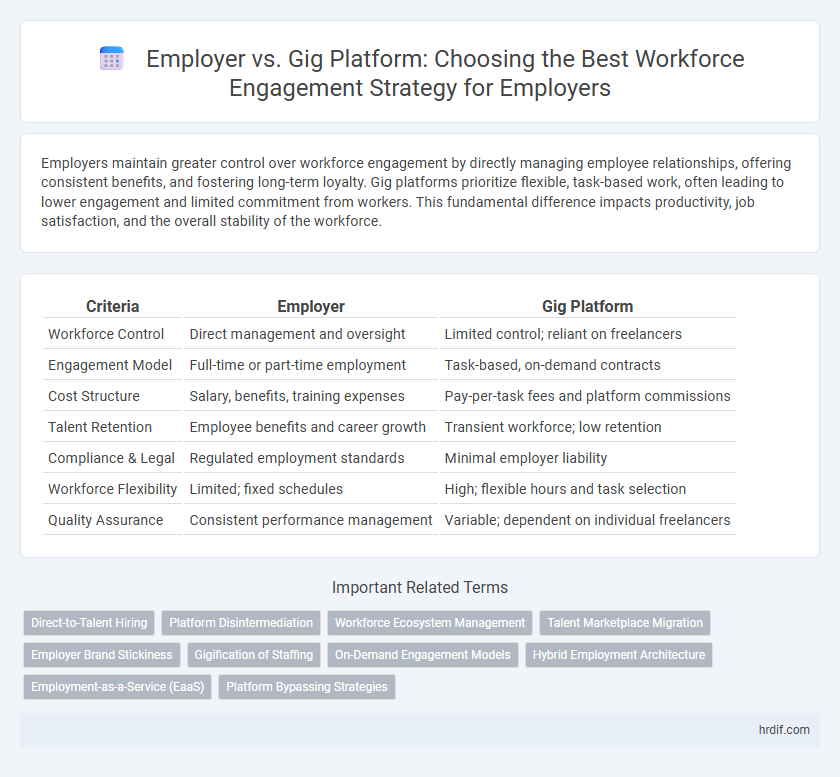
| Criteria | Employer | Gig Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Workforce Control | Direct management and oversight | Limited control; reliant on freelancers |
| Engagement Model | Full-time or part-time employment | Task-based, on-demand contracts |
| Cost Structure | Salary, benefits, training expenses | Pay-per-task fees and platform commissions |
| Talent Retention | Employee benefits and career growth | Transient workforce; low retention |
| Compliance & Legal | Regulated employment standards | Minimal employer liability |
| Workforce Flexibility | Limited; fixed schedules | High; flexible hours and task selection |
| Quality Assurance | Consistent performance management | Variable; dependent on individual freelancers |
Defining Traditional Employers and Gig Platforms
Traditional employers offer structured, long-term employment relationships with benefits, job security, and clear career progression, emphasizing direct management and accountability. Gig platforms facilitate flexible, on-demand work arrangements by connecting independent contractors with short-term tasks, prioritizing scalability and workforce fluidity over permanence. The key distinction lies in employment status: traditional employers maintain formal contracts, while gig platforms enable task-based engagements without standard employee protections.
Workforce Engagement Models: Full-Time vs. On-Demand
Employers traditionally rely on full-time workforce engagement models, offering stability, benefits, and long-term commitment, which fosters employee loyalty and skill development. Gig platforms emphasize on-demand workforce engagement, providing flexibility, scalable labor costs, and access to diverse talent pools for project-based or peak-demand tasks. Choosing between these models depends on business needs for consistency versus agility in workforce management.
Hiring Processes: Structured Recruitment vs. App-Based Matching
Employers utilize structured recruitment processes involving detailed job descriptions, credential verification, and multi-stage interviews to ensure precise candidate-employer alignment. Gig platforms rely on algorithm-driven app-based matching that prioritizes speed and task-specific skills, often bypassing traditional vetting methods. This contrast affects workforce engagement by balancing thorough evaluation against rapid onboarding, impacting the quality and stability of hired talent.
Job Security and Benefits Comparison
Employers typically offer greater job security through stable contracts and consistent work schedules, while gig platforms often provide flexible but unpredictable opportunities lacking long-term guarantees. Traditional employers are more likely to provide comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, which gig platform workers usually do not receive. This fundamental difference impacts workforce engagement by influencing employee loyalty and overall financial stability.
Flexibility and Autonomy for Workers
Employers typically offer structured roles with fixed schedules, limiting worker flexibility and autonomy compared to gig platforms. Gig platforms empower workers by enabling them to choose projects, set their own hours, and work from various locations, enhancing personal freedom. This flexibility boosts job satisfaction and appeals to a workforce seeking control over work-life balance and diverse income opportunities.
Performance Management Methods
Employers typically use structured performance management methods involving regular evaluations, goal-setting, and personalized feedback to enhance workforce productivity. Gig platforms rely on algorithm-driven rating systems and real-time client reviews to measure worker performance quickly and at scale. These contrasting approaches impact engagement by balancing detailed, developmental oversight with flexible, instantaneous assessment.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Employers face complex legal and regulatory considerations when engaging workers through traditional employment or gig platforms, including compliance with labor laws, wage and hour regulations, and benefits obligations. Gig platforms often challenge existing employment classifications, raising issues regarding worker rights, tax responsibilities, and liability protections. Understanding dynamic regulatory frameworks is essential for employers to mitigate risks and ensure lawful workforce engagement strategies.
Cost Implications for Employers and Gig Platforms
Employers face higher fixed costs related to benefits, payroll taxes, and long-term employee retention compared to gig platforms, which leverage flexible, on-demand labor to minimize overhead expenses. Gig platforms reduce operational costs by shifting administrative responsibilities and compliance risks onto workers, enabling more scalable and cost-efficient workforce engagement. However, the variable nature of gig labor may increase transaction costs and quality management expenses for employers seeking consistent performance.
Employee Loyalty and Retention
Employers investing in tailored workforce engagement strategies foster stronger employee loyalty and higher retention rates compared to gig platforms that emphasize transactional relationships. Direct employment offers clearer career development opportunities and benefits, which promote long-term commitment and reduced turnover. The structured environment of traditional employment enhances organizational culture and employee satisfaction, essential factors in retaining skilled talent.
Future Trends in Workforce Engagement
Employers are increasingly integrating advanced AI-driven tools to enhance workforce engagement, contrasting with gig platforms that prioritize task-based, flexible labor solutions. Future trends indicate a shift toward hybrid models combining direct employer relationships with gig platform efficiencies, emphasizing personalized employee experiences and real-time performance analytics. Data-driven strategies and adaptive workforce management will shape engagement, balancing job security with flexibility in evolving labor markets.
Related Important Terms
Direct-to-Talent Hiring
Direct-to-talent hiring enables employers to bypass gig platforms, fostering stronger, long-term relationships with skilled workers and reducing dependency on third-party intermediaries. This approach enhances workforce engagement by providing greater control over talent acquisition, improved retention rates, and personalized workforce management strategies.
Platform Disintermediation
Employers benefit from platform disintermediation by directly engaging with the workforce, reducing reliance on gig platforms that often impose fees and control access to talent pools. This shift enhances cost efficiency and strengthens employer-worker relationships through transparent communication and tailored engagement strategies.
Workforce Ecosystem Management
Employers leveraging Workforce Ecosystem Management integrate diverse workforces, including full-time, gig, and freelance talent, to optimize engagement and operational efficiency. Gig platforms provide scalable access to flexible labor pools but lack centralized control and personalized workforce engagement that employers achieve through ecosystem strategies.
Talent Marketplace Migration
Employers increasingly leverage talent marketplace migration to shift workforce engagement from traditional models to gig platforms, optimizing access to specialized skills and flexible labor pools. This transition enhances operational agility by enabling dynamic talent acquisition while reducing long-term employment costs and administrative overhead.
Employer Brand Stickiness
Employers investing in strong brand stickiness through authentic values and consistent employee experience outperform gig platforms in retaining a loyal workforce. Unlike gig platforms that prioritize transactional relationships, employers build long-term engagement by fostering trust and career growth opportunities.
Gigification of Staffing
Employers increasingly leverage gig platforms to access flexible, scalable talent pools, driving the gigification of staffing by transforming traditional workforce engagement into on-demand, task-based labor models. This shift enables businesses to optimize labor costs and project-specific staffing needs while gig platforms provide streamlined hiring, payroll, and compliance management solutions.
On-Demand Engagement Models
Employers utilizing on-demand engagement models benefit from direct control over workforce management, enabling tailored skill matching and enhanced compliance with labor regulations compared to gig platforms. Gig platforms offer flexible access to a broad talent pool but often lack integration with company culture and long-term employee development strategies.
Hybrid Employment Architecture
Hybrid employment architecture integrates traditional employer roles with gig platform functionalities to enhance workforce engagement by combining job security and flexibility. This model leverages centralized employer control alongside decentralized gig task distribution, optimizing talent allocation and operational efficiency.
Employment-as-a-Service (EaaS)
Employment-as-a-Service (EaaS) offers employers scalable workforce engagement by integrating flexible talent acquisition, management, and payroll solutions, contrasting gig platforms that primarily provide transactional task-based labor. EaaS enhances employer control over employee experience and compliance while leveraging technology for streamlined workforce operations beyond the gig economy's project-specific focus.
Platform Bypassing Strategies
Employers increasingly adopt platform bypassing strategies to directly engage skilled workers, reducing reliance on gig platforms and preserving control over labor costs and job quality. By leveraging proprietary apps and exclusive talent pools, employers enhance workforce engagement and minimize platform fees, fostering stronger long-term employee relationships.
Employer vs Gig Platform for workforce engagement. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com