Front-end development involves building the user interface and experience using frameworks like React or Angular, enabling dynamic and interactive web applications. Jamstack development focuses on decoupling the front-end from the back-end by leveraging static site generators, APIs, and CDN delivery, resulting in faster load times and enhanced security. Choosing between the two depends on project requirements for scalability, performance, and ease of maintenance.
Table of Comparison
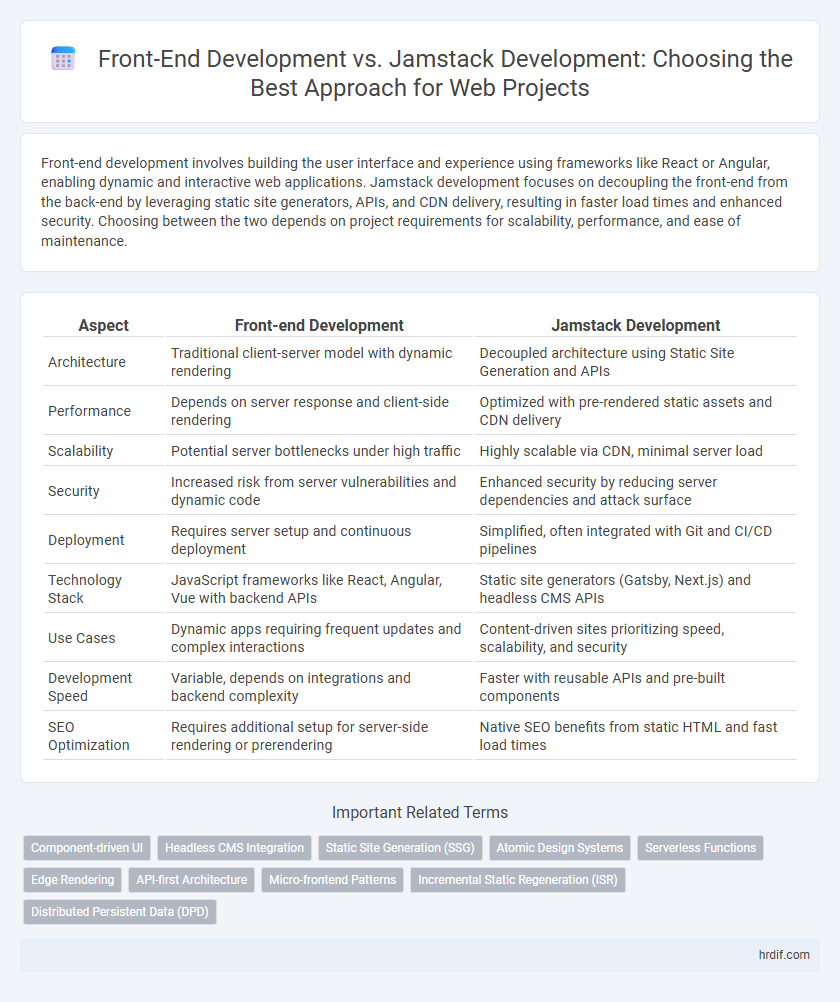
| Aspect | Front-end Development | Jamstack Development |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Traditional client-server model with dynamic rendering | Decoupled architecture using Static Site Generation and APIs |
| Performance | Depends on server response and client-side rendering | Optimized with pre-rendered static assets and CDN delivery |
| Scalability | Potential server bottlenecks under high traffic | Highly scalable via CDN, minimal server load |
| Security | Increased risk from server vulnerabilities and dynamic code | Enhanced security by reducing server dependencies and attack surface |
| Deployment | Requires server setup and continuous deployment | Simplified, often integrated with Git and CI/CD pipelines |
| Technology Stack | JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, Vue with backend APIs | Static site generators (Gatsby, Next.js) and headless CMS APIs |
| Use Cases | Dynamic apps requiring frequent updates and complex interactions | Content-driven sites prioritizing speed, scalability, and security |
| Development Speed | Variable, depends on integrations and backend complexity | Faster with reusable APIs and pre-built components |
| SEO Optimization | Requires additional setup for server-side rendering or prerendering | Native SEO benefits from static HTML and fast load times |
Front-end Development vs Jamstack: Core Concepts
Front-end development centers on building user interfaces with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, focusing on dynamic rendering and interactivity within the browser. Jamstack development leverages pre-rendered static pages, APIs, and serverless functions to enhance performance, scalability, and security. Core concepts of front-end development involve client-side rendering and state management, whereas Jamstack emphasizes decoupling the front end from the backend and delivering content via CDNs for faster load times.
Key Differences in Architecture
Front-end development primarily relies on client-side rendering with dynamic content fetched from servers or APIs, whereas Jamstack development emphasizes pre-rendered static sites served via Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) for faster load times. Jamstack architecture separates the frontend from backend services, leveraging APIs and microservices to enhance scalability and security. In contrast, traditional front-end frameworks often integrate tightly with backend systems, making deployment and scalability more complex.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Jamstack development leverages pre-rendered static content served via CDNs, resulting in significantly faster load times and improved performance compared to traditional front-end development reliant on server-side rendering and dynamic content generation. By decoupling the front end from back-end services, Jamstack reduces server response time and minimizes client-side processing, enhancing user experience in web projects. Performance metrics often show Jamstack sites achieving higher scores in Google Lighthouse tests, especially in metrics like Time to First Byte (TTFB) and First Contentful Paint (FCP), underscoring its superior speed advantages.
Scalability and Flexibility for Projects
Jamstack development offers superior scalability by decoupling the front end from the backend, enabling faster load times and easier integration with various APIs and services. Traditional front-end development often faces limitations in flexibility due to tightly coupled architectures, making large-scale updates more complex and time-consuming. Leveraging Jamstack's static site generation and CDN distribution enhances project scalability and allows developers to adapt rapidly to evolving requirements.
Developer Experience and Productivity
Front-end development often involves complex frameworks and state management, which can slow down developer productivity due to steep learning curves and debugging challenges. Jamstack development streamlines the process by decoupling the front end from backend services, enabling faster builds, easier scalability, and improved developer experience through pre-rendering and serverless functions. Tools like static site generators and APIs reduce deployment times and increase code maintainability, enhancing overall project efficiency.
Tools and Frameworks: A Comparative Overview
Front-end development traditionally relies on frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js, enabling dynamic user interfaces built with JavaScript, HTML, and CSS. Jamstack development emphasizes static site generators such as Gatsby, Next.js, and Hugo, integrating APIs and pre-built markup to optimize performance and scalability. Tools like Netlify and Vercel enhance Jamstack workflows by providing seamless deployment and CDN integration, contrasting with the often server-dependent environments of conventional front-end setups.
Security Considerations in Front-end and Jamstack
Front-end development often faces security risks such as cross-site scripting (XSS) and data exposure due to dynamic content rendering directly in the browser. Jamstack development enhances security by serving pre-built static assets through content delivery networks (CDNs), significantly reducing the attack surface and eliminating server-side vulnerabilities. Tokenized API calls and serverless functions in Jamstack further isolate backend processes, minimizing the risk of data breaches compared to conventional front-end architectures.
SEO and Accessibility Implications
Front-end Development often relies on dynamic rendering, which can slow page load times and hinder SEO performance due to delayed content indexing by search engines. Jamstack Development pre-renders static pages served via CDNs, enhancing page speed and ensuring better accessibility compliance through consistent HTML structure. Improved load speeds and semantic markup in Jamstack projects significantly boost search engine rankings and provide a more inclusive user experience.
Cost Efficiency and Project Maintenance
Front-end development often involves higher ongoing costs due to frequent updates, complex frameworks, and server management, whereas Jamstack development significantly reduces expenses by serving pre-built static assets through CDNs, minimizing server costs and downtime. Jamstack's modular architecture enables easier scalability and streamlined maintenance with decoupled APIs, contrasting with traditional front-end projects that require more intensive testing and debugging efforts. Overall, Jamstack offers superior cost efficiency and simplified project maintenance, making it ideal for scalable, high-performance web applications.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Career
Front-end development emphasizes building interactive user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular, focusing on dynamic content and direct client-side interaction. Jamstack development prioritizes pre-rendered static sites enhanced with APIs and serverless functions, optimizing performance, security, and scalability with tools like Gatsby or Next.js. Choosing between front-end and Jamstack development for your career depends on your interest in hands-on UI design versus modern web architecture trends driving faster, more maintainable web projects.
Related Important Terms
Component-driven UI
Component-driven UI in front-end development emphasizes reusable, modular elements built with frameworks like React or Vue, enhancing maintainability and scalability in web projects. Jamstack development leverages pre-built components served via CDN with static site generators, optimizing performance, security, and developer experience by decoupling the front end from backend services.
Headless CMS Integration
Front-end development traditionally relies on monolithic architectures where the CMS and front-end are tightly coupled, limiting flexibility in content delivery and scalability. Jamstack development leverages headless CMS integration, decoupling the content management from the front-end, enabling faster builds, improved security, and seamless API-driven content updates across multiple platforms.
Static Site Generation (SSG)
Front-end development traditionally relies on dynamic rendering through frameworks like React or Angular, while Jamstack development emphasizes Static Site Generation (SSG) to deliver pre-built HTML files, resulting in faster load times and improved scalability. Utilizing SSG in Jamstack reduces server dependencies, enhances security, and optimizes performance by serving static assets via Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), making it ideal for high-traffic web projects.
Atomic Design Systems
Front-end development with traditional frameworks often involves tightly coupled components, whereas Jamstack development leverages decoupled architectures that enhance scalability and performance through static site generators and APIs. Implementing Atomic Design Systems in Jamstack projects facilitates modular, reusable UI components that streamline maintenance and accelerate development cycles.
Serverless Functions
Front-end Development traditionally relies on server-side rendering and monolithic architectures, whereas Jamstack Development leverages serverless functions to handle backend processes, enabling faster load times and enhanced scalability. Serverless functions in Jamstack projects execute on-demand, reducing server maintenance and optimizing resource usage for dynamic content delivery and API integrations.
Edge Rendering
Front-end development traditionally relies on client-side rendering, which can lead to slower load times and reduced performance on mobile devices, whereas Jamstack development leverages edge rendering to serve pre-built content from CDN nodes, dramatically reducing latency and improving scalability. Edge rendering in Jamstack enables dynamic, personalized content delivery closer to the user, enhancing user experience and SEO performance by minimizing server dependencies.
API-first Architecture
Front-end development focuses on building user interfaces with traditional frameworks, while Jamstack development leverages an API-first architecture to separate the frontend from backend services, enhancing scalability and performance. Jamstack's use of pre-rendered static pages combined with dynamic APIs reduces server load and improves loading times in web projects.
Micro-frontend Patterns
Micro-frontend patterns in front-end development enable independent teams to build, deploy, and maintain discrete components, enhancing scalability and reducing coupling. Jamstack development leverages static site generation and pre-rendered micro-frontends, optimizing performance and security by minimizing runtime dependencies and server load.
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR) enhances Jamstack development by enabling static pages to be updated incrementally without rebuilding the entire site, improving performance and scalability for web projects. Traditional front-end development often relies on client-side rendering, whereas ISR in Jamstack optimizes load times through static generation combined with selective content updates.
Distributed Persistent Data (DPD)
Front-end Development typically handles user interface rendering and state management on the client side, but Jamstack Development leverages Distributed Persistent Data (DPD) architectures to enhance scalability, performance, and data reliability through decoupled APIs and static site generation. Utilizing Jamstack with DPD allows web projects to optimize content delivery by distributing data storage across edge locations, reducing latency and improving user experience compared to traditional front-end approaches.
Front-end Development vs Jamstack Development for web projects. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com