Choosing between Frontend Developer and Micro-Frontend Engineer specialization depends on project scale and architectural preferences. Frontend Developers concentrate on building cohesive user interfaces using frameworks like React or Vue, ensuring seamless user experiences within a single application context. Micro-Frontend Engineers architect and implement modular frontend components that operate independently, enabling scalable development and deployment workflows across diverse teams and applications.
Table of Comparison
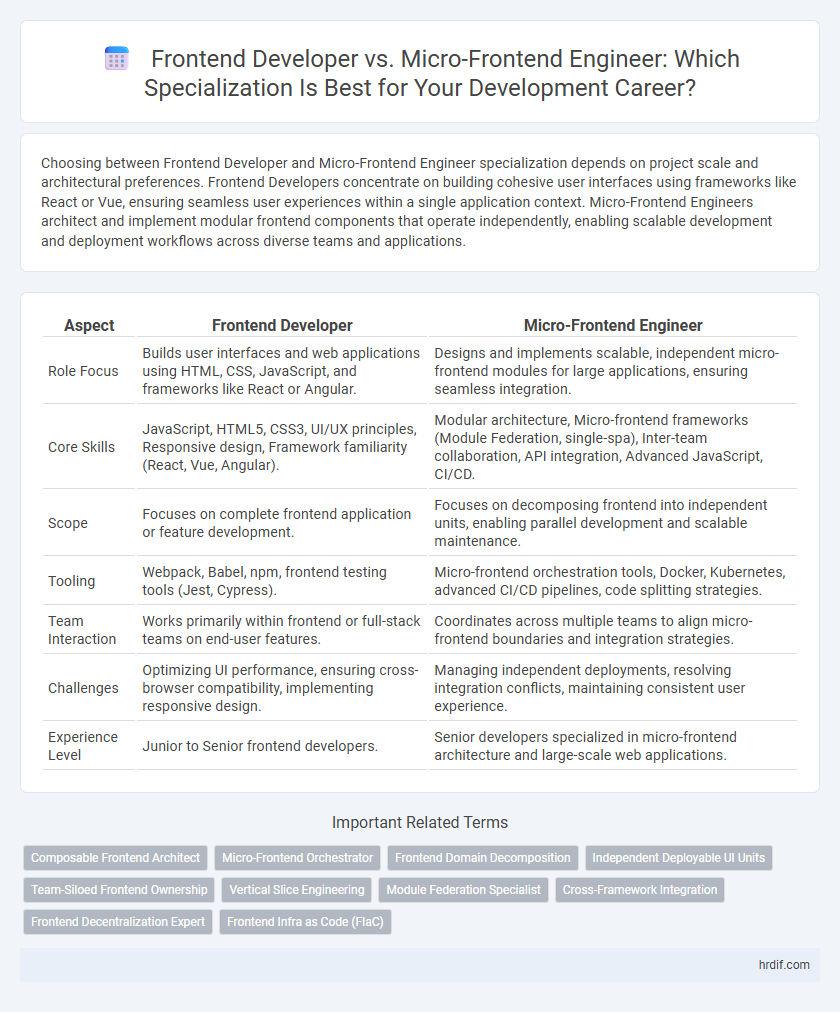
| Aspect | Frontend Developer | Micro-Frontend Engineer |
|---|---|---|
| Role Focus | Builds user interfaces and web applications using HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Angular. | Designs and implements scalable, independent micro-frontend modules for large applications, ensuring seamless integration. |
| Core Skills | JavaScript, HTML5, CSS3, UI/UX principles, Responsive design, Framework familiarity (React, Vue, Angular). | Modular architecture, Micro-frontend frameworks (Module Federation, single-spa), Inter-team collaboration, API integration, Advanced JavaScript, CI/CD. |
| Scope | Focuses on complete frontend application or feature development. | Focuses on decomposing frontend into independent units, enabling parallel development and scalable maintenance. |
| Tooling | Webpack, Babel, npm, frontend testing tools (Jest, Cypress). | Micro-frontend orchestration tools, Docker, Kubernetes, advanced CI/CD pipelines, code splitting strategies. |
| Team Interaction | Works primarily within frontend or full-stack teams on end-user features. | Coordinates across multiple teams to align micro-frontend boundaries and integration strategies. |
| Challenges | Optimizing UI performance, ensuring cross-browser compatibility, implementing responsive design. | Managing independent deployments, resolving integration conflicts, maintaining consistent user experience. |
| Experience Level | Junior to Senior frontend developers. | Senior developers specialized in micro-frontend architecture and large-scale web applications. |
Understanding Frontend Development: Core Skills and Roles
Frontend Developers specialize in building user interfaces using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, focusing on performance, accessibility, and responsive design within monolithic applications. Micro-Frontend Engineers extend this expertise by decomposing the frontend into smaller, independent modules that enable scalable, team-oriented development and seamless integration across diverse technologies. Mastery of component-based architecture, inter-team communication, and deployment strategies is essential for Micro-Frontend Engineers, distinguishing their role from traditional frontend development.
What is a Micro-Frontend Engineer? Key Concepts and Responsibilities
A Micro-Frontend Engineer specializes in breaking down web applications into smaller, independently deployable frontend components, enabling scalable and modular development. Core responsibilities include designing and integrating micro-frontend architectures, ensuring seamless communication between components, and maintaining consistent user experiences across diverse teams. This role demands expertise in frameworks like React or Angular, as well as proficiency in API orchestration, containerization, and version control to manage diverse codebases effectively.
Required Technical Skills: Frontend Developer vs Micro-Frontend Engineer
Frontend Developers must be proficient in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js, alongside skills in responsive design and UI/UX principles. Micro-Frontend Engineers require expertise in modular architecture, integration of independently deployable front-end components, advanced knowledge of microservices communication, and proficiency with tools such as Webpack Module Federation, single-spa, and containerization techniques. Both roles demand strong version control practices and familiarity with CI/CD pipelines, but Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize further in orchestration and maintaining isolation between micro-frontends for scalable, large-scale applications.
Project Scale and Complexity: When to Specialize
Frontend Developers excel in smaller to mid-sized projects where a cohesive and unified user interface is essential, allowing them to manage the entire client-side architecture efficiently. Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in large-scale, complex applications by breaking down the frontend into independent, deployable modules, facilitating parallel development and scalability. Choosing specialization depends on project scale and complexity, with Micro-Frontends offering advantages in modularity and team autonomy for enterprise-level systems.
Career Growth: Advancement Opportunities in Each Path
Frontend Developers gain career growth through mastering core JavaScript frameworks and building comprehensive UI/UX skills, enabling progression to senior roles and full-stack development. Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in decomposing complex applications into independent modules, increasing demand in large-scale, enterprise environments and opening paths to system architecture and platform engineering roles. Both paths offer advancement opportunities, with Micro-Frontend specialization providing a niche expertise that aligns with evolving scalable web application trends.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics in Frontend vs Micro-Frontend
Frontend Developers typically focus on building cohesive user interfaces within a single application, enabling tight collaboration through shared codebases and unified design systems. Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in decomposing frontend architecture into independent, self-contained modules, facilitating distributed team ownership and parallel development workflows. This modular approach enhances scalability and reduces integration conflicts, promoting agile team dynamics in large-scale projects.
Industry Demand: Job Market Trends and Salaries
Frontend developers remain in high demand due to their essential role in creating user interfaces, with average salaries ranging from $70,000 to $110,000 annually depending on experience and location. Micro-frontend engineers are gaining traction as enterprises adopt modular architectures, commanding higher salaries typically between $90,000 and $130,000 due to their specialized skills in scalable frontend solutions. Market trends show a growing preference for micro-frontend expertise in large-scale projects, reflecting a shift towards microservices in frontend development.
Toolsets and Frameworks: Essential Technologies Compared
Frontend Developers primarily utilize core technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript alongside frameworks such as React, Angular, and Vue.js to build cohesive user interfaces. Micro-Frontend Engineers, however, specialize in architectural patterns that enable independent deployment of frontend components, leveraging tools like Module Federation, single-spa, and Webpack for seamless integration and scalability. This specialization demands a deeper understanding of microservices principles and orchestration frameworks to manage distributed frontend systems effectively.
Learning Curve: Training and Resources for Specialization
Frontend Developers benefit from a vast array of training materials, comprehensive frameworks, and extensive community support, facilitating a smoother learning curve. Micro-Frontend Engineers require specialized knowledge in modular architecture, orchestration tools, and integration strategies, which demands focused training and hands-on experience. Access to targeted resources such as domain-specific tutorials, advanced workshops, and micro-frontend platforms accelerates proficiency in this niche field.
Which Role Fits You? Assessing Personal Strengths and Interests
Frontend Developers excel in creating seamless user interfaces with strong skills in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React or Angular, focusing on building cohesive single applications. Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in decomposing frontend architectures into independent, scalable components, utilizing expertise in container orchestration, module federation, and cross-team collaboration. Choose Frontend Developer if you prefer deep UI/UX craftsmanship, or Micro-Frontend Engineer if you thrive in complex system integration and distributed development environments.
Related Important Terms
Composable Frontend Architect
Frontend Developers typically focus on building monolithic user interfaces using frameworks like React or Angular, while Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in decomposing applications into independently deployable, composable frontend modules that align with a Composable Frontend Architecture. Emphasizing micro-frontends enables scalable team autonomy, improved maintainability, and seamless integration of heterogeneous technologies within complex development ecosystems.
Micro-Frontend Orchestrator
Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in breaking down complex applications into independently deployable micro-applications, leveraging orchestration layers to ensure seamless integration and consistent user experience. Frontend Developers typically manage monolithic or component-based interfaces, while Micro-Frontend Orchestrators coordinate communication, routing, and state management across diverse frontends to optimize scalability and maintainability.
Frontend Domain Decomposition
Frontend Developers specialize in building and maintaining user interfaces using frameworks like React or Angular, focusing on monolithic frontend architecture. Micro-Frontend Engineers decompose frontend applications into smaller, independently deployable modules that enable scalability and team autonomy, leveraging domain-driven design and integration techniques such as Web Components or Module Federation.
Independent Deployable UI Units
Frontend Developers typically build monolithic applications with tightly coupled UI components, whereas Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in creating independent deployable UI units enabling scalable, maintainable, and team-autonomous front-end architectures. Micro-Frontends allow separate teams to develop, test, and deploy UI components independently, enhancing development velocity and reducing integration conflicts.
Team-Siloed Frontend Ownership
Front-end developers typically manage the entire front-end stack for a single application, while micro-frontend engineers specialize in decomposing front-ends into independently deployable modules, enabling team-siloed ownership and parallel development. This specialization enhances scalability and reduces inter-team dependencies by allowing distinct teams to own, develop, and deploy specific front-end features autonomously.
Vertical Slice Engineering
Frontend Developers typically specialize in crafting cohesive user interfaces within a single application scope, emphasizing vertical slice engineering to deliver fully functional, end-to-end features. Micro-Frontend Engineers focus on decomposing large applications into independent, deployable vertical slices managed by distinct teams, optimizing scalability and maintainability across complex systems.
Module Federation Specialist
A Module Federation Specialist excels in designing scalable micro-frontend architectures that enable independent deployment and seamless integration of multiple frontend modules, enhancing application modularity and maintainability. Compared to a general Frontend Developer, this specialization demands deep expertise in Webpack's Module Federation plugin and advanced knowledge of distributed frontend systems to optimize performance and facilitate team collaboration.
Cross-Framework Integration
Frontend Developers typically specialize in building applications within a single framework, focusing on depth of knowledge in React, Angular, or Vue, while Micro-Frontend Engineers excel in Cross-Framework Integration, orchestrating multiple frontend frameworks to create modular, scalable, and independently deployable application components. Expertise in micro-frontend architecture enables seamless interoperability between diverse technologies, improving maintainability and accelerating development cycles in complex enterprise environments.
Frontend Decentralization Expert
A Frontend Decentralization Expert specializes in architecting micro-frontend systems that enable independent deployment, scalability, and maintainability of frontend components across diverse teams and projects, unlike traditional Frontend Developers who focus on monolithic application development. Expertise in technologies such as Web Components, module federation, and container orchestration is essential for driving frontend decentralization and enhancing collaborative workflows in large-scale enterprise environments.
Frontend Infra as Code (FIaC)
Frontend Developers primarily craft user interfaces using frameworks like React or Angular, focusing on component-driven design and state management, while Micro-Frontend Engineers specialize in decomposing large applications into independently deployable micro-applications. Emphasizing Frontend Infrastructure as Code (FIaC) enables Micro-Frontend Engineers to automate environment setups, streamline CI/CD pipelines, and manage deployment configurations, enhancing scalability and maintainability across distributed frontends.
Frontend Developer vs Micro-Frontend Engineer for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com