Employees provide long-term stability and deep organizational knowledge, making them essential for roles requiring continuity and company culture alignment. Agile talent offers flexibility and specialized skills for project-based work, enabling faster adaptation to market changes and innovation demands. Balancing employees and agile talent within an organizational structure maximizes efficiency by combining consistent core expertise with dynamic, scalable resources.
Table of Comparison
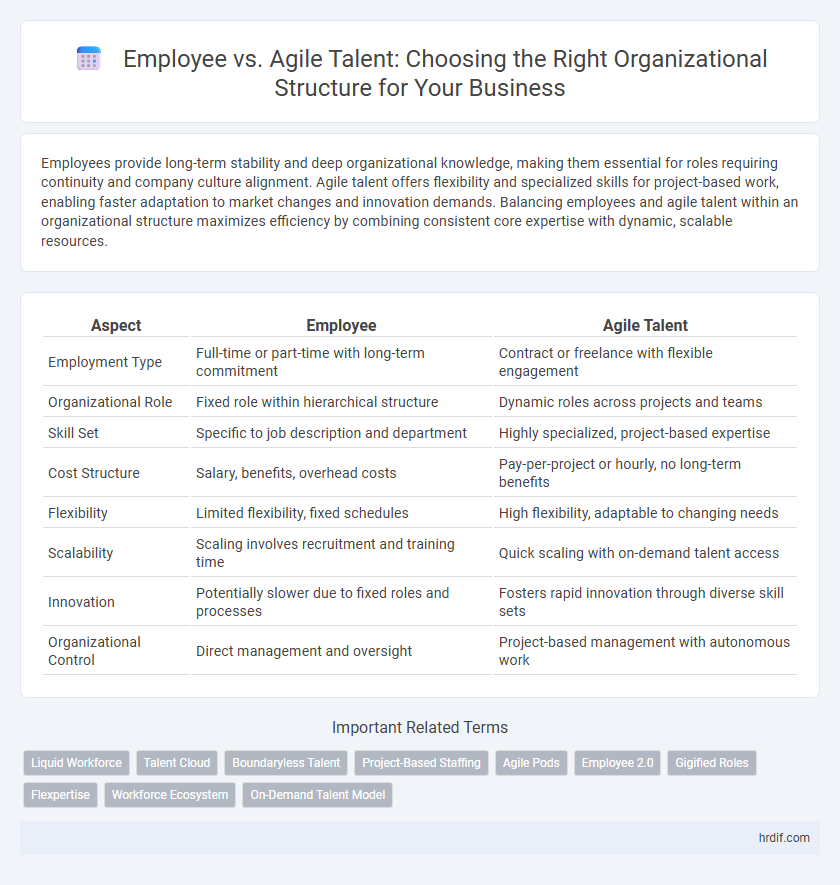
| Aspect | Employee | Agile Talent |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Type | Full-time or part-time with long-term commitment | Contract or freelance with flexible engagement |
| Organizational Role | Fixed role within hierarchical structure | Dynamic roles across projects and teams |
| Skill Set | Specific to job description and department | Highly specialized, project-based expertise |
| Cost Structure | Salary, benefits, overhead costs | Pay-per-project or hourly, no long-term benefits |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility, fixed schedules | High flexibility, adaptable to changing needs |
| Scalability | Scaling involves recruitment and training time | Quick scaling with on-demand talent access |
| Innovation | Potentially slower due to fixed roles and processes | Fosters rapid innovation through diverse skill sets |
| Organizational Control | Direct management and oversight | Project-based management with autonomous work |
Defining Employees and Agile Talent
Employees are traditionally defined as full-time, long-term members of an organization with fixed roles, responsibilities, and hierarchical reporting structures. Agile talent refers to a flexible, on-demand workforce comprising freelancers, contractors, and gig workers who adapt quickly to changing project needs and offer specialized skills. Organizations integrating agile talent can enhance scalability and innovation while maintaining core employee stability.
Key Differences in Employment Structure
Employee roles are typically structured with fixed responsibilities and defined hierarchies, providing stability and long-term commitment within the organization. Agile Talent operates on a flexible, project-based model, allowing companies to rapidly scale workforce capacity and expertise according to shifting demands. This distinction highlights key differences in organizational agility, resource allocation, and cost management strategies between traditional employee frameworks and Agile Talent integration.
Cost Implications: Employees vs Agile Talent
Cost implications of traditional employees often include fixed salaries, benefits, and long-term commitments that can strain organizational budgets. Agile talent offers flexible cost structures by enabling companies to scale workforce expenses based on project needs without incurring overhead costs like healthcare or retirement plans. Organizations leveraging agile talent benefit from reduced financial risk and improved budget alignment related to fluctuating workload demands.
Flexibility and Adaptability in the Workforce
Agile talent enhances organizational flexibility by providing specialized skills on demand, allowing companies to quickly adapt to market changes and project needs. Traditional employees offer deep institutional knowledge and long-term commitment, which supports stability and consistent performance. Balancing permanent employees with agile talent creates a dynamic workforce capable of responding efficiently to evolving business environments.
Skills Access and Talent Pools
Employee roles provide organizations with stable, long-term access to specialized skills within their existing talent pools, fostering deep institutional knowledge and consistent team collaboration. Agile Talent offers flexible access to a broad spectrum of skills, enabling companies to rapidly scale expertise based on project demands and tap into diverse external talent pools. Combining Employee and Agile Talent strategies allows organizations to optimize skills access by balancing internal proficiency with external innovation and adaptability.
Impact on Organizational Culture
Employee roles foster long-term commitment, embedding stability and consistent values into organizational culture, which enhances trust and team cohesion over time. Agile talent introduces flexibility and diverse perspectives, accelerating innovation while challenging traditional hierarchical norms within the work environment. Balancing permanent employees with agile talent optimizes adaptability and cultural resilience, supporting sustainable growth and dynamic team dynamics.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Employee arrangements involve formal contracts with defined legal obligations, providing clear compliance with labor laws, tax regulations, and benefits requirements. Agile talent, often classified as contractors or freelancers, requires organizations to navigate complex compliance issues like worker classification, intellectual property rights, and varying jurisdictional labor laws. Ensuring adherence to employment regulations mitigates risks such as misclassification penalties and ensures organizational accountability in both employee and agile talent models.
Performance Management Approaches
Employee performance management relies on structured evaluations, goal setting, and continuous feedback within fixed roles to drive long-term organizational growth. Agile talent employs adaptive performance metrics, real-time project assessments, and dynamic feedback loops, optimizing flexibility and rapid skill alignment to evolving business needs. Integrating both approaches enables a balanced organizational structure that enhances productivity and responsiveness.
Retention and Turnover Dynamics
Organizations balancing Employee and Agile Talent models experience distinct retention and turnover dynamics, with traditional employees often showing higher long-term retention due to stronger institutional loyalty and benefits alignment. Agile Talent, characterized by project-based or freelance engagements, enables rapid scaling but faces increased turnover as these workers prioritize flexibility and diverse opportunities. Strategically integrating both models optimizes workforce stability while maintaining adaptability in dynamic market conditions.
Strategic Considerations for Organizational Growth
Employees provide continuity, institutional knowledge, and long-term commitment essential for building a stable organizational culture, while agile talent offers flexibility, specialized skills, and rapid adaptation to evolving market demands. Strategic considerations for organizational growth involve balancing these human capital models to optimize innovation and operational efficiency without compromising core competencies. Integrating agile talent with a committed employee base enables scalable resource allocation and fosters a dynamic yet resilient workforce suited for competitive environments.
Related Important Terms
Liquid Workforce
Organizations adopting a liquid workforce leverage agile talent alongside traditional employees to enhance flexibility and responsiveness in dynamic markets. This hybrid structure enables seamless integration of specialized skills, optimizing project outcomes while maintaining core operational stability.
Talent Cloud
Employee roles within Talent Cloud frameworks provide consistent institutional knowledge and long-term strategic alignment, ensuring stability in organizational structures. Agile Talent, sourced through Talent Clouds, offers dynamic scalability and specialized expertise, enabling rapid adaptation to market changes and project-specific demands.
Boundaryless Talent
Boundaryless talent integrates seamlessly into organizational structures by leveraging agile talent models that bypass traditional employee limitations, fostering flexibility and innovation. Emphasizing project-based contributions over fixed roles, boundaryless talent enhances responsiveness and access to specialized skills beyond the conventional employee framework.
Project-Based Staffing
Employee roles offer stability and deep organizational knowledge, making them essential for maintaining core functions, while Agile Talent provides flexibility and specialized skills crucial for dynamic project-based staffing. Leveraging Agile Talent enables organizations to scale quickly and adapt to fluctuating project demands without long-term commitments.
Agile Pods
Agile Pods leverage Agile Talent by assembling cross-functional experts who adapt quickly to project needs, enhancing flexibility and innovation within organizational structures. Unlike traditional Employees fixed in hierarchical roles, Agile Talent within Pods accelerates decision-making and drives continuous delivery through collaborative and dynamic team formations.
Employee 2.0
Employee 2.0 represents a digitally savvy workforce integrating advanced skills and collaborative tools, enhancing organizational agility and innovation. Unlike Agile Talent, these employees offer long-term commitment and deep institutional knowledge crucial for sustaining competitive advantage.
Gigified Roles
Employees offer organizational stability and deep institutional knowledge, while agile talent in gigified roles provides flexibility and rapid scalability tailored to project-specific needs. Integrating gigified roles within the organizational structure enables companies to dynamically allocate expertise and optimize workforce agility without long-term commitments.
Flexpertise
Flexpertise blends the reliability of traditional employees with the adaptability of agile talent, creating a dynamic organizational structure that enhances innovation and responsiveness. By integrating full-time experts and flexible specialists, companies optimize workforce efficiency while maintaining deep domain knowledge and scalability.
Workforce Ecosystem
Employee roles within a workforce ecosystem provide stability, deep organizational knowledge, and long-term commitment essential for maintaining core business functions. Agile talent complements this structure by offering flexible, specialized skills and rapid scalability, enabling organizations to adapt swiftly to market changes and project-specific demands.
On-Demand Talent Model
The On-Demand Talent Model leverages Agile Talent for organizational flexibility, enabling companies to scale skills and expertise dynamically without the long-term commitment of traditional employees. This model optimizes cost efficiency and innovation by integrating specialized, project-based talent that complements core employee roles within the organization.
Employee vs Agile Talent for organizational structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com