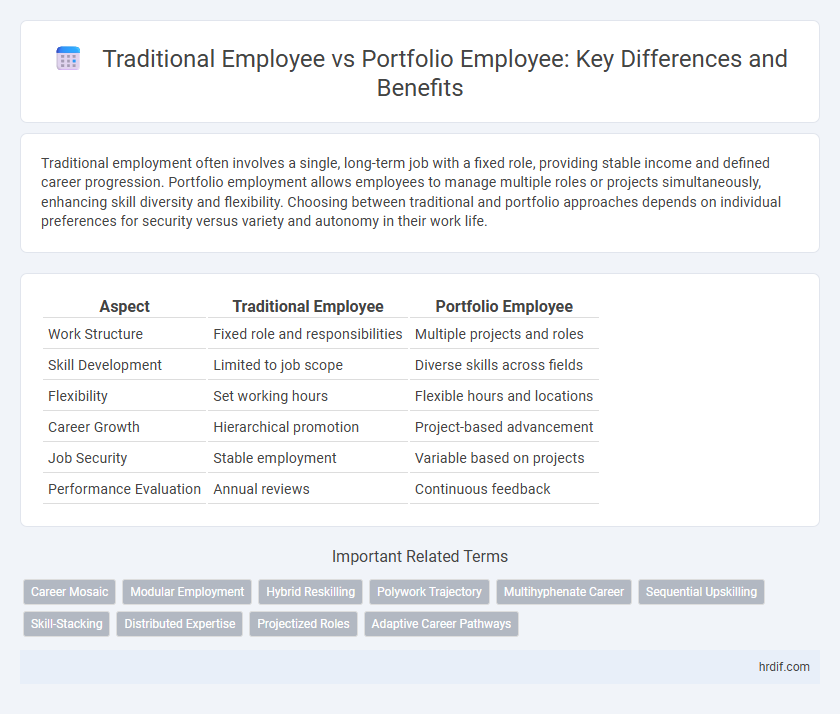
Traditional employment often involves a single, long-term job with a fixed role, providing stable income and defined career progression. Portfolio employment allows employees to manage multiple roles or projects simultaneously, enhancing skill diversity and flexibility. Choosing between traditional and portfolio approaches depends on individual preferences for security versus variety and autonomy in their work life.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Traditional Employee | Portfolio Employee |
|---|---|---|
| Work Structure | Fixed role and responsibilities | Multiple projects and roles |
| Skill Development | Limited to job scope | Diverse skills across fields |
| Flexibility | Set working hours | Flexible hours and locations |
| Career Growth | Hierarchical promotion | Project-based advancement |
| Job Security | Stable employment | Variable based on projects |
| Performance Evaluation | Annual reviews | Continuous feedback |
Understanding Traditional Employment
Traditional employment typically involves a long-term contract with a single employer, offering stable income, benefits, and defined career progression paths. Employees in this model often engage in specific roles within organizational hierarchies, emphasizing job security and consistent workload. Understanding the predictability and structure of traditional employment helps in assessing its suitability compared to portfolio careers involving multiple concurrent roles or freelance projects.
What is a Portfolio Career?
A portfolio career involves an employee working multiple part-time jobs, freelance projects, or consulting roles simultaneously rather than holding a single traditional full-time position. This approach allows for greater flexibility, skill diversity, and income streams, aligning with the demands of a dynamic labor market. Employees managing portfolio careers often develop a broad professional network and adapt more quickly to changing industry trends.
Key Differences: Traditional vs Portfolio Careers
Traditional careers involve long-term employment with a single organization, emphasizing job security, clear hierarchy, and steady progression. Portfolio careers consist of multiple part-time roles, freelance projects, or entrepreneurial ventures, prioritizing flexibility, diverse skill development, and income streams. Key differences include stability versus variety, fixed roles versus multiple engagements, and conventional growth paths versus personalized career design.
Job Security: Steady vs Flexible Paths
Traditional employment offers steady job security through long-term contracts and predictable career progression, often accompanied by benefits like pensions and health insurance. Portfolio careers provide flexible paths, allowing employees to diversify skills and income streams but with less guaranteed job stability. Balancing these approaches depends on an individual's tolerance for risk and preference for stability or adaptability.
Income Stability and Growth Opportunities
Traditional employment offers steady income stability through fixed salaries and established benefits, providing financial predictability for employees. Portfolio employment, involving multiple freelance or contract roles, presents greater growth opportunities by allowing skill diversification and access to varied projects. Balancing stable income with potential income growth depends on individual risk tolerance and career priorities.
Work-Life Balance: Which Model Wins?
Traditional work models often enforce fixed hours and limited flexibility, which can hinder an employee's work-life balance and increase stress levels. Portfolio work, characterized by varied projects and flexible schedules, promotes autonomy, allowing employees to better manage their time between professional tasks and personal life. Data from recent studies indicate that employees engaged in portfolio careers report higher satisfaction and improved mental health compared to those in traditional roles.
Skill Development and Career Progression
Traditional employee development emphasizes linear career progression through predefined roles and skill acquisition aligned with a set job description. Portfolio-based development encourages employees to cultivate diverse skills across multiple projects, enhancing adaptability and accelerating career growth by showcasing a broad range of competencies. Investing in skill diversification through portfolio experiences often leads to higher job satisfaction and increased opportunities for advancement in dynamic industries.
Risk Factors in Both Career Approaches
Traditional careers often carry risks such as job insecurity during organizational restructuring and limited skill diversification, which can lead to reduced adaptability in changing markets. Portfolio careers expose employees to varied projects and income streams, mitigating dependency on a single employer but increasing uncertainty in stable earnings and benefits. Both approaches require strategic risk management to balance financial stability and professional growth in dynamic economic conditions.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Goals
Choosing between a traditional career path and a portfolio approach depends on individual goals and risk tolerance. A traditional employee benefits from stability, clear progression, and structured responsibilities, ideal for those seeking steady income and defined roles. In contrast, a portfolio career offers flexibility, diverse experiences, and multiple income streams, appealing to employees who value autonomy and varied skill development.
Transitioning from Traditional to Portfolio Careers
Transitioning from traditional to portfolio careers empowers employees to diversify their skill sets and income streams by engaging in multiple projects or part-time roles instead of a single full-time position. This shift fosters greater flexibility, autonomy, and professional growth, allowing employees to adapt to changing job markets and technological advancements. Embracing a portfolio career enhances resilience against economic fluctuations and boosts long-term career sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Career Mosaic
The Career Mosaic approach empowers employees to develop diverse skill sets and experiences across multiple roles, offering greater flexibility compared to the Traditional career path that emphasizes linear progression within a single function. Portfolio careers enhance adaptability and engagement by enabling individuals to manage various projects or jobs simultaneously, aligning with evolving market demands and personal growth goals.
Modular Employment
Traditional employment typically involves fixed roles and responsibilities within a single organization, while portfolio employment allows employees to manage multiple projects or roles across different companies, emphasizing flexibility and diverse skill application. Modular employment enhances this portfolio approach by enabling workers to assemble customizable job components tailored to their expertise and career goals, increasing adaptability in the evolving job market.
Hybrid Reskilling
Traditional employee development relies on fixed skill sets and linear career paths, while portfolio approaches emphasize diverse, project-based experiences that enhance adaptability. Hybrid reskilling combines structured training with real-world portfolio tasks, accelerating skill acquisition and maximizing workforce agility.
Polywork Trajectory
Traditional employee career paths emphasize linear progression within a single role or company, whereas the Polywork trajectory encourages a dynamic portfolio of roles, projects, and skills accumulation that better aligns with modern gig economies and multifaceted professional identities. Embracing a portfolio approach promotes adaptability and continuous growth, leveraging diverse experiences to enhance employability and innovation in an ever-evolving job market.
Multihyphenate Career
A traditional career typically involves specializing in a single field with steady progression, while a portfolio career combines multiple roles and skills, allowing an employee to work on diverse projects simultaneously. Embracing a multihyphenate career enables employees to leverage various talents, increase adaptability, and enhance long-term job satisfaction and marketability.
Sequential Upskilling
Traditional employee development follows a linear path with fixed skill acquisition stages, while portfolio approaches enable sequential upskilling through diverse, project-based experiences tailored to evolving industry demands. Sequential upskilling in portfolio models enhances adaptability and fosters continuous learning by integrating cross-functional skills across varied roles.
Skill-Stacking
Traditional employee development emphasizes deep expertise in a single area, while portfolio career paths prioritize skill-stacking by combining diverse competencies to enhance adaptability and innovation. Skill-stacking enables employees to blend technical skills, soft skills, and industry knowledge, creating a unique value proposition that drives career growth in dynamic job markets.
Distributed Expertise
Traditional employees typically possess specialized skills within a narrow domain, while portfolio employees bring distributed expertise across multiple disciplines, enhancing organizational agility and innovation. This diverse skill set enables portfolio employees to adapt quickly to various roles, driving cross-functional collaboration and complex problem-solving.
Projectized Roles
Projectized roles emphasize employee involvement in specific projects, enhancing focus and accountability compared to traditional roles where employees maintain functional responsibilities across multiple tasks. This approach optimizes resource allocation, improves project delivery speed, and fosters specialized skill development within project teams.
Adaptive Career Pathways
Traditional career pathways often follow a linear progression within a single function or department, limiting skill diversification and adaptability. Portfolio career models emphasize cross-functional experiences and skill acquisition, enabling employees to navigate adaptive career pathways that align with evolving industry demands and personal growth objectives.
Traditional vs Portfolio for employee. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com