Traditional employees typically work fixed hours in a designated office, following structured routines and direct supervision, which ensures consistent team collaboration and immediate access to company resources. Digital nomad employees embrace flexible schedules and remote locations, leveraging technology to maintain productivity and work-life balance while adapting to diverse environments. This contrast highlights the shift towards autonomy and location independence in modern work styles, driven by technological advancements and evolving organizational cultures.
Table of Comparison
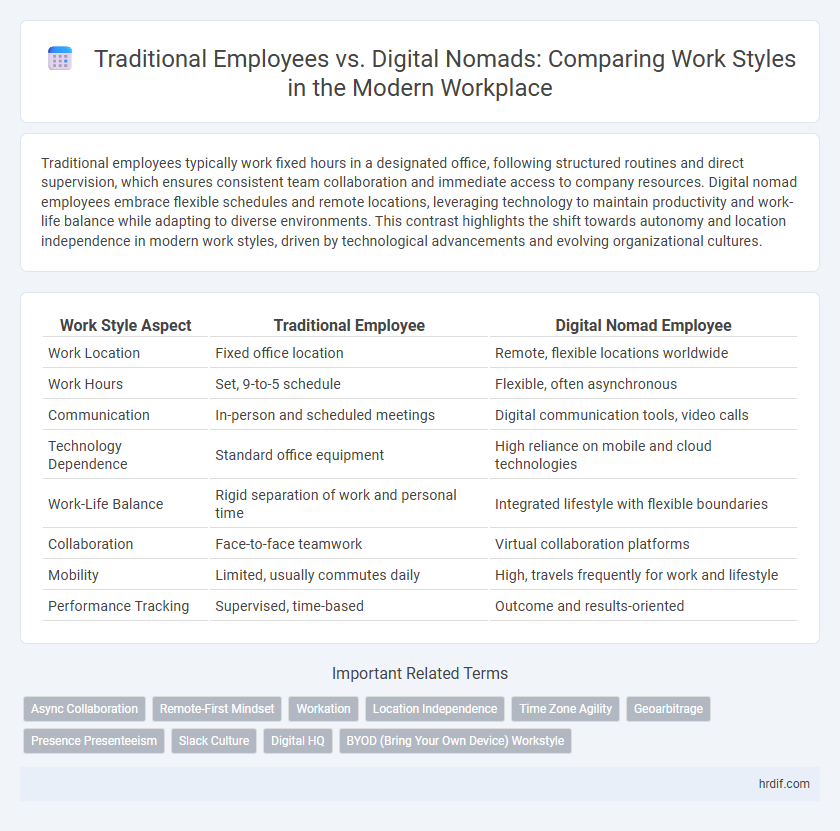
| Work Style Aspect | Traditional Employee | Digital Nomad Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Work Location | Fixed office location | Remote, flexible locations worldwide |
| Work Hours | Set, 9-to-5 schedule | Flexible, often asynchronous |
| Communication | In-person and scheduled meetings | Digital communication tools, video calls |
| Technology Dependence | Standard office equipment | High reliance on mobile and cloud technologies |
| Work-Life Balance | Rigid separation of work and personal time | Integrated lifestyle with flexible boundaries |
| Collaboration | Face-to-face teamwork | Virtual collaboration platforms |
| Mobility | Limited, usually commutes daily | High, travels frequently for work and lifestyle |
| Performance Tracking | Supervised, time-based | Outcome and results-oriented |
Defining Traditional Employees and Digital Nomads
Traditional employees typically work fixed hours in a designated office environment, adhering to structured schedules and direct supervision. Digital nomads operate remotely, leveraging digital technology to work from various locations, emphasizing flexibility and autonomy. The rise of digital nomadism reflects a shift towards results-oriented work styles, contrasting with the stability and routine valued by traditional employees.
Core Differences in Work Environment
Traditional employees typically work in a fixed office setting with a structured schedule, relying on physical presence for collaboration and supervision. Digital nomad employees operate remotely from various locations worldwide, leveraging cloud-based tools and flexible hours to manage tasks independently. The core difference lies in workspace stability and autonomy, where traditional roles emphasize consistent environments and digital nomads prioritize adaptability and self-directed workflows.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
Traditional employees typically follow fixed schedules and work from designated office locations, which may limit flexibility and impact work-life balance. Digital nomad employees leverage remote work technology to choose their work environment and hours, enhancing flexibility and enabling a better integration of personal and professional life. This adaptable work style supports improved employee well-being and productivity through greater autonomy and location independence.
Communication and Collaboration Methods
Traditional employees rely heavily on face-to-face communication and structured collaboration within physical office environments, fostering immediate feedback and team cohesion. Digital nomad employees utilize digital tools such as video conferencing, instant messaging, and cloud-based project management platforms to facilitate asynchronous communication and remote collaboration across diverse time zones. Both work styles demand clear communication protocols, but digital nomads prioritize flexibility and tech proficiency to maintain productivity without physical presence.
Impact on Productivity and Efficiency
Traditional employees often benefit from structured environments and direct supervision, enhancing focus and consistent output, which can lead to steady productivity and efficiency. Digital nomad employees leverage flexibility and autonomy, optimizing work-life balance and creative problem-solving, often resulting in higher engagement and adaptive productivity. Technology integration and self-discipline crucially impact how both styles influence overall work performance and operational efficiency.
Technological Requirements and Adaptability
Traditional employees often rely on fixed technological setups, including desktop computers and stable office networks, which support routine tasks but limit flexibility. Digital nomad employees prioritize portable devices like laptops and smartphones, cloud-based applications, and reliable high-speed internet to enable remote collaboration and seamless work from diverse locations. Adaptability in digital nomads is demonstrated through proficiency with virtual communication tools, cybersecurity practices, and the ability to quickly adjust to varying technological environments.
Career Growth and Skill Development
Traditional employees often benefit from structured career growth opportunities and formal skill development programs within a stable organizational framework. Digital nomad employees experience accelerated skill acquisition through diverse cultural exposures and remote project collaborations, enhancing adaptability and global competence. Both work styles present unique pathways for career advancement, with traditional roles favoring specialization and digital nomadism promoting versatility and self-directed learning.
Challenges and Solutions in Each Work Style
Traditional employees often face challenges such as rigid schedules, commuting stress, and limited flexibility, which can impact work-life balance and productivity. Solutions include implementing flexible work hours, encouraging remote work options, and enhancing office ergonomics to reduce physical strain. Digital nomad employees encounter obstacles like unreliable internet, time zone differences, and isolation, addressed by leveraging reliable mobile technology, adopting asynchronous communication tools, and fostering virtual team-building activities.
Employer Expectations and Management Approaches
Employers expect traditional employees to follow structured schedules, maintain physical presence, and adhere to standardized workflows, enabling direct supervision and consistent team collaboration. In contrast, digital nomad employees require flexible management approaches emphasizing outcome-based performance metrics, remote communication technologies, and trust in autonomous work habits. Effective management of both types necessitates adapting leadership styles to balance control with employee autonomy while ensuring productivity and engagement.
Future Trends: Traditional Employment vs. Digital Nomadism
Traditional employment maintains structured office environments and fixed schedules, emphasizing in-person collaboration and long-term job stability. Digital nomadism leverages remote work technologies and flexible hours, enabling professionals to work from diverse global locations while prioritizing work-life integration. Future trends suggest increasing hybrid models combining traditional stability with digital nomads' mobility, driven by advancements in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and evolving corporate culture.
Related Important Terms
Async Collaboration
Traditional employees often follow synchronous, office-based schedules with fixed hours that facilitate immediate communication, while digital nomads rely heavily on asynchronous collaboration tools to manage work across different time zones and maintain productivity without real-time interaction. Leveraging platforms like Slack, Trello, and email, digital nomads optimize task management and information flow, enabling flexible work styles that empower autonomy and global collaboration.
Remote-First Mindset
Traditional employees often work within fixed office environments, adhering to structured schedules and relying on in-person interactions, while digital nomad employees embrace a remote-first mindset that prioritizes flexibility, autonomy, and leveraging technology to perform tasks from any location. This shift promotes productivity through asynchronous communication, cloud-based collaboration tools, and a results-oriented approach rather than hours logged in a physical workspace.
Workation
Traditional employees typically adhere to fixed office locations and standard working hours, limiting flexibility and direct exposure to diverse environments. Digital nomad employees embrace workation by combining remote work with travel, enhancing creativity and productivity through flexible schedules and culturally enriching experiences.
Location Independence
Traditional employees typically work from fixed office locations with limited mobility, relying on physical presence for collaboration and supervision. Digital nomad employees embrace location independence, leveraging remote work technologies to perform tasks from diverse settings globally, enhancing flexibility and work-life balance.
Time Zone Agility
Traditional employees typically operate within fixed office hours tied to a single time zone, limiting cross-regional collaboration and flexibility. Digital nomad employees leverage time zone agility by working asynchronously across global locations, enhancing productivity and enabling continuous operations.
Geoarbitrage
Traditional employees typically maintain a fixed work location, often in high-cost urban centers, limiting their ability to leverage geoarbitrage for cost savings or lifestyle improvements. Digital nomad employees maximize geoarbitrage by working remotely from low-cost regions, enabling higher disposable income and enhanced work-life balance through strategic geographic flexibility.
Presence Presenteeism
Traditional employees often exhibit presenteeism by physically remaining at the workplace despite reduced productivity, while digital nomad employees prioritize results and flexible presence, leveraging remote technology to maintain efficiency without constant physical attendance. The emphasis for digital nomads shifts from visible presence to measurable output, reducing time lost to unproductive office hours and promoting work-life balance.
Slack Culture
Traditional employees often rely on in-office interactions and scheduled meetings, fostering a Slack culture centered around synchronous communication and direct supervision. Digital nomad employees, embracing remote and flexible work styles, leverage asynchronous messaging and collaborative tools within Slack to maintain productivity and team cohesion across time zones.
Digital HQ
Digital nomad employees leverage cloud-based collaboration tools and flexible schedules to enhance productivity from remote locations, contrasting with traditional employees who typically work in fixed office environments. Digital HQ platforms centralize communication, project management, and resource access, enabling seamless integration and real-time collaboration across dispersed teams.
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) Workstyle
Traditional employees typically use company-provided devices within a fixed office environment, ensuring controlled IT security and standardized workflows, while digital nomad employees rely heavily on BYOD workstyle, leveraging personal laptops, smartphones, and tablets to maintain productivity remotely across diverse locations. BYOD adoption in digital nomad workstyles demands robust cybersecurity protocols and flexible IT support to mitigate risks such as data breaches and unauthorized access.
Traditional employee vs Digital nomad employee for work style. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com