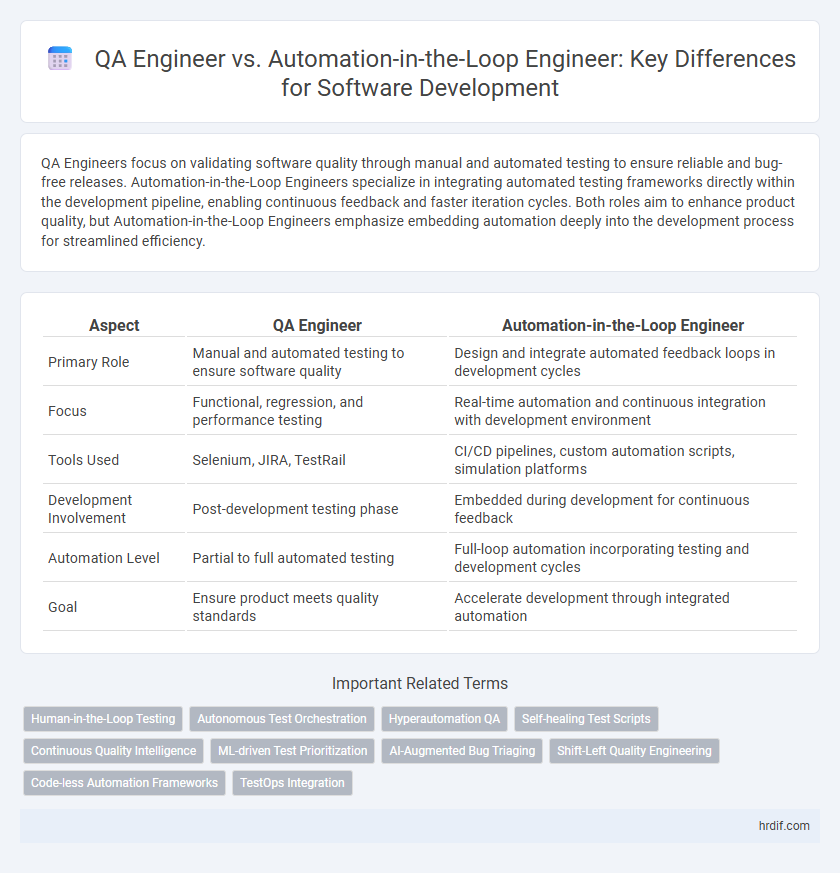
QA Engineers focus on validating software quality through manual and automated testing to ensure reliable and bug-free releases. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers specialize in integrating automated testing frameworks directly within the development pipeline, enabling continuous feedback and faster iteration cycles. Both roles aim to enhance product quality, but Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers emphasize embedding automation deeply into the development process for streamlined efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | QA Engineer | Automation-in-the-Loop Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Manual and automated testing to ensure software quality | Design and integrate automated feedback loops in development cycles |
| Focus | Functional, regression, and performance testing | Real-time automation and continuous integration with development environment |
| Tools Used | Selenium, JIRA, TestRail | CI/CD pipelines, custom automation scripts, simulation platforms |
| Development Involvement | Post-development testing phase | Embedded during development for continuous feedback |
| Automation Level | Partial to full automated testing | Full-loop automation incorporating testing and development cycles |
| Goal | Ensure product meets quality standards | Accelerate development through integrated automation |
Roles and Responsibilities: QA Engineer vs Automation-in-the-Loop Engineer
QA Engineers focus on manual and exploratory testing to identify defects, ensuring software quality through test case design, execution, and reporting. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers specialize in integrating automated testing processes within development pipelines, designing frameworks that embed automated test scripts into continuous integration and deployment systems. Their responsibilities overlap in defect detection but differ as QA Engineers emphasize manual validation while Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers prioritize automated testing and toolchain optimization.
Core Skill Sets Required in Each Position
QA Engineers require strong expertise in manual testing methodologies, bug tracking, and comprehensive understanding of software development life cycles (SDLC) to identify and document defects effectively. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers specialize in scripting languages, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, and automated test frameworks like Selenium or Appium to streamline and accelerate testing processes. Both roles demand proficiency in programming languages such as Java or Python, but Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers must also excel in developing and maintaining automation scripts integrated within the development pipeline.
Impact on Software Development Lifecycle
QA Engineers enhance the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) by systematically identifying bugs, verifying requirements, and ensuring product quality through manual and exploratory testing techniques. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers further optimize the SDLC by integrating automated test scripts directly within development pipelines, enabling continuous validation and faster feedback cycles. Their combined efforts reduce defect rates, accelerate release timelines, and improve overall software robustness.
Automation Tools and Frameworks: A Comparative Overview
QA Engineers primarily focus on manual and exploratory testing while leveraging automation tools such as Selenium, JUnit, and TestNG to enhance test coverage and efficiency. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers emphasize integrating automated testing frameworks like Jenkins, Robot Framework, and custom CI/CD pipelines to continuously validate code quality within development cycles. Comparing both roles reveals that Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers drive seamless automation across the software lifecycle, whereas QA Engineers balance manual oversight with targeted automation strategies.
Manual Testing vs. Automated Testing Approaches
QA Engineers primarily focus on manual testing methods to identify bugs and ensure software quality through exploratory and user-centric test cases, emphasizing human judgment and adaptability. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers integrate automated testing tools and scripts into the development pipeline, enhancing efficiency and consistency by executing predefined test scenarios rapidly and frequently. Balancing manual testing's thoroughness with automation's speed is essential for comprehensive quality assurance in modern software development cycles.
Collaboration with Development Teams
QA Engineers ensure product quality through manual testing and defect reporting, facilitating close collaboration with development teams to identify and resolve issues early. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers integrate automated testing frameworks within the development pipeline, enabling continuous testing and faster feedback cycles. Both roles emphasize seamless communication with developers to enhance code reliability and accelerate release timelines.
Career Growth and Learning Opportunities
QA Engineers develop expertise in manual and automated testing methodologies, gaining a strong foundation in quality assurance processes essential for software development. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers focus on integrating automated testing frameworks directly into continuous integration pipelines, enhancing skills in scripting, robotics, and machine learning applications. Career growth in QA emphasizes broadening testing strategies and leadership roles, while Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers advance through specialization in automation technologies and AI-driven development environments.
Industry Demand and Future Trends
QA Engineers remain essential in development for manual testing, quality assurance, and defect management, with steady demand in industries prioritizing software reliability. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers are gaining traction due to the rise of CI/CD pipelines and AI-driven testing, optimizing development cycles through integrated automated test systems. Future trends indicate a growing preference for Automation-in-the-Loop roles as AI and machine learning technologies push the boundaries of continuous testing and deployment efficiency.
Salary Expectations and Job Market Outlook
QA Engineers typically earn a median salary ranging from $70,000 to $100,000 annually, reflecting steady demand in manual and exploratory testing roles within software development. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers command higher salaries, often between $90,000 and $130,000, driven by expertise in integrating automated testing within continuous development pipelines and AI-driven test generation. Job market trends indicate growing demand for Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers as organizations prioritize faster, more reliable deployment cycles and leverage automation to enhance quality assurance processes.
Choosing the Right Path: Which Role Suits You?
QA Engineers specialize in manual and exploratory testing to ensure software quality through detailed test case execution and bug reporting, fostering a deep understanding of user experience and product functionality. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers focus on integrating automated testing frameworks within development pipelines, creating scripts and tools that enable continuous testing and faster delivery cycles. Choosing the right path depends on your preference for hands-on quality assurance with a user-centric approach versus developing and maintaining automation systems that streamline testing processes.
Related Important Terms
Human-in-the-Loop Testing
QA Engineers specialize in manual and automated testing to ensure software quality through comprehensive test case design and defect tracking. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers integrate human feedback into automated testing workflows, enhancing AI model accuracy and system reliability through Human-in-the-Loop testing methodologies.
Autonomous Test Orchestration
A QA Engineer concentrates on manual and automated test execution, identifying defects and ensuring software quality through established testing frameworks, while an Automation-in-the-Loop Engineer specializes in integrating autonomous test orchestration systems that dynamically adapt test cases using AI-driven analytics. Leveraging autonomous test orchestration enhances scalability and efficiency in continuous integration pipelines by automating test selection, execution, and result analysis with minimal human intervention.
Hyperautomation QA
QA Engineers primarily focus on designing and executing manual and automated tests to ensure software quality, while Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers integrate hyperautomation tools to develop continuous testing frameworks that enhance efficiency and reduce human intervention. Hyperautomation QA leverages AI-driven automation, robotic process automation (RPA), and analytics to optimize testing cycles, enabling faster defect detection and improved software reliability throughout the development lifecycle.
Self-healing Test Scripts
A QA Engineer focuses on creating and executing manual and automated test cases to ensure software quality, whereas an Automation-in-the-Loop Engineer specializes in integrating self-healing test scripts that automatically detect and adapt to UI changes, reducing maintenance overhead. Self-healing test scripts leverage AI-driven algorithms to dynamically update locators and test logic, enhancing test reliability and development velocity.
Continuous Quality Intelligence
QA Engineers focus on manual and automated testing to ensure software quality, while Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers integrate automated feedback systems within the development cycle, enhancing Continuous Quality Intelligence by enabling real-time defect detection and adaptive test optimization. This integration accelerates development velocity and improves reliability through continuous monitoring, data-driven insights, and seamless orchestration of testing automation within CI/CD pipelines.
ML-driven Test Prioritization
QA Engineers specialize in manual and automated testing strategies to ensure software quality, while Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers integrate ML-driven test prioritization frameworks that dynamically optimize test execution based on predictive models. Leveraging machine learning algorithms, Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers enhance test efficiency by focusing on high-risk code paths and reducing regression cycles, significantly accelerating continuous integration pipelines.
AI-Augmented Bug Triaging
QA Engineers specialize in manual and automated testing methods to identify and document software defects, whereas Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers integrate AI-augmented bug triaging systems that continuously learn from test results to prioritize and resolve issues more efficiently. Leveraging AI-driven analytics, Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers enhance defect detection accuracy, reduce false positives, and streamline development cycles by automating decision-making in bug management workflows.
Shift-Left Quality Engineering
Shift-Left Quality Engineering accelerates defect identification by embedding QA Engineers early in the development cycle, ensuring rigorous manual testing and exploratory analysis. Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers enhance this approach by integrating continuous automated testing frameworks within development pipelines, enabling immediate feedback and reducing time-to-release.
Code-less Automation Frameworks
QA Engineers primarily focus on manual testing and quality assurance processes, while Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers specialize in integrating code-less automation frameworks directly into the development pipeline to accelerate testing cycles and improve continuous integration. Code-less automation frameworks enable Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers to design and execute automated test cases without extensive coding, enhancing collaboration between development and QA teams and reducing time-to-market.
TestOps Integration
QA Engineers ensure software quality through manual and automated testing, focusing on defect identification and validation processes, while Automation-in-the-Loop Engineers specialize in integrating automated test frameworks within continuous development pipelines, enhancing TestOps efficiency by enabling real-time feedback and seamless deployment. The Automation-in-the-Loop role emphasizes embedding automation deeply into TestOps workflows, optimizing test execution speed, reliability, and scalability in fast-paced DevOps environments.
QA Engineer vs Automation-in-the-Loop Engineer for Development Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com