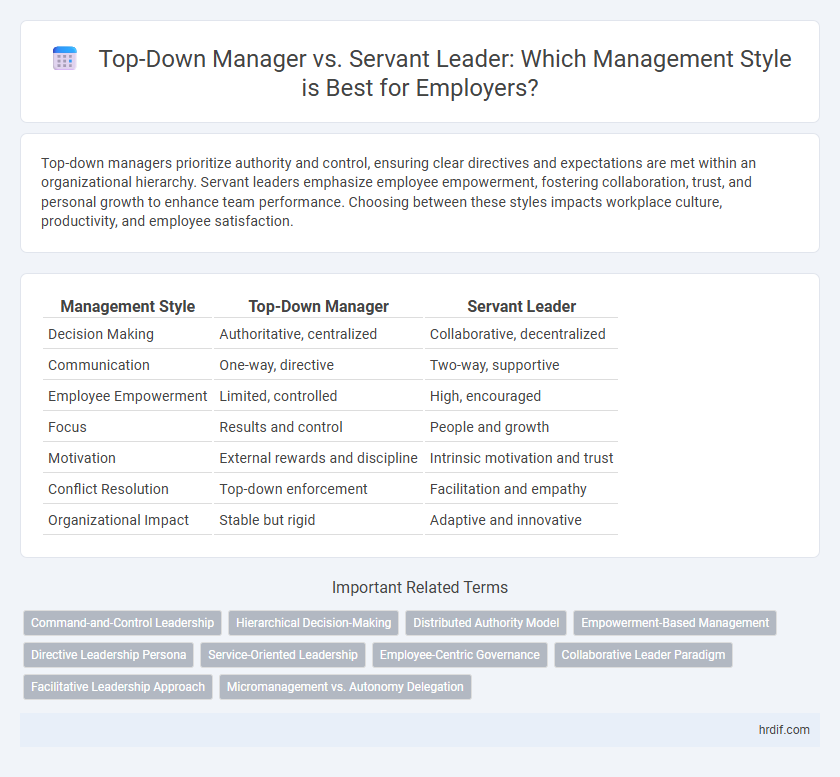
Top-down managers prioritize authority and control, ensuring clear directives and expectations are met within an organizational hierarchy. Servant leaders emphasize employee empowerment, fostering collaboration, trust, and personal growth to enhance team performance. Choosing between these styles impacts workplace culture, productivity, and employee satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
| Management Style | Top-Down Manager | Servant Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Authoritative, centralized | Collaborative, decentralized |
| Communication | One-way, directive | Two-way, supportive |
| Employee Empowerment | Limited, controlled | High, encouraged |
| Focus | Results and control | People and growth |
| Motivation | External rewards and discipline | Intrinsic motivation and trust |
| Conflict Resolution | Top-down enforcement | Facilitation and empathy |
| Organizational Impact | Stable but rigid | Adaptive and innovative |
Introduction to Management Styles: Top-Down vs Servant Leadership
Top-Down management relies on hierarchical decision-making where leaders dictate tasks and employees follow instructions, emphasizing control and efficiency. Servant Leadership prioritizes empowering employees, fostering collaboration, and focusing on their growth and well-being to enhance organizational performance. Understanding these management styles helps employers align leadership approaches with company culture and business goals.
Defining the Top-Down Manager Approach
The Top-Down Manager approach centralizes decision-making authority, where directives flow from senior leadership to lower-level employees, emphasizing control and efficiency. This management style relies heavily on hierarchical structures, with managers setting clear expectations and enforcing compliance across teams. It often prioritizes organizational goals over individual employee needs, aiming to maintain order and achieve predictable outcomes.
Exploring Servant Leadership in the Workplace
Servant leadership in the workplace emphasizes prioritizing employee well-being, fostering a collaborative environment, and enhancing team engagement, which contrasts sharply with the authoritative nature of top-down management. Research shows servant leaders promote higher job satisfaction, increased trust, and improved organizational performance by empowering employees and encouraging open communication. Companies implementing servant leadership often see reduced turnover rates and stronger innovation due to a culture that values empathy and support.
Key Differences Between Top-Down and Servant Leadership
Top-down managers rely on hierarchical authority and centralized decision-making, emphasizing control and directive leadership to achieve organizational goals. Servant leaders prioritize employee empowerment, active listening, and fostering collaboration to enhance team performance and well-being. The key differences lie in power distribution, communication style, and the leader's focus on either authority or support.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Motivation
Top-Down Managers typically exert control through hierarchical commands, which can suppress employee autonomy and reduce intrinsic motivation, leading to lower engagement levels. Servant Leaders prioritize employee needs and foster collaboration, resulting in higher job satisfaction and enhanced motivation by empowering team members. Research shows organizations with servant leadership cultures experience up to 30% greater employee engagement and 20% lower turnover rates compared to top-down hierarchical models.
Decision-Making Processes: Authority vs Collaboration
Top-down managers centralize decision-making authority, driving swift execution but often limiting employee input and innovation. Servant leaders prioritize collaboration, empowering teams to contribute insights that enhance problem-solving and foster engagement. This collaborative approach promotes adaptability and collective ownership of outcomes, contrasting with the authoritative control of top-down leadership.
Effects on Team Performance and Productivity
Top-down managers often enforce strict hierarchies, which can lead to clear directives but may stifle creativity and reduce team engagement, negatively impacting productivity. Servant leaders prioritize employee empowerment and collaboration, fostering higher motivation, innovation, and stronger team cohesion, which typically enhances overall performance. Studies indicate teams led by servant leaders experience increased job satisfaction and lower turnover rates, directly benefiting organizational outcomes.
Adapting Management Styles to Organizational Goals
Top-down managers emphasize authority and clear directives, which can drive rapid decision-making and enforce strategic goals in hierarchical organizations. Servant leaders prioritize employee growth and empowerment, fostering collaboration that aligns with innovation-driven or mission-focused companies. Adapting management styles to organizational goals ensures optimal team performance and sustains long-term success by matching leadership approaches to company culture and objectives.
Challenges and Benefits of Each Management Style
Top-down managers face challenges in employee engagement and innovation due to rigid hierarchies but benefit from clear authority and quick decision-making. Servant leaders foster collaboration and high morale by prioritizing team needs, enhancing creativity and loyalty, yet may struggle with slower decisions and maintaining control in crisis. Balancing these approaches depends on organizational culture and goals, with top-down suits for structure, servant leadership excels in empowerment.
Choosing the Right Management Style for Your Business
Top-down managers enforce clear hierarchical structures, enabling swift decision-making and accountability in fast-paced industries. Servant leaders prioritize employee empowerment and collaboration, fostering innovation and long-term engagement. Selecting the optimal management style depends on business goals, organizational culture, and the need for agility versus employee development.
Related Important Terms
Command-and-Control Leadership
Top-down managers emphasize command-and-control leadership, enforcing strict hierarchies and centralized decision-making to maintain order and efficiency within organizations. This style often limits employee autonomy and innovation compared to servant leadership, which prioritizes support, empowerment, and collaboration to drive performance and engagement.
Hierarchical Decision-Making
Top-down managers centralize hierarchical decision-making, directing tasks and strategies from upper management to employees, which ensures clear authority but may reduce team autonomy. Servant leaders decentralize decisions, empowering team members to contribute insights and fostering collaboration, improving engagement and innovation.
Distributed Authority Model
Top-down managers typically centralize decision-making authority, which can limit innovation and responsiveness within teams. In contrast, servant leaders embrace a distributed authority model, empowering employees to take initiative and fostering collaborative problem-solving that enhances organizational agility and employee engagement.
Empowerment-Based Management
Empowerment-based management prioritizes servant leadership by fostering team autonomy, encouraging collaboration, and promoting personal growth, which enhances employee engagement and innovation. In contrast, top-down management relies on hierarchical control and directive decision-making, often limiting empowerment and reducing adaptability within the workforce.
Directive Leadership Persona
Directive leadership in a top-down management style emphasizes clear instructions, centralized decision-making, and strict oversight to achieve organizational goals efficiently. This contrasts with servant leadership, which prioritizes employee empowerment and collaboration over authoritative control.
Service-Oriented Leadership
Service-oriented leadership fosters employee engagement and innovation by prioritizing team needs and empowering individuals, contrasting the authoritative control seen in top-down management. Organizations adopting servant leadership report higher job satisfaction, increased productivity, and stronger organizational commitment due to the emphasis on support, trust, and collaborative decision-making.
Employee-Centric Governance
Top-down managers enforce strict hierarchical decision-making, often limiting employee autonomy and stifling innovation, whereas servant leaders prioritize employee-centric governance by empowering staff, fostering collaboration, and enhancing overall job satisfaction. Research shows organizations led by servant leaders experience higher employee engagement, reduced turnover, and improved team performance compared to those managed with a top-down approach.
Collaborative Leader Paradigm
Top-down managers prioritize hierarchical control and directive decision-making, often limiting team autonomy and innovation, whereas servant leaders emphasize empathy, active listening, and empowerment, fostering a collaborative leader paradigm that drives employee engagement and organizational agility. Embracing servant leadership in modern workplaces enhances communication, trust, and shared responsibility, leading to improved performance and sustainable growth.
Facilitative Leadership Approach
Facilitative leadership in management emphasizes empowering employees by fostering collaboration, active listening, and support, contrasting sharply with the authoritative, directive nature of top-down managers. Servant leaders prioritize facilitating team growth and removing obstacles, enhancing engagement and innovation through a people-centered approach that drives sustainable organizational success.
Micromanagement vs. Autonomy Delegation
Top-down managers often engage in micromanagement by closely supervising employee tasks and limiting decision-making autonomy, which can reduce innovation and employee satisfaction. In contrast, servant leaders prioritize autonomy delegation, empowering team members to take ownership and drive performance, ultimately fostering a more collaborative and motivated workforce.
Top-Down Manager vs Servant Leader for management style. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com