Embedded Systems Developers specialize in programming hardware-constrained devices, optimizing software for efficient resource use and real-time performance in development pet projects. Edge Computing Developers focus on creating applications that process data locally on edge devices, reducing latency and bandwidth by bringing computation closer to the source. Both roles require expertise in low-level programming and hardware integration, but Edge Computing Developers emphasize distributed computing and connectivity in development environments.
Table of Comparison
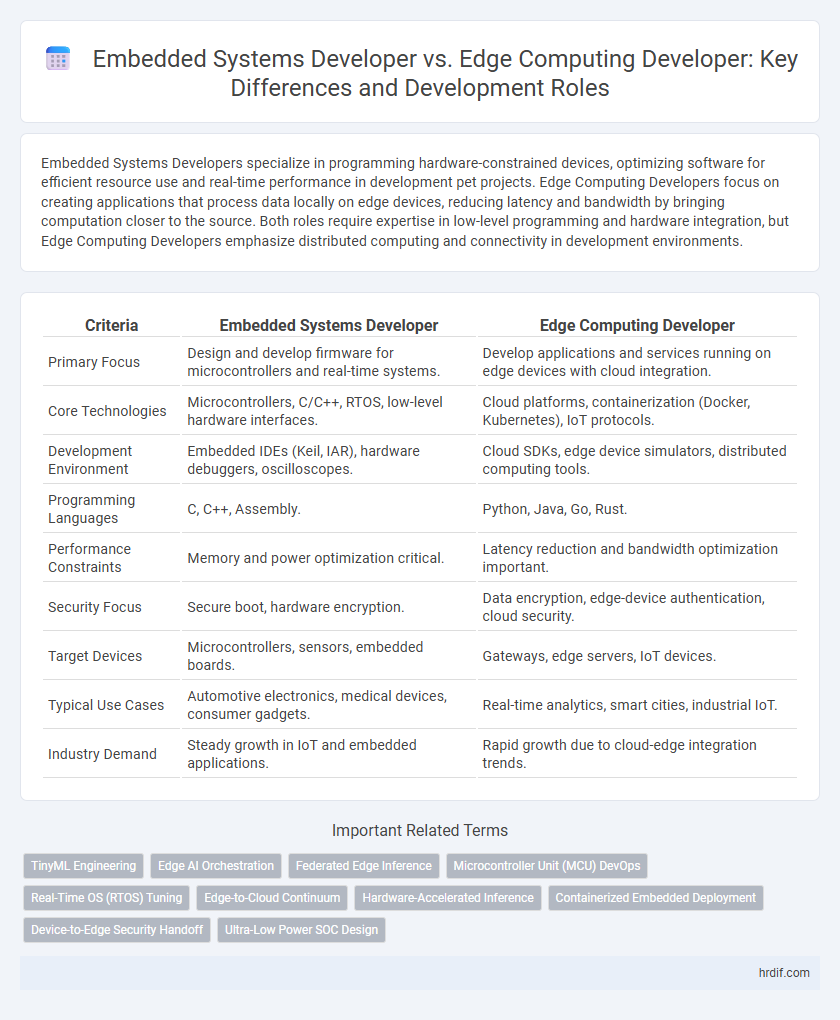
| Criteria | Embedded Systems Developer | Edge Computing Developer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Design and develop firmware for microcontrollers and real-time systems. | Develop applications and services running on edge devices with cloud integration. |
| Core Technologies | Microcontrollers, C/C++, RTOS, low-level hardware interfaces. | Cloud platforms, containerization (Docker, Kubernetes), IoT protocols. |
| Development Environment | Embedded IDEs (Keil, IAR), hardware debuggers, oscilloscopes. | Cloud SDKs, edge device simulators, distributed computing tools. |
| Programming Languages | C, C++, Assembly. | Python, Java, Go, Rust. |
| Performance Constraints | Memory and power optimization critical. | Latency reduction and bandwidth optimization important. |
| Security Focus | Secure boot, hardware encryption. | Data encryption, edge-device authentication, cloud security. |
| Target Devices | Microcontrollers, sensors, embedded boards. | Gateways, edge servers, IoT devices. |
| Typical Use Cases | Automotive electronics, medical devices, consumer gadgets. | Real-time analytics, smart cities, industrial IoT. |
| Industry Demand | Steady growth in IoT and embedded applications. | Rapid growth due to cloud-edge integration trends. |
Introduction to Embedded Systems and Edge Computing Development
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in creating software tailored for hardware-constrained environments, focusing on real-time processing, low power consumption, and efficient resource management in devices like microcontrollers and IoT hardware. Edge Computing Developers design applications that perform data processing near the data source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by enabling localized computation and analytics on edge devices such as gateways and edge servers. Both roles require proficiency in embedded programming languages and system-level optimization, but Edge Computing emphasizes distributed computing architectures and scalability in decentralized networks.
Key Roles and Responsibilities: Embedded vs Edge Developers
Embedded Systems Developers design and implement software for hardware-constrained environments, focusing on real-time processing, firmware development, and low-level programming with languages like C and assembly. Edge Computing Developers specialize in deploying distributed computing resources close to data sources, ensuring low latency, data processing, and integration with cloud services using platforms like Kubernetes and Docker. Both roles require expertise in system optimization, but embedded developers prioritize hardware interaction, whereas edge developers emphasize network architecture and scalable application deployment.
Technical Skills Required for Each Developer Role
Embedded Systems Developers require proficiency in low-level programming languages such as C and Assembly, real-time operating systems (RTOS), and hardware interfacing techniques including microcontrollers and sensors. Edge Computing Developers need expertise in distributed computing frameworks, cloud-native technologies, container orchestration tools like Kubernetes, and experience with AI/ML model deployment at the network edge. Both roles demand strong knowledge of networking protocols and security practices, but Embedded Systems focus more on hardware constraints while Edge Computing emphasizes data processing and scalability at edge locations.
Core Differences in Development Environments
Embedded Systems Developers work primarily with low-level hardware integration, real-time operating systems, and resource-constrained environments, focusing on firmware and hardware interfacing. Edge Computing Developers specialize in distributed computing architectures, managing data processing closer to data sources with scalable, networked systems often using containerization and cloud-native tools. The core difference lies in embedded developers emphasizing hardware-software co-design and minimal resource usage, while edge developers prioritize distributed system scalability, low-latency data processing, and cloud integration.
Industry Applications: Embedded Systems vs Edge Computing
Embedded Systems Developers design and optimize firmware for real-time control in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical devices, ensuring low latency and high reliability within constrained hardware environments. Edge Computing Developers focus on deploying scalable, distributed applications closer to data sources across sectors such as smart cities, manufacturing IoT, and telecommunications, enabling faster data processing and reduced bandwidth usage. Both roles drive innovation in Industry 4.0, with Embedded Systems emphasizing device-level integration and Edge Computing enhancing system-level data analytics and responsiveness.
Tools and Technologies: What Developers Use
Embedded Systems Developers primarily utilize low-level programming languages such as C and assembly, along with integrated development environments (IDEs) like Keil and MPLAB for microcontroller programming. Edge Computing Developers often work with high-level languages like Python and JavaScript, leveraging cloud platforms (AWS IoT Greengrass, Microsoft Azure IoT Edge) and container technologies such as Docker and Kubernetes for deploying distributed applications. Both roles require proficiency in hardware interfacing tools and debugging suites, but Edge Computing emphasizes scalable, networked architecture tools, while Embedded Systems focus on real-time operating systems and firmware development kits.
Career Pathways: Growth and Opportunities
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in designing software for hardware-constrained environments, with career growth linked to industries like automotive, aerospace, and IoT, often advancing into roles such as systems architect or firmware engineer. Edge Computing Developers focus on building distributed computing frameworks close to data sources, enabling real-time processing and scalability, with pathways leading to positions like cloud-edge integration specialist or AI model deployment engineer. Both careers offer expanding opportunities driven by the proliferation of connected devices and demand for low-latency computing solutions.
Salary Trends and Job Market Demand
Embedded Systems Developers often command competitive salaries due to expertise in low-level programming and hardware integration, with median salaries ranging from $80,000 to $120,000 annually depending on industry and experience. Edge Computing Developers are experiencing rapid salary growth, frequently earning between $90,000 and $130,000, driven by high demand for skills in distributed computing and real-time data processing. Job market demand favors Edge Computing roles in IoT and AI sectors, while Embedded Systems remain critical in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries.
Challenges Faced by Embedded and Edge Computing Developers
Embedded systems developers face challenges such as limited processing power, stringent real-time constraints, and power consumption optimization within constrained hardware environments. Edge computing developers contend with issues related to data latency reduction, secure data transmission, and managing distributed computing resources across diverse edge nodes. Both roles require expertise in hardware integration, efficient coding practices, and addressing scalability while ensuring robust performance under varying network conditions.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Career Suits You?
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in designing and programming hardware-integrated software for devices with real-time constraints, focusing on microcontrollers, firmware, and low-level optimization. Edge Computing Developers work on creating distributed computing solutions closer to data sources, emphasizing cloud integration, data processing efficiency, and scalable architectures. Choosing the right path depends on your preference for hardware-level programming and real-time systems versus cloud-based, distributed data processing and networked environments.
Related Important Terms
TinyML Engineering
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in designing and optimizing hardware-software integration for constrained devices, crucial for deploying TinyML models on microcontrollers with limited resources. Edge Computing Developers focus on creating scalable solutions that process data locally on edge devices, enabling real-time TinyML inference and reducing latency in decentralized environments.
Edge AI Orchestration
Edge Computing Developers specialize in designing AI orchestration frameworks that enable real-time data processing and decision-making at the network's edge, optimizing latency and bandwidth usage. Embedded Systems Developers focus on integrating hardware and software for constrained environments, but edge AI orchestration requires advanced skills in distributed AI models and scalable deployment across heterogeneous IoT devices.
Federated Edge Inference
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in programming hardware-efficient algorithms tailored for constrained devices, enabling real-time data processing at the source. Edge Computing Developers focus on designing scalable federated edge inference frameworks that distribute machine learning models across decentralized nodes, optimizing latency and preserving data privacy.
Microcontroller Unit (MCU) DevOps
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in MCU firmware optimization and real-time processing within constrained hardware environments, ensuring efficient DevOps pipelines for continuous integration and deployment at the microcontroller level. Edge Computing Developers focus on integrating MCUs with distributed network architectures, optimizing data processing latency and reliability through edge-enabled DevOps frameworks that manage device firmware updates, security patches, and resource allocation across heterogeneous edge nodes.
Real-Time OS (RTOS) Tuning
Embedded Systems Developers prioritize Real-Time Operating System (RTOS) tuning to optimize hardware-software interaction for low-latency, deterministic task execution in constrained environments. Edge Computing Developers leverage RTOS tuning to enhance data processing speed and reliability at edge nodes, ensuring efficient real-time analytics and minimal network dependency.
Edge-to-Cloud Continuum
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in designing and programming microcontroller-based devices with real-time constraints, optimizing hardware-software integration at the device level. Edge Computing Developers focus on deploying applications across the Edge-to-Cloud Continuum, enabling seamless data processing and analytics closer to data sources for improved latency and bandwidth efficiency.
Hardware-Accelerated Inference
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in integrating hardware-accelerated inference within constrained devices to optimize real-time AI performance and power efficiency. Edge Computing Developers focus on deploying and managing hardware-accelerated inference models at the network edge, enabling low-latency processing and enhanced scalability for distributed AI applications.
Containerized Embedded Deployment
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in designing and optimizing software for resource-constrained devices, focusing on real-time performance and hardware-specific integration, while Edge Computing Developers emphasize scalable, containerized deployment to enable distributed processing near data sources. Containerized embedded deployment bridges these roles by packaging lightweight, portable applications tailored for embedded hardware, enhancing flexibility and maintainability in edge environments.
Device-to-Edge Security Handoff
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in low-level programming and real-time operating systems to ensure secure data transmission from IoT devices, while Edge Computing Developers design scalable architectures that manage data processing and security handoff between edge nodes and cloud services. The critical difference lies in their approach to device-to-edge security handoff: embedded developers embed encryption and authentication protocols directly on hardware, whereas edge developers implement dynamic security policies and multi-layered defenses across distributed nodes.
Ultra-Low Power SOC Design
Embedded Systems Developers specialize in ultra-low power SoC design by optimizing hardware and firmware to achieve minimal energy consumption for IoT devices, ensuring efficient performance within constrained environments. Edge Computing Developers focus on integrating ultra-low power SoCs into distributed computing nodes, enabling real-time data processing and reduced latency while prioritizing energy efficiency in decentralized networks.
Embedded Systems Developer vs Edge Computing Developer for Development. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com