Traditional employees typically follow established procedures and focus on completing assigned tasks within defined roles, ensuring stability and consistency in organizational operations. Intrapreneurs, however, act like internal entrepreneurs by driving innovation, taking initiative, and seeking new opportunities that contribute to the company's growth and competitive edge. Balancing both roles enables organizations to maintain operational efficiency while fostering a culture of creativity and adaptability.
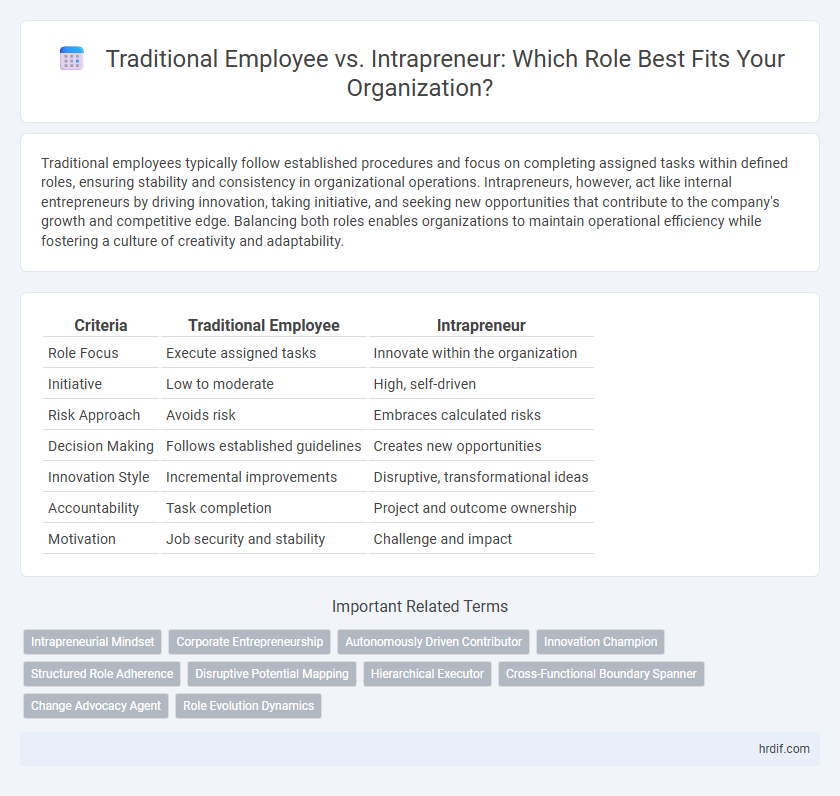
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Traditional Employee | Intrapreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Execute assigned tasks | Innovate within the organization |
| Initiative | Low to moderate | High, self-driven |
| Risk Approach | Avoids risk | Embraces calculated risks |
| Decision Making | Follows established guidelines | Creates new opportunities |
| Innovation Style | Incremental improvements | Disruptive, transformational ideas |
| Accountability | Task completion | Project and outcome ownership |
| Motivation | Job security and stability | Challenge and impact |
Defining the Traditional Employee and Intrapreneur
The traditional employee typically follows established procedures and focuses on executing assigned tasks within defined roles to maintain organizational stability and efficiency. In contrast, an intrapreneur proactively drives innovation by leveraging entrepreneurial skills to develop new ideas and projects while operating inside the company. This differentiation highlights the traditional employee's emphasis on reliability versus the intrapreneur's focus on creativity and business growth within the organizational structure.
Key Characteristics: Employee vs Intrapreneur
Traditional employees typically follow established protocols, prioritize job security, and focus on executing assigned tasks within a structured environment. Intrapreneurs, on the other hand, exhibit entrepreneurial mindset within the organization, driving innovation, taking calculated risks, and proactively identifying new business opportunities. While employees contribute to operational stability, intrapreneurs foster growth and transformation by leveraging creativity and strategic thinking.
Mindset Differences: Task-Focused vs Innovation-Driven
Traditional employees typically adopt a task-focused mindset, prioritizing routine responsibilities and adherence to established procedures to ensure organizational stability. Intrapreneurs, by contrast, embrace an innovation-driven mindset that encourages creativity, risk-taking, and proactive problem-solving to drive organizational growth and transformation. These divergent mindsets shape their roles within the company, with traditional employees maintaining operational consistency and intrapreneurs spearheading strategic advancements.
Impact on Organizational Culture
Traditional employees contribute to organizational culture by maintaining established procedures and ensuring consistent performance, fostering stability and predictability. Intrapreneurs drive innovation and adaptability within the company, promoting a culture of creativity, risk-taking, and proactive problem-solving. Their roles collectively balance operational efficiency with dynamic growth, shaping a resilient and forward-thinking organizational environment.
Approach to Problem-Solving and Risk
Traditional employees typically follow established protocols and avoid risks, relying on structured problem-solving methods to maintain stability and efficiency. Intrapreneurs embrace innovative approaches and proactively tackle challenges by taking calculated risks to drive growth and change within the organization. This distinction in risk tolerance and problem-solving reflects their contrasting roles in fostering operational consistency versus transformational innovation.
Career Growth Opportunities
Traditional employees often experience structured career growth through clearly defined roles, promotions, and skill development programs within an organization. Intrapreneurs drive innovation by acting as entrepreneurial agents internally, creating opportunities for accelerated career advancement linked to project ownership and strategic impact. Organizations benefit from balancing traditional employee stability with intrapreneurial agility to foster diverse career growth pathways.
Empowerment and Autonomy at Work
Traditional employees often operate within defined roles and hierarchical structures, with limited autonomy and decision-making power, which can restrict their ability to drive innovation. Intrapreneurs, by contrast, are empowered with greater autonomy and resources to take initiative, fostering creativity and proactive problem-solving within the organization. This empowerment enhances organizational agility and employee engagement, leading to improved business outcomes and competitive advantage.
Rewards and Recognition Systems
Traditional employees often receive standardized rewards and recognition based on tenure, attendance, and performance metrics, which emphasizes consistency and reliability. Intrapreneurs, driving innovation within the organization, benefit from more dynamic recognition systems that highlight creativity, risk-taking, and project impact. Tailoring rewards to intrapreneurial contributions fosters motivation and aligns with organizational goals for growth and competitive advantage.
Contribution to Organizational Success
Traditional employees contribute to organizational success by efficiently executing assigned tasks and maintaining consistent performance within established roles. Intrapreneurs drive innovation by identifying new opportunities, taking initiative to develop projects, and pushing organizational boundaries to achieve growth. Combining both roles enhances overall success through operational stability and creative advancement.
Choosing the Right Fit for Your Organization
Traditional employees excel in executing defined tasks and maintaining operational stability, ensuring consistent productivity within established frameworks. Intrapreneurs bring innovation and entrepreneurial thinking, driving internal growth and adaptability through proactive problem-solving and strategic initiatives. Selecting the right fit depends on your organization's goals: prioritize traditional employees for reliability and structure, or intrapreneurs to foster creativity and competitive advantage.
Related Important Terms
Intrapreneurial Mindset
An intrapreneurial mindset empowers employees to innovate within organizational boundaries by embracing risk-taking, proactivity, and ownership, contrasting with traditional employees who typically follow predefined roles and routines. Organizations benefit from fostering intrapreneurs as they drive internal growth, adapt to market changes, and create competitive advantages through continuous innovation.
Corporate Entrepreneurship
Traditional employees typically follow established workflows and contribute to organizational stability, while intrapreneurs drive innovation by proactively identifying opportunities and leading projects within the company. Emphasizing corporate entrepreneurship, intrapreneurs foster growth by leveraging internal resources to develop new products and business models, thereby enhancing competitive advantage.
Autonomously Driven Contributor
Traditional employees typically follow structured roles with defined responsibilities, executing tasks under direct supervision, while intrapreneurs act as autonomously driven contributors who innovate and drive projects independently within the organization. Intrapreneurs leverage entrepreneurial thinking to identify opportunities, take initiative, and deliver value beyond conventional job descriptions, fostering organizational growth and adaptability.
Innovation Champion
Traditional employees typically follow established procedures to maintain operational consistency, while intrapreneurs act as innovation champions by proactively developing and implementing creative solutions within the organization. Intrapreneurs drive organizational growth by taking ownership of innovation projects, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and strategic transformation.
Structured Role Adherence
Traditional employees follow well-defined job descriptions and adhere strictly to organizational hierarchies, ensuring consistent role execution and minimizing ambiguity. Intrapreneurs, while operating within the company, embrace flexibility and innovation, often expanding beyond structured roles to drive internal ventures and transformative projects.
Disruptive Potential Mapping
Traditional employees typically follow established workflows and contribute to incremental improvements, exhibiting limited disruptive potential within organizational role frameworks, while intrapreneurs drive innovation by leveraging creativity and risk-taking to transform business models. Disruptive potential mapping highlights intrapreneurs as catalysts for groundbreaking change, positioned at the intersection of opportunity recognition and agile execution, contrasting with traditional employees' focus on operational stability.
Hierarchical Executor
Traditional employees typically function as hierarchical executors, following established protocols and directives within defined organizational structures to maintain stability and efficiency. In contrast, intrapreneurs operate with greater autonomy, leveraging creativity and innovation to drive change and generate value while still aligning with corporate goals.
Cross-Functional Boundary Spanner
Traditional employees typically operate within defined roles and departments, following established procedures with limited interaction across functional boundaries; intrapreneurs act as cross-functional boundary spanners by driving innovation, collaborating across departments, and leveraging diverse expertise to create value within the organization. Their ability to bridge gaps between teams enhances organizational agility and fosters a culture of continuous improvement and entrepreneurial thinking.
Change Advocacy Agent
Traditional employees follow established processes and maintain organizational stability, while intrapreneurs act as change advocacy agents by driving innovation, championing new initiatives, and fostering transformational growth within the company. Intrapreneurs leverage entrepreneurial thinking to challenge the status quo, accelerate adaptation to market shifts, and facilitate sustainable competitive advantage.
Role Evolution Dynamics
Traditional employees primarily execute defined tasks within established organizational frameworks, ensuring stability and consistency in operations. Intrapreneurs drive innovation by leveraging entrepreneurial skills internally, catalyzing transformation and fostering agile role evolution to adapt to dynamic market demands.
Traditional employee vs Intrapreneur for organizational role. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com