Salaried employees receive consistent, predictable pay with benefits such as health insurance and retirement contributions, ensuring financial stability. Gig workers are paid per task or project, offering flexibility but with income variability and minimal job security. Understanding these differences helps both workers and employers choose the best pay structure for their needs.
Table of Comparison
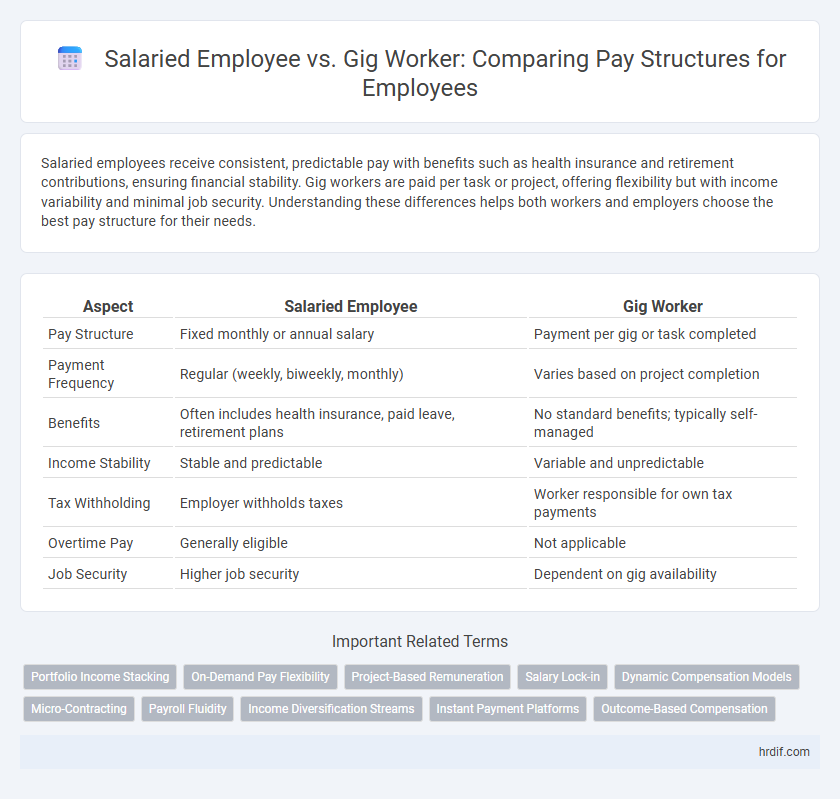
| Aspect | Salaried Employee | Gig Worker |
|---|---|---|
| Pay Structure | Fixed monthly or annual salary | Payment per gig or task completed |
| Payment Frequency | Regular (weekly, biweekly, monthly) | Varies based on project completion |
| Benefits | Often includes health insurance, paid leave, retirement plans | No standard benefits; typically self-managed |
| Income Stability | Stable and predictable | Variable and unpredictable |
| Tax Withholding | Employer withholds taxes | Worker responsible for own tax payments |
| Overtime Pay | Generally eligible | Not applicable |
| Job Security | Higher job security | Dependent on gig availability |
Understanding Salaried Employment Pay Structures
Salaried employees receive a fixed annual income divided into regular pay periods, ensuring consistent financial stability and predictable budgeting. Their compensation often includes benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, which are typically excluded in gig work arrangements. Understanding salaried pay structures involves recognizing the value of guaranteed wages combined with job security, contrasting with the variable income and flexibility common in gig worker roles.
The Gig Economy: How Gig Workers Get Paid
Gig workers in the gig economy receive payments based on task completion or hourly rates, often through digital platforms that facilitate instant or weekly transactions. Unlike salaried employees who earn fixed monthly wages with benefits, gig workers experience variable income without traditional employment protections or steady paychecks. Payment methods for gig work typically include direct deposits, electronic wallets, or app-based payouts tied to service delivery and client ratings.
Salary Stability vs. Gig Income Variability
Salaried employees benefit from consistent monthly paychecks, providing financial stability and predictable budgeting throughout the year. Gig workers experience income variability due to fluctuating demand for their services, leading to potential periods of high earnings followed by dry spells. This variability can complicate financial planning and may require gig workers to maintain greater cash reserves to manage income uncertainty.
Benefits and Perks: Employee vs. Gig Worker
Salaried employees receive comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security, which contribute to long-term financial stability. Gig workers often lack access to employer-sponsored perks but enjoy flexible work schedules and the ability to choose projects, trading off guaranteed income for independence. The disparity in benefits influences overall job satisfaction and compensation packages between traditional employees and gig workers.
Work Hours and Flexibility: Comparing Compensation Models
Salaried employees typically receive a fixed annual income regardless of hours worked, ensuring consistent pay and often standard work hours with limited flexibility. Gig workers are paid per task or project, offering greater flexibility in choosing work hours but leading to variable income dependent on job availability. The compensation model for salaried roles prioritizes stability, while gig work emphasizes adaptability and potential for fluctuating earnings based on time invested.
Taxes and Deductions: Employee Salary vs. Gig Payments
Salaried employees have taxes like federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare automatically deducted from their paychecks, simplifying their tax filing process. Gig workers receive gross payments without tax withholdings, requiring them to calculate and pay estimated taxes quarterly, including self-employment tax covering Social Security and Medicare. Understanding these tax differences is crucial for managing liabilities and maximizing net income effectively.
Overtime and Bonuses: Who Benefits More?
Salaried employees typically receive consistent pay regardless of hours worked, but may qualify for overtime compensation and structured bonuses tied to performance metrics, offering financial predictability and potential extra income. Gig workers, paid per task or project, often lack formal overtime rules yet can earn higher immediate income through multiple gigs, though bonuses are rare or sporadic. Evaluating benefits depends on individual priorities: salaried roles favor stability with occasional financial boosts, while gig work emphasizes flexibility with variable earnings.
Long-Term Financial Security: Salary vs. Gig Work
Salaried employees benefit from steady, predictable income and often receive benefits such as retirement plans and health insurance, which contribute to long-term financial security. Gig workers face variable pay rates and income fluctuations, making it challenging to secure consistent savings or stable retirement contributions. Companies like Uber and Upwork highlight the growth of gig work, but financial planners often recommend salaried positions for reliable long-term wealth accumulation.
Job Security and Income Predictability
Salaried employees benefit from consistent paychecks and stronger job security due to contractual obligations and employee benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Gig workers, while enjoying flexibility, face income variability and less job stability, often lacking guaranteed minimum earnings or access to traditional employment benefits. The predictability of income for salaried roles supports long-term financial planning, contrasting with the often unpredictable revenue streams of gig work.
Choosing the Right Path: Salary or Gig Payment Structure
Choosing between a salaried employee and a gig worker payment structure depends on job stability, income predictability, and flexibility needs. Salaried employees receive fixed, regular pay with benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, ensuring financial security and consistent cash flow. Gig workers earn per task or project, offering flexible schedules and potential for varied income but lacking traditional benefits and long-term employment guarantees.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Income Stacking
Salaried employees receive a consistent, fixed income providing financial stability, whereas gig workers benefit from portfolio income stacking by combining multiple freelance or contract jobs, maximizing revenue streams and tax advantages. This diversified pay structure allows gig workers to optimize earnings through varied projects but often lacks the predictable cash flow and benefits associated with salaried employment.
On-Demand Pay Flexibility
Salaried employees typically receive fixed, predictable pay on a regular schedule, while gig workers benefit from on-demand pay flexibility, allowing access to earnings immediately after completing tasks. This pay structure difference supports financial agility for gig workers but offers stability and planned budgeting for salaried employees.
Project-Based Remuneration
Salaried employees receive a fixed, regular income regardless of project completion, ensuring financial stability, while gig workers are compensated on a project-based remuneration model that links pay directly to specific tasks or deliverables. This pay structure allows gig workers greater flexibility but may result in income variability tied to project availability and completion rates.
Salary Lock-in
Salaried employees benefit from a fixed salary lock-in, ensuring consistent monthly income regardless of workload fluctuations, which provides financial stability and predictability. Gig workers, on the other hand, receive variable pay based on completed tasks or projects, lacking a guaranteed minimum income and making their earnings subject to market demand and availability.
Dynamic Compensation Models
Salaried employees benefit from fixed, predictable income structures with periodic bonuses, ensuring financial stability and consistent benefits. Gig workers experience dynamic compensation models based on task completion and demand fluctuations, offering flexibility but variable earnings and limited traditional benefits.
Micro-Contracting
Salaried employees receive fixed, regular payments with benefits, providing financial stability and predictable income, whereas gig workers engaged in micro-contracting earn based on individual tasks or projects, allowing flexible work but often lacking consistent pay and traditional employment benefits. Micro-contracting in the gig economy emphasizes task-specific remuneration, highlighting the shift from salaried roles to performance-based earnings in modern work structures.
Payroll Fluidity
Salaried employees benefit from consistent, predictable pay through regular payroll cycles, ensuring financial stability and streamlined payroll management. Gig workers experience payroll fluidity with variable earnings based on task completion, requiring dynamic payment systems to accommodate fluctuating income and flexible work schedules.
Income Diversification Streams
Salaried employees benefit from a stable, predictable paycheck that supports consistent financial planning but often lack flexible income diversification streams. Gig workers leverage multiple platforms and projects simultaneously, enhancing income diversification but facing irregular earnings and less financial security.
Instant Payment Platforms
Salaried employees receive fixed, regular payments regardless of hours worked, while gig workers benefit from instant payment platforms that provide immediate compensation after task completion. Instant payment platforms enhance cash flow flexibility for gig workers, enabling faster access to earned wages compared to traditional payroll cycles.
Outcome-Based Compensation
Outcome-based compensation for salaried employees typically involves fixed salaries with performance bonuses tied to specific goals, ensuring steady income plus incentives for productivity. Gig workers receive payment based on task completion or project outcomes, allowing flexible earnings directly linked to individual output without guaranteed base pay.
Salaried employee vs Gig worker for pay structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com