Junior employees bring fresh perspectives and eagerness to learn, which can fuel their growth and contribution within the organization. Reverse mentoring involves junior employees guiding senior staff on emerging technologies and modern trends, fostering mutual knowledge exchange. This dynamic enhances collaboration, promotes innovation, and bridges generational gaps in the workplace.
Table of Comparison
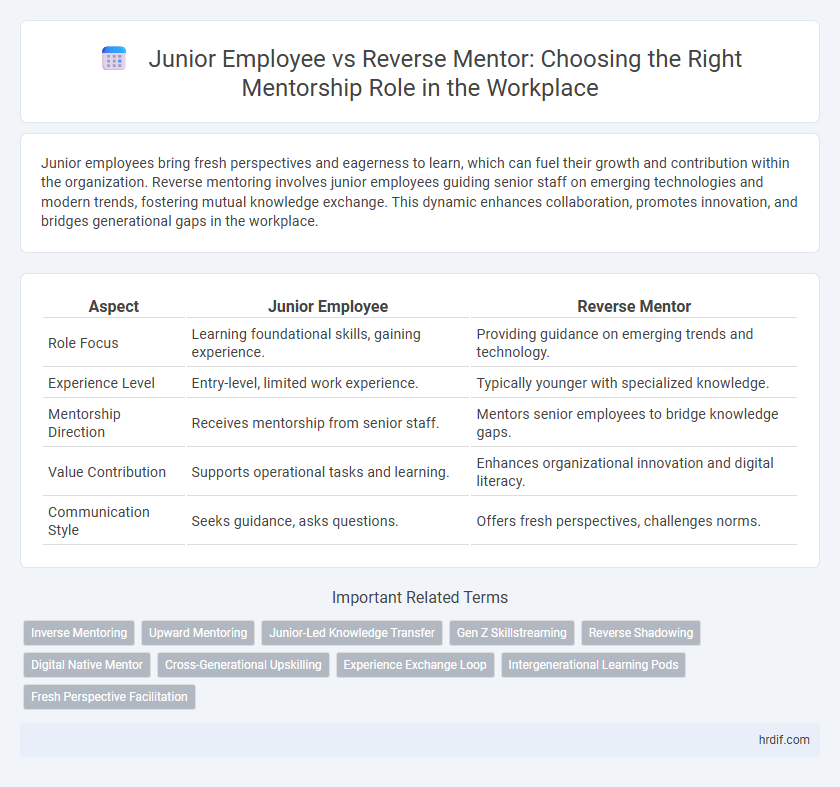
| Aspect | Junior Employee | Reverse Mentor |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Learning foundational skills, gaining experience. | Providing guidance on emerging trends and technology. |
| Experience Level | Entry-level, limited work experience. | Typically younger with specialized knowledge. |
| Mentorship Direction | Receives mentorship from senior staff. | Mentors senior employees to bridge knowledge gaps. |
| Value Contribution | Supports operational tasks and learning. | Enhances organizational innovation and digital literacy. |
| Communication Style | Seeks guidance, asks questions. | Offers fresh perspectives, challenges norms. |
Defining Junior Employees and Reverse Mentors in Modern Workplaces
Junior employees typically possess limited professional experience and are in the early stages of their careers, requiring guidance to develop essential skills and understand organizational culture. Reverse mentors are usually younger or less experienced employees who share fresh perspectives, technological expertise, and innovative ideas with senior colleagues to foster mutual learning. Modern workplaces leverage both roles to create dynamic mentorship programs that enhance knowledge exchange and support professional growth across all levels.
Key Responsibilities: Junior Employees vs. Reverse Mentors
Junior employees primarily focus on learning job-specific skills, completing assigned tasks, and contributing to team projects while seeking guidance. Reverse mentors take on the responsibility of sharing fresh perspectives, technological expertise, and fostering intergenerational knowledge exchange to support senior employees' growth. Both roles emphasize development, but junior employees prioritize skill acquisition while reverse mentors drive innovation and cultural adaptability within the organization.
Skills Development: Traditional vs. Reverse Mentorship Approaches
Junior employees typically benefit from traditional mentorship, gaining industry-specific knowledge and technical skills from experienced mentors who provide structured guidance and feedback. Reverse mentorship accelerates skills development by allowing younger employees to share digital literacy, social media expertise, and innovative problem-solving techniques with senior colleagues, fostering a bi-directional learning environment. Organizations leveraging both traditional and reverse mentorship approaches enhance overall workforce agility and close generational skill gaps effectively.
Enhancing Team Dynamics: Impact of Junior Employees and Reverse Mentors
Junior employees bring fresh perspectives and up-to-date technical skills that invigorate team innovation and adaptability. Reverse mentors, often younger or less experienced, foster intergenerational learning by sharing digital expertise and contemporary cultural insights with senior colleagues. Integrating both roles enhances team dynamics through reciprocal knowledge exchange, increased collaboration, and bridging generational gaps.
Knowledge Transfer: Bottom-Up vs. Top-Down Mentorship Models
Junior employees bring fresh perspectives and digital skills in bottom-up mentorship models, facilitating knowledge transfer from newer to more experienced staff. Reverse mentorship enables senior leaders to gain insights on emerging technologies and contemporary trends, enhancing organizational adaptability. In contrast, traditional top-down mentorship typically emphasizes the transfer of institutional knowledge and leadership skills from seasoned employees to juniors.
Career Advancement: Benefits for Junior Employees and Reverse Mentors
Junior employees gain accelerated career advancement through reverse mentorship by acquiring insights into leadership skills and strategic thinking from experienced mentors. Reverse mentors benefit by refining their communication and coaching abilities, which enhances their professional growth and visibility within the organization. This reciprocal mentorship fosters a dynamic learning environment that bridges generational gaps and promotes continuous development.
Building a Learning Culture: The Role of Reverse Mentoring
Junior employees bring fresh perspectives and digital skills that are valuable in reverse mentoring, where they guide senior staff to foster continuous learning. Reverse mentoring accelerates knowledge exchange and breaks down hierarchical barriers, promoting a culture where learning is reciprocal and dynamic. Emphasizing this approach helps organizations adapt to change rapidly while enhancing employee engagement and development.
Challenges in Junior Employee and Reverse Mentor Roles
Junior employees often face challenges such as limited experience, unclear role expectations, and difficulty asserting their ideas within established teams. Reverse mentors encounter obstacles like gaining respect from senior colleagues, bridging generational gaps, and effectively communicating new technologies or perspectives. Both roles require overcoming barriers related to confidence, credibility, and adapting to organizational culture for successful mentorship outcomes.
Measuring Success: Evaluating Mentorship Outcomes
Measuring success in mentorship roles involves assessing skill development, increased job performance, and enhanced confidence for both junior employees and reverse mentors. Key performance indicators include goal achievement rates, feedback quality, and career progression metrics tracked through regular evaluations. Data-driven analyses of mentorship impact provide actionable insights to optimize programs and foster mutual professional growth.
Future Trends: Evolving Mentorship in the Workplace
Future mentorship trends emphasize reverse mentoring, where junior employees share digital skills and fresh perspectives with senior leaders, fostering mutual growth. This role reversal enhances intergenerational collaboration, addressing the rapid pace of technological advancements and evolving workplace dynamics. Organizations increasingly adopt hybrid mentorship models that integrate both traditional and reverse mentoring to cultivate a diverse and adaptive talent pipeline.
Related Important Terms
Inverse Mentoring
Inverse mentoring leverages the unique perspectives and technological expertise of junior employees to foster innovation and digital transformation within organizations. This approach enhances leadership skills in junior staff while providing senior employees with fresh insights and updated knowledge critical for adapting to evolving market trends.
Upward Mentoring
Reverse mentoring leverages junior employees' fresh perspectives and digital expertise to guide senior staff, fostering a dynamic exchange that transcends traditional top-down mentorship; upward mentoring enhances leadership skills in juniors while accelerating cultural and technological adaptability in organizations. This innovative practice bridges generational gaps, empowering junior employees to influence strategic decisions and promoting continuous learning in a rapidly evolving business environment.
Junior-Led Knowledge Transfer
Junior employees acting as reverse mentors facilitate Junior-Led Knowledge Transfer by sharing fresh digital skills and contemporary industry insights with senior staff, enhancing overall organizational agility. This mentorship approach accelerates innovation, promotes continuous learning, and bridges generational knowledge gaps effectively.
Gen Z Skillstreaming
Junior employees in Gen Z Skillstreaming programs benefit from reverse mentorship by gaining real-time digital skills and innovative problem-solving approaches, while reverse mentors enhance leadership abilities through active knowledge sharing. This symbiotic relationship accelerates professional growth and fosters a dynamic workplace culture centered on continuous learning and adaptability.
Reverse Shadowing
Reverse shadowing enhances the traditional mentorship model by allowing experienced employees to learn from junior employees' fresh perspectives and digital skills, fostering a two-way knowledge exchange. This approach accelerates professional growth for both parties and drives innovation within the organization by bridging generational knowledge gaps.
Digital Native Mentor
Junior employees often serve as digital native mentors, leveraging their inherent tech-savviness to guide senior staff in adopting new technologies and digital workflows. Reverse mentorship fosters a dynamic exchange where junior talent accelerates digital transformation and innovation within organizations.
Cross-Generational Upskilling
Junior employees often benefit from reverse mentorship by gaining insights into emerging technologies and digital trends from younger colleagues, fostering cross-generational upskilling. This approach enhances organizational knowledge transfer and accelerates skill development across diverse age groups.
Experience Exchange Loop
Junior employees bring fresh perspectives and technological proficiency, while reverse mentors offer seasoned insights and strategic understanding, creating a dynamic Experience Exchange Loop that enhances mutual growth. This reciprocal mentorship model fosters continuous knowledge transfer, bridging generational gaps and accelerating professional development within organizations.
Intergenerational Learning Pods
Junior employees often bring fresh perspectives and digital fluency that enhance Intergenerational Learning Pods, fostering mutual growth and innovation. Reverse mentors, typically younger employees guiding senior staff, accelerate knowledge exchange and bridge generational gaps in mentorship roles.
Fresh Perspective Facilitation
Junior employees bring fresh perspectives that challenge existing norms, enabling innovation and adaptability within organizations. Reverse mentors facilitate this exchange by guiding seasoned professionals to embrace new technologies and cultural shifts, fostering mutual growth and dynamic leadership.
Junior employee vs Reverse mentor for mentorship roles. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com