Salaried workers receive a consistent income with fixed benefits, providing financial stability and predictable budgeting. Gig professionals, on the other hand, earn variable pay based on completed tasks, offering flexibility but often lacking traditional benefits. Choosing between these models depends on one's preference for stability versus autonomy in compensation.
Table of Comparison
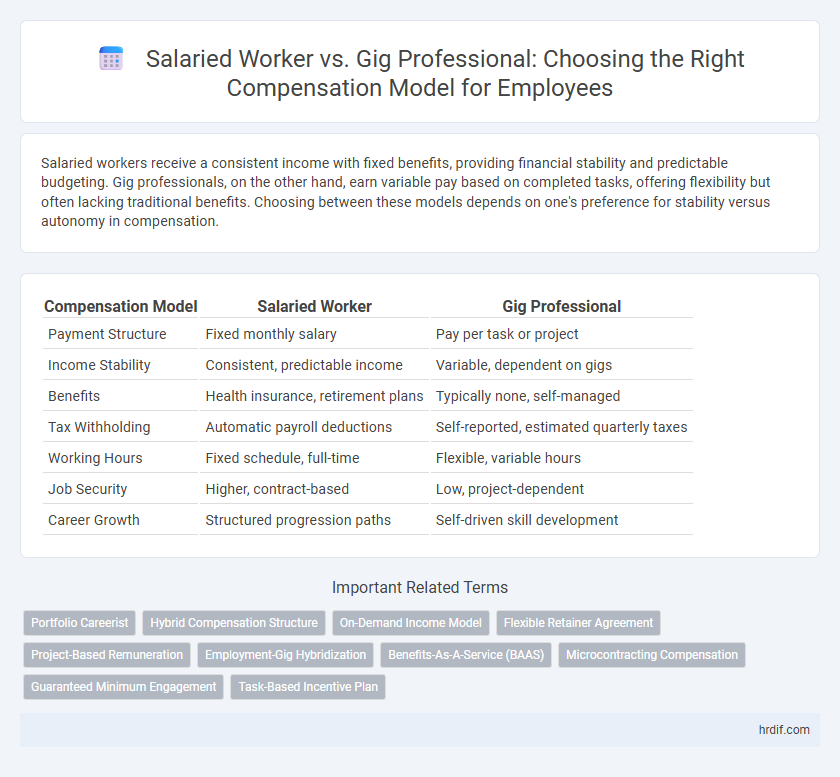
| Compensation Model | Salaried Worker | Gig Professional |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Structure | Fixed monthly salary | Pay per task or project |
| Income Stability | Consistent, predictable income | Variable, dependent on gigs |
| Benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans | Typically none, self-managed |
| Tax Withholding | Automatic payroll deductions | Self-reported, estimated quarterly taxes |
| Working Hours | Fixed schedule, full-time | Flexible, variable hours |
| Job Security | Higher, contract-based | Low, project-dependent |
| Career Growth | Structured progression paths | Self-driven skill development |
Understanding Salaried Employment: Stability and Structure
Salaried workers receive a fixed regular income, providing financial stability and predictable monthly earnings, essential for long-term budgeting and benefits eligibility such as health insurance and retirement plans. This compensation model includes structured work hours, defined job roles, and employer-provided resources, fostering consistent career growth and protections under labor laws. Understanding these elements helps distinguish salaried employment's advantages over gig professionals, who face variable income and less job security.
The Gig Professional Model: Flexibility and Freedom
The gig professional compensation model offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing workers to choose projects and set their own schedules, which enhances work-life balance and personal autonomy. Unlike salaried workers tied to fixed hours and consistent pay, gig professionals earn income based on completed tasks or projects, providing potential for varied and scalable earnings. This model appeals to individuals seeking independence and the ability to diversify their income streams across multiple clients or platforms.
Income Consistency: Salary vs. Gig Earnings Variability
Salaried workers benefit from stable, predictable income with fixed monthly paychecks, ensuring financial security and easier budgeting. Gig professionals experience significant earnings variability, with income fluctuating based on project availability, client demand, and hours worked. This inconsistency often requires freelancers to build financial buffers and manage irregular cash flow to sustain their livelihoods.
Benefits Packages: Health, Retirement, and Perks Comparison
Salaried workers typically receive comprehensive benefits packages including health insurance, retirement plans like 401(k) with employer matches, and paid time off, providing financial stability and long-term security. Gig professionals often lack access to employer-sponsored health coverage and retirement plans, relying on individual marketplace options and self-funded savings, which can result in variable financial security. Perks such as wellness programs, professional development, and bonuses are more common in salaried roles, while gig workers prioritize flexible schedules and project-based income over traditional benefits.
Work-Life Balance: Scheduled Hours vs. Gig Autonomy
Salaried workers benefit from predictable, scheduled hours that promote consistent work-life balance and routine, while gig professionals enjoy greater autonomy to choose when and how much they work, allowing for flexible personal time management. The salaried model often includes benefits such as paid leave and health insurance, supporting overall employee well-being. Gig workers face variable income and less job security but gain independence, which can enhance their work-life integration when managed effectively.
Tax Implications: Employee Withholding vs. Independent Reporting
Salaried workers experience tax withholding directly from their employer, ensuring payroll taxes such as Social Security, Medicare, and income taxes are automatically deducted and remitted, simplifying their tax compliance. Gig professionals, classified as independent contractors, must manage quarterly estimated tax payments, covering self-employment tax and income tax without employer withholding, increasing the complexity of tax reporting. This fundamental difference impacts cash flow, tax planning strategies, and the potential for underpayment penalties among gig workers compared to traditional employees.
Career Growth: Traditional Paths vs. Gig Portfolio Building
Salaried workers benefit from structured career growth with predictable compensation, performance reviews, and promotion paths within established organizations. Gig professionals cultivate diverse skill sets by managing multiple projects across industries, enabling portfolio building and greater autonomy but facing variable income and less job security. Career advancement for salaried employees often depends on tenure and company hierarchy, whereas gig workers rely on reputation, client acquisition, and continuous skill development.
Job Security: Permanent Positions vs. Contractual Engagements
Salaried workers benefit from permanent positions that provide consistent income, job security, and access to benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Gig professionals operate under contractual engagements, which offer flexibility but often lack guaranteed income and traditional employment protections. The distinction in compensation models impacts long-term financial stability and career predictability for employees.
Risk and Reward: Predictable Paychecks vs. Potential Upside
Salaried workers benefit from predictable paychecks, ensuring financial stability and reduced income risk through fixed monthly earnings and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Gig professionals face income variability with no guaranteed minimum pay, exposing them to higher financial risk but offering the potential for greater rewards based on task volume and client demand. The compensation model choice directly impacts an employee's risk tolerance and reward opportunities within their career.
Choosing the Right Compensation Model: Factors to Consider
Selecting the ideal compensation model requires evaluating job stability, income predictability, and flexibility needs. Salaried workers benefit from consistent pay and structured benefits, while gig professionals prioritize autonomy and variable earnings based on project influx. Understanding workforce preferences, industry standards, and financial planning goals ensures alignment with organizational strategy and employee satisfaction.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Careerist
Portfolio careerists often prefer gig professional compensation models that offer flexibility and diversified income streams, contrasting with salaried workers who receive fixed, predictable pay and benefits. The gig model supports varied projects and clients, enabling portfolio careerists to maximize earnings potential and work-life balance.
Hybrid Compensation Structure
A hybrid compensation structure combines the stability of a salaried worker's fixed income with the flexibility and performance incentives typical of gig professionals, enabling companies to optimize cost efficiency and motivate diverse talent pools. This model integrates base salary with variable pay components such as bonuses, commissions, or project-based fees, aligning compensation with both long-term commitment and short-term productivity.
On-Demand Income Model
The on-demand income model offers gig professionals flexible, task-based compensation that aligns earnings directly with workload and availability, contrasting with salaried workers who receive fixed, predictable pay. This model enhances financial agility for gig workers but may lead to income variability and less traditional employment benefits compared to salaried roles.
Flexible Retainer Agreement
A Flexible Retainer Agreement offers salaried workers a stable compensation model with predictable income and benefits, while gig professionals benefit from adaptable terms that align payment with project scope and workload variability. This hybrid approach enhances workforce management by balancing security for employees and flexibility for gig workers, optimizing cost-efficiency and talent retention.
Project-Based Remuneration
Project-based remuneration offers gig professionals tailored payment aligned with specific deliverables, enhancing flexibility and incentivizing performance, while salaried workers receive fixed compensation regardless of project outcomes, ensuring income stability but potentially limiting motivation for project efficiency. This model favors gig professionals in dynamic industries where output and timelines vary, contrasting with salaried employment suited for consistent workload and long-term organizational roles.
Employment-Gig Hybridization
The employment-gig hybridization model blends the stability of salaried work with the flexibility of gig assignments, offering employees a diversified income stream and adaptive work schedules. This compensation structure enhances workforce agility by integrating fixed salaries with performance-based gig earnings, promoting both job security and entrepreneurial autonomy.
Benefits-As-A-Service (BAAS)
Salaried workers typically receive comprehensive Benefits-As-A-Service (BAAS) packages including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid leave, ensuring financial stability and well-being. Gig professionals often rely on flexible, on-demand BAAS options tailored to variable income, emphasizing portability and customization over traditional benefits.
Microcontracting Compensation
Microcontracting compensation offers gig professionals flexible, project-based earnings without fixed monthly salaries, contrasting sharply with salaried workers who receive consistent, predetermined pay regardless of task volume. This model enables companies to scale workforce expenses precisely to workload demands while providing professionals with diversified income streams linked directly to completed micro-tasks.
Guaranteed Minimum Engagement
Salaried workers receive a fixed, guaranteed minimum engagement with consistent monthly pay, ensuring financial stability regardless of workload fluctuations. Gig professionals lack guaranteed minimum engagement, with compensation tied directly to task completion and project availability, leading to variable income streams.
Task-Based Incentive Plan
Task-based incentive plans for salaried workers typically involve predefined performance metrics linked to specific job responsibilities, ensuring consistent compensation aligned with company goals. In contrast, gig professionals receive direct payments per completed task or project, fostering flexibility but requiring clear agreements on task scope and delivery timelines to optimize earnings.
Salaried worker vs Gig professional for compensation model. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com