DevOps Engineers streamline software development and IT operations by automating workflows, managing infrastructure, and ensuring continuous integration and delivery pipelines. GitOps Engineers specialize in using Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application management, enabling version-controlled, automated deployments and rollbacks. Both roles enhance operational efficiency, but GitOps Engineers emphasize infrastructure as code through Git workflows, while DevOps Engineers cover broader automation and collaboration practices.
Table of Comparison
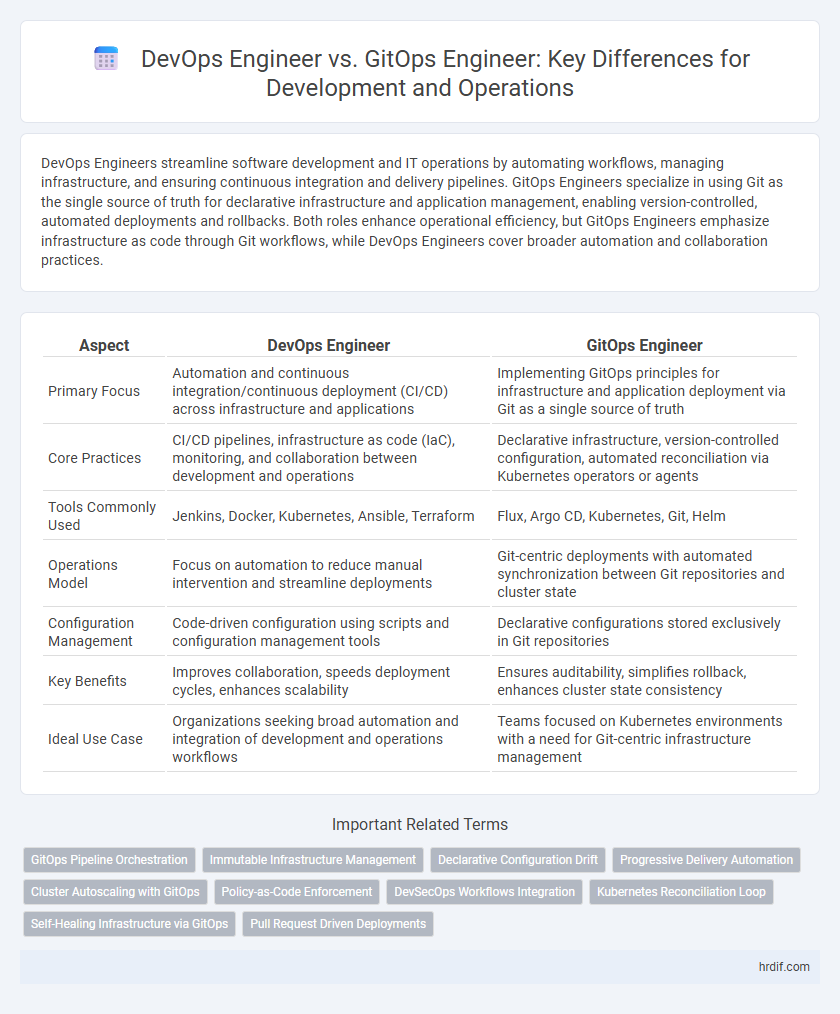
| Aspect | DevOps Engineer | GitOps Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Automation and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) across infrastructure and applications | Implementing GitOps principles for infrastructure and application deployment via Git as a single source of truth |
| Core Practices | CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code (IaC), monitoring, and collaboration between development and operations | Declarative infrastructure, version-controlled configuration, automated reconciliation via Kubernetes operators or agents |
| Tools Commonly Used | Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible, Terraform | Flux, Argo CD, Kubernetes, Git, Helm |
| Operations Model | Focus on automation to reduce manual intervention and streamline deployments | Git-centric deployments with automated synchronization between Git repositories and cluster state |
| Configuration Management | Code-driven configuration using scripts and configuration management tools | Declarative configurations stored exclusively in Git repositories |
| Key Benefits | Improves collaboration, speeds deployment cycles, enhances scalability | Ensures auditability, simplifies rollback, enhances cluster state consistency |
| Ideal Use Case | Organizations seeking broad automation and integration of development and operations workflows | Teams focused on Kubernetes environments with a need for Git-centric infrastructure management |
Overview: DevOps Engineer vs GitOps Engineer
DevOps Engineers focus on automating and streamlining the entire software development lifecycle, integrating development and operations through continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines and monitoring tools. GitOps Engineers specialize in using Git as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployments, leveraging Kubernetes and tools like Argo CD or Flux for automated reconciliation and version control. While DevOps Engineers emphasize process optimization and collaboration across teams, GitOps Engineers prioritize infrastructure-as-code and Git-based operational workflows for enhanced reliability and auditability.
Core Responsibilities in Operations
DevOps Engineers focus on automating infrastructure provisioning, continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, and monitoring system performance to ensure reliable software releases. GitOps Engineers specialize in leveraging Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure and application deployment, emphasizing version control and automated rollbacks. Both roles prioritize operational stability and efficiency, but GitOps engineers emphasize infrastructure as code through Git workflows while DevOps engineers manage broader CI/CD and infrastructure automation tasks.
Key Skills and Toolsets
DevOps Engineers excel in continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, infrastructure as code (IaC), and automated testing, leveraging tools like Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and Ansible. GitOps Engineers specialize in declarative infrastructure management using Git as the single source of truth, focusing on tools such as Flux, Argo CD, and Kubernetes Operators to ensure automated and auditable operations. Both roles require strong scripting abilities, cloud platform expertise, and proficiency in monitoring and security practices for efficient system reliability and scalability.
Approach to Infrastructure Management
DevOps Engineers manage infrastructure through automated scripts, continuous integration pipelines, and configuration management tools to ensure scalable and reliable deployments. GitOps Engineers adopt a declarative approach, leveraging Git repositories as the single source of truth for infrastructure state, enabling version-controlled, auditable, and automated operations. This shift to GitOps improves collaboration, rollback capabilities, and enhances consistency across development and production environments.
Automation and Deployment Strategies
DevOps Engineers focus on automating software development and IT operations processes using continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, configuration management tools like Ansible or Chef, and infrastructure as code (IaC) to streamline deployment workflows. GitOps Engineers leverage Git repositories as the single source of truth for automated deployment and infrastructure management, employing tools like Flux or Argo CD to enforce declarative infrastructure and application states in Kubernetes environments. Automation in GitOps emphasizes version-controlled automation and rollback capabilities, while DevOps automation prioritizes comprehensive pipeline orchestration across diverse technology stacks.
CI/CD Pipeline Differences
A DevOps Engineer designs and manages CI/CD pipelines emphasizing automation, integration, and collaboration across development and operations teams to streamline software delivery. In contrast, a GitOps Engineer leverages Git as the single source of truth, using Git repositories to drive automated deployments and infrastructure management via declarative configurations in the CI/CD pipeline. GitOps pipelines prioritize version control, auditability, and rollback capabilities, enhancing operational security and reliability compared to traditional DevOps CI/CD workflows.
Security and Compliance Practices
DevOps Engineers focus on integrating security and compliance through continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, embedding automated vulnerability scanning, and enforcing role-based access control to ensure secure and compliant operations. GitOps Engineers enhance security by managing infrastructure and application configurations declaratively through Git repositories, enabling version-controlled change tracking and automated policy enforcement for compliance. Both roles collaborate to implement secure secret management and audit logging, minimizing risks and ensuring adherence to regulatory standards in operational workflows.
Collaboration with Development and Operations
DevOps Engineers streamline collaboration between development and operations by implementing continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines, enabling faster and more reliable software releases. GitOps Engineers enhance this collaboration by using Git as the single source of truth for both application and infrastructure deployment, automating operations with declarative configuration and ensuring version-controlled changes. The approach in GitOps fosters improved transparency and auditability, bridging silos more effectively between development and operations teams.
Scalability and Maintenance Considerations
DevOps engineers focus on automating and streamlining software delivery pipelines, ensuring scalability through modular infrastructure and continuous monitoring. GitOps engineers leverage Git repositories as the single source of truth, enhancing maintainability by enabling declarative infrastructure management and automated rollback capabilities. Scalability in GitOps is driven by version-controlled configuration changes, while maintenance benefits from improved traceability and reduced manual intervention.
Career Pathways and Growth Opportunities
DevOps Engineers focus on streamlining software delivery through automation and collaboration, often mastering CI/CD pipelines, infrastructure as code, and cloud platforms, which opens pathways to roles like Site Reliability Engineer (SRE) or Cloud Architect. GitOps Engineers specialize in managing operations using Git as the single source of truth, emphasizing declarative infrastructure and automated deployments, leading to career growth in Kubernetes administration, platform engineering, and advanced infrastructure automation. Both roles offer robust growth opportunities, but GitOps Engineers are increasingly in demand due to the rise of Kubernetes and cloud-native technologies, positioning them well for future-oriented operational leadership roles.
Related Important Terms
GitOps Pipeline Orchestration
GitOps Engineers specialize in pipeline orchestration by utilizing declarative configurations and Kubernetes-native tools to automate application deployments, ensuring consistency and version control across environments. DevOps Engineers focus broadly on integrating development and operations through CI/CD processes, but GitOps provides a more streamlined, automated approach to managing infrastructure and application states via Git repositories.
Immutable Infrastructure Management
DevOps Engineers manage infrastructure automation and continuous integration pipelines, emphasizing automation scripts and configuration management to achieve consistent environments. GitOps Engineers specialize in immutable infrastructure management by leveraging Git repositories as the single source of truth, enabling declarative infrastructure control and automated synchronization for reliable, version-controlled deployments.
Declarative Configuration Drift
DevOps Engineers manage infrastructure and deployments using imperative scripts, increasing the risk of configuration drift due to manual interventions. GitOps Engineers leverage declarative configuration stored in version-controlled repositories, minimizing drift by automatically reconciling system state with the declared desired state.
Progressive Delivery Automation
DevOps Engineers streamline Progressive Delivery Automation by integrating CI/CD pipelines and infrastructure as code to accelerate software releases and ensure operational stability. GitOps Engineers enhance these processes by leveraging Git repositories as the single source of truth, enabling automated, declarative management of infrastructure and application deployments for consistent and auditable operations.
Cluster Autoscaling with GitOps
GitOps Engineers leverage declarative configurations and automated workflows to implement cluster autoscaling efficiently, ensuring real-time adjustments based on resource demand through continuous monitoring tools like Prometheus and Kubernetes metrics-server. DevOps Engineers traditionally manage autoscaling using manual scripts and CI/CD pipelines, but GitOps approaches streamline operations by automating cluster state reconciliation and enhancing scalability, reliability, and auditability in cloud-native environments.
Policy-as-Code Enforcement
DevOps Engineers implement Policy-as-Code by integrating security and compliance checks directly into CI/CD pipelines, ensuring operational policies are automatically enforced during software delivery. GitOps Engineers leverage declarative Git repositories to enforce Policy-as-Code, enabling version-controlled, auditable, and automated policy management that enhances operational consistency and security.
DevSecOps Workflows Integration
DevOps Engineers streamline continuous integration and delivery pipelines by automating infrastructure and application deployment, while GitOps Engineers leverage Git repositories as the single source of truth for declarative infrastructure management, enhancing traceability and version control. Integrating DevSecOps workflows, GitOps emphasizes security automation within the CI/CD process, enabling proactive vulnerability scanning, policy enforcement, and compliance monitoring directly through Git-based configuration management.
Kubernetes Reconciliation Loop
DevOps Engineers manage continuous integration and deployment pipelines to ensure smooth application delivery, while GitOps Engineers specifically leverage Kubernetes reconciliation loops to automate infrastructure and application state management through Git as the single source of truth. Kubernetes reconciliation loops continuously monitor cluster states, enabling GitOps workflows to detect and rectify drifts by comparing desired configurations in Git repositories against actual cluster states.
Self-Healing Infrastructure via GitOps
GitOps Engineers leverage declarative infrastructure as code and automated reconciliation loops to enable self-healing infrastructure, minimizing manual intervention and downtime. DevOps Engineers focus on broader operational workflows but may lack the specialized continuous reconciliation capabilities inherent in GitOps-driven self-healing systems.
Pull Request Driven Deployments
DevOps Engineers traditionally manage deployments through CI/CD pipelines integrating manual approval steps, while GitOps Engineers leverage Pull Request driven deployments that automate infrastructure changes via version-controlled Git workflows. This approach enhances auditability, reduces errors, and accelerates deployment cycles by treating Git repositories as the single source of truth for operational states.
DevOps Engineer vs GitOps Engineer for operations. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com