A QA Tester primarily focuses on manual testing, identifying bugs, and ensuring that software meets user requirements through hands-on evaluation. An Automation Engineer develops and maintains automated test scripts to increase testing efficiency and coverage, often using tools like Selenium or Appium. Both roles collaborate closely to deliver high-quality software by combining thorough manual inspection with scalable automation solutions.
Table of Comparison
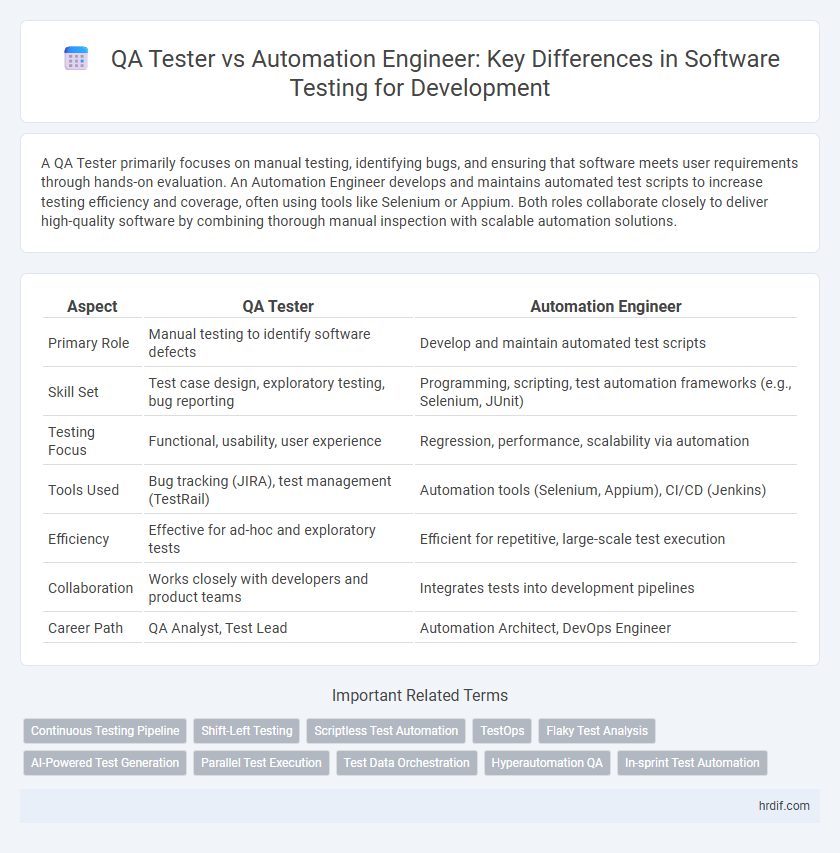
| Aspect | QA Tester | Automation Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manual testing to identify software defects | Develop and maintain automated test scripts |
| Skill Set | Test case design, exploratory testing, bug reporting | Programming, scripting, test automation frameworks (e.g., Selenium, JUnit) |
| Testing Focus | Functional, usability, user experience | Regression, performance, scalability via automation |
| Tools Used | Bug tracking (JIRA), test management (TestRail) | Automation tools (Selenium, Appium), CI/CD (Jenkins) |
| Efficiency | Effective for ad-hoc and exploratory tests | Efficient for repetitive, large-scale test execution |
| Collaboration | Works closely with developers and product teams | Integrates tests into development pipelines |
| Career Path | QA Analyst, Test Lead | Automation Architect, DevOps Engineer |
Overview: Roles of QA Tester and Automation Engineer
QA Testers primarily focus on manual testing processes, identifying bugs, and validating software functionality to ensure quality from an end-user perspective. Automation Engineers design, develop, and maintain automated test scripts using tools like Selenium, enhancing test efficiency and coverage for regression and performance testing. Both roles are essential for comprehensive software testing, combining human insight with automated precision to optimize product reliability.
Key Responsibilities: Manual vs Automated Testing
QA Testers primarily perform manual testing by executing test cases, identifying defects, and ensuring software meets user requirements through exploratory and usability testing. Automation Engineers focus on designing, developing, and maintaining automated test scripts using tools like Selenium, Appium, or TestComplete to increase test coverage and efficiency. While QA Testers excel in detecting user interface and experience issues through hands-on testing, Automation Engineers optimize regression and performance testing by integrating automated frameworks into continuous integration pipelines.
Required Skills and Qualifications
QA Testers require strong analytical skills, proficiency in manual testing methodologies, and expertise in test case design and defect tracking tools like JIRA. Automation Engineers need advanced programming skills in languages such as Java, Python, or C#, along with experience in automation frameworks like Selenium, Appium, or TestNG. Both roles demand a solid understanding of software development life cycle (SDLC), version control systems like Git, and familiarity with continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Career Growth and Advancement Opportunities
QA Testers typically start with manual testing skills and gain experience in identifying software defects, which provides a solid foundation for career growth into specialized roles such as Automation Engineers or Quality Analysts. Automation Engineers often experience faster career advancement due to their proficiency in scripting, test automation frameworks, and continuous integration, making them key contributors to DevOps and agile teams. Both roles offer pathways to leadership positions like QA Manager or Test Architect, but expertise in automation technology significantly enhances promotion prospects in the evolving software development landscape.
Tools and Technologies Used
QA Testers primarily utilize manual testing tools such as JIRA, TestRail, and Postman to execute test cases and track defects, ensuring software functionality meets requirements. Automation Engineers focus on scripting and automated frameworks using Selenium, Appium, Cypress, and TestNG to increase test coverage and efficiency through continuous integration pipelines. Both roles leverage version control systems like Git and CI/CD tools such as Jenkins or GitLab to maintain test reliability and workflow automation.
Salary Comparison: QA Tester vs Automation Engineer
Automation engineers typically command higher salaries than QA testers due to their specialized skills in scripting, coding, and test automation frameworks such as Selenium and Jenkins. According to recent industry surveys, the average annual salary for an automation engineer ranges from $85,000 to $120,000, whereas QA testers earn between $55,000 and $80,000 depending on experience and location. The demand for automation engineers continues to grow as companies prioritize efficient, scalable testing processes.
Workflows and Testing Processes
QA Testers primarily focus on manual testing workflows, executing predefined test cases to identify functional defects and ensure software quality through exploratory and regression testing. Automation Engineers design, develop, and maintain automated test scripts using frameworks like Selenium or Appium to streamline repetitive testing processes and increase test coverage. Effective collaboration between QA Testers and Automation Engineers optimizes testing processes, combining manual analysis with scalable automated workflows to accelerate release cycles and improve defect detection.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
The demand for QA Testers remains strong due to their expertise in manual testing and user experience validation, critical for agile development cycles. Automation Engineers are increasingly sought after for their skills in scripting, continuous integration, and deploying automated test frameworks, aligning with industry trends toward DevOps and faster release cycles. Job market analysis shows a growing preference for hybrid roles combining manual testing acumen with automation proficiency to meet evolving software quality standards.
Challenges Faced in Each Role
QA Testers face challenges such as maintaining detailed test cases, manually identifying edge cases, and ensuring comprehensive coverage across multiple platforms. Automation Engineers struggle with selecting the right testing frameworks, scripting reliable automated tests, and integrating these tests seamlessly into continuous integration pipelines. Both roles require constant adaptation to evolving software environments and collaboration with development teams to improve test accuracy and efficiency.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Selecting between QA Tester and Automation Engineer roles hinges on expertise in manual testing versus proficiency in scripting and tool-based automation. Consider project complexity, team size, and long-term career goals, as Automation Engineers typically drive efficiency in repetitive tasks while QA Testers focus on exploratory and usability testing. Familiarity with programming languages such as Python or Java and experience with automation frameworks like Selenium significantly influence the suitability for an Automation Engineer position.
Related Important Terms
Continuous Testing Pipeline
QA Testers primarily focus on manual testing to identify user experience issues and functional defects, ensuring comprehensive validation within a Continuous Testing Pipeline. Automation Engineers design and implement automated test scripts and frameworks that integrate seamlessly with CI/CD tools, accelerating feedback loops and maintaining test coverage throughout rapid development cycles.
Shift-Left Testing
QA Testers in Shift-Left Testing focus on early defect detection through manual exploratory testing and requirement validation, ensuring quality from the initial development stages. Automation Engineers complement this by designing and implementing automated test scripts that integrate with continuous integration pipelines, accelerating feedback and improving test coverage during the development lifecycle.
Scriptless Test Automation
QA Testers primarily focus on manual testing and identifying defects through exploratory and scripted testing, while Automation Engineers design and develop automated test scripts using coding frameworks. Scriptless test automation bridges this gap by enabling QA Testers to create automated tests through visual interfaces without deep programming skills, accelerating test coverage and reducing dependency on specialized Automation Engineers.
TestOps
QA Testers primarily focus on manual testing, creating and executing test cases to identify bugs and ensure software quality, while Automation Engineers develop and maintain automated test scripts to optimize test coverage and efficiency. TestOps integrates these roles by streamlining test management, continuous integration, and deployment processes, enhancing collaboration and accelerating software delivery cycles.
Flaky Test Analysis
QA Testers primarily focus on identifying flaky tests through manual test execution and detailed issue documentation, while Automation Engineers develop robust test scripts and implement continuous integration tools to detect and mitigate test flakiness automatically. Effective flaky test analysis requires combining the manual insight of QA Testers with the script optimization and environment stabilization techniques employed by Automation Engineers.
AI-Powered Test Generation
QA testers ensure software quality through manual and exploratory testing, identifying bugs and usability issues, while automation engineers develop AI-powered test generation frameworks that create efficient, scalable test scripts using machine learning algorithms. Leveraging AI enables automation engineers to generate adaptive test cases that enhance coverage, reduce test maintenance, and accelerate continuous integration pipelines.
Parallel Test Execution
QA Testers typically focus on manual testing methods to identify defects through exploratory and functional testing, while Automation Engineers design and implement automated test scripts for faster, repeatable test execution. Parallel test execution, enabled by automation frameworks like Selenium Grid or TestNG, significantly reduces overall testing time by running multiple tests simultaneously across different environments, a process less feasible with manual QA testing.
Test Data Orchestration
QA Testers primarily focus on manual test data orchestration to validate application functionality and identify defects through exploratory and predefined test scenarios. Automation Engineers develop scripts and frameworks to automate test data generation, management, and orchestration, enhancing efficiency and consistency in regression testing and continuous integration pipelines.
Hyperautomation QA
QA Testers manually evaluate software functionality to identify defects, relying on exploratory and regression testing methods; Automation Engineers develop scripts using tools like Selenium and QTP to automate repetitive test cases, enhancing coverage and efficiency. Hyperautomation QA leverages AI-driven frameworks and intelligent testing bots to accelerate testing cycles, integrate continuous testing in CI/CD pipelines, and reduce human intervention in quality assurance processes.
In-sprint Test Automation
In-sprint test automation enhances software development efficiency by integrating automated tests directly into the sprint cycle, allowing QA Testers to execute manual exploratory tests while Automation Engineers focus on creating and maintaining test scripts that validate new features continuously. This collaboration ensures faster feedback, reduces regression risks, and accelerates deployment without compromising software quality.
QA Tester vs Automation Engineer for software testing. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com