Specialization in a traditional role often involves deep expertise in a single domain, allowing professionals to master specific skills and deliver consistent results. In contrast, a portfolio career emphasizes versatility, combining multiple specializations to adapt to varying market demands and explore diverse opportunities. Both approaches offer unique advantages depending on individual goals and industry trends.
Table of Comparison
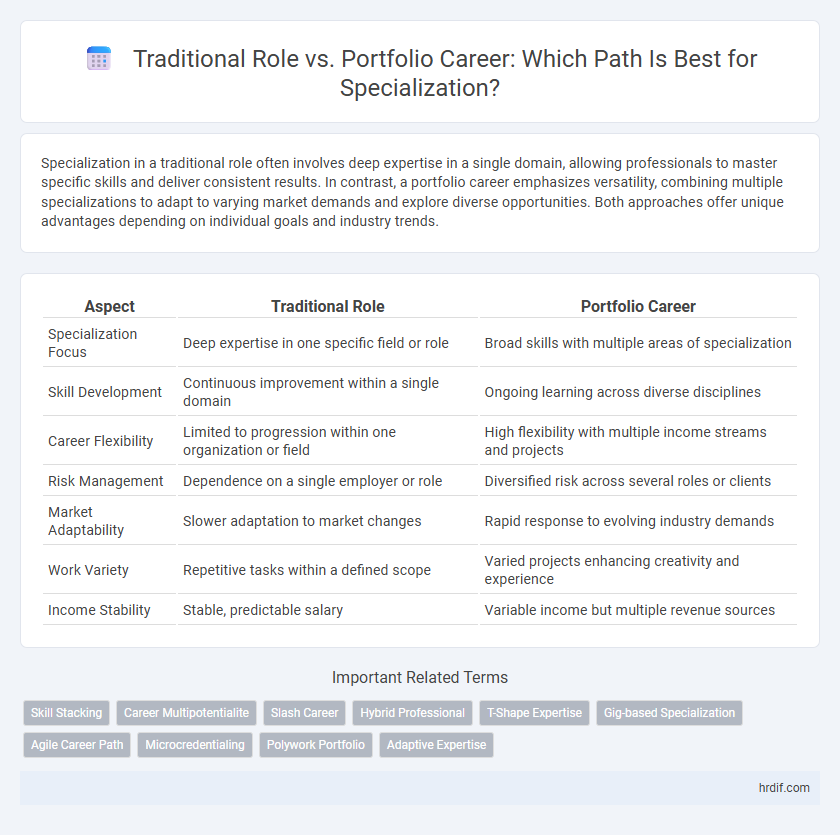
| Aspect | Traditional Role | Portfolio Career |
|---|---|---|
| Specialization Focus | Deep expertise in one specific field or role | Broad skills with multiple areas of specialization |
| Skill Development | Continuous improvement within a single domain | Ongoing learning across diverse disciplines |
| Career Flexibility | Limited to progression within one organization or field | High flexibility with multiple income streams and projects |
| Risk Management | Dependence on a single employer or role | Diversified risk across several roles or clients |
| Market Adaptability | Slower adaptation to market changes | Rapid response to evolving industry demands |
| Work Variety | Repetitive tasks within a defined scope | Varied projects enhancing creativity and experience |
| Income Stability | Stable, predictable salary | Variable income but multiple revenue sources |
Understanding Traditional Roles in Career Specialization
Traditional roles in career specialization emphasize deep expertise in a single field, promoting mastery and long-term stability within one industry or function. This approach fosters clear professional identity and predictable progression paths, often supported by formal education and structured career ladders. In contrast, portfolio careers blend diverse skills and roles, offering flexibility but potentially diluting specialized knowledge.
Defining Portfolio Careers: A New Approach to Specialization
Portfolio careers represent a new approach to specialization by combining multiple skill sets and roles across different industries, enabling professionals to adapt to evolving market demands. Unlike traditional roles that focus on deep expertise in a single domain, portfolio careers emphasize versatility, continuous learning, and diverse income streams. This model fosters innovation and resilience, making it ideal for individuals seeking dynamic career paths in today's competitive landscape.
Core Differences: Traditional vs Portfolio Career Paths
Traditional roles emphasize deep expertise within a single domain, fostering long-term specialization and stability through consistent job functions. Portfolio careers involve diverse skill sets across multiple fields, allowing professionals to adapt, innovate, and leverage varied experiences for specialization. Core differences lie in commitment duration, skill diversification, and career flexibility, where traditional paths prioritize depth and portfolio paths prioritize breadth.
Skills Development: Focused vs Diverse Specializations
Traditional roles emphasize focused specialization, allowing deep expertise in a single skill set, which drives mastery and long-term career stability. Portfolio careers promote diverse specialization, encouraging the development of multiple skills across different domains to enhance adaptability and resilience in dynamic job markets. Balancing focused skills with diverse capabilities can optimize career growth and meet evolving industry demands.
Financial Stability: Steady Job vs Multiple Income Streams
Traditional roles offer financial stability through a steady paycheck, consistent benefits, and predictable career growth, providing security in fluctuating economic conditions. Portfolio careers diversify income streams by combining multiple roles or gigs, enhancing resilience against job loss but requiring effective time and risk management. Balancing specialization with diverse opportunities can optimize financial stability while expanding skill sets.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: Comparing Career Structures
Traditional roles often provide stable work hours and predictable responsibilities, fostering consistent work-life balance but limiting flexibility. Portfolio careers offer diverse projects and varied schedules, enhancing flexibility and personal fulfillment at the potential cost of stability. Evaluating specialization through these career structures highlights a trade-off between routine security and adaptive work-life integration.
Career Growth: Advancement Opportunities in Both Models
Traditional roles often provide clear, structured career paths with defined advancement opportunities within a single organization, fostering deep specialization in a specific domain. Portfolio careers enable professionals to develop a diverse skill set across multiple projects or industries, accelerating growth through varied experiences and adaptability. Career growth in traditional roles emphasizes hierarchical progression, while portfolio careers prioritize breadth of expertise and entrepreneurial advancement.
Risk and Security: Navigating Uncertainties in Specialization
Traditional roles in risk and security emphasize deep expertise within a specific domain, providing stability and clear career progression but may limit adaptability in volatile environments. Portfolio careers offer diverse experiences across multiple sectors, enhancing agility and innovation to navigate uncertainties yet demand continuous learning and self-management. Balancing specialization with versatility fosters resilience, enabling professionals to mitigate risks and respond effectively to evolving security challenges.
Impact on Professional Identity: Deep Expert vs Versatile Professional
Traditional roles foster a deep expert identity rooted in specialized knowledge and consistent job functions, reinforcing professional credibility in a singular domain. Portfolio careers cultivate versatile professionals who integrate diverse skills and experiences, enhancing adaptability and broader market relevance. The shift from deep specialization to multifaceted expertise shapes how professionals define their value and career trajectory in dynamic industries.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider for Specialization
Choosing the right path for specialization involves evaluating personal strengths, market demand, and long-term career goals to determine whether a traditional role or a portfolio career aligns best. Traditional roles emphasize deep expertise within a specific field, offering stability and clear progression, while portfolio careers offer diverse experiences and flexibility by combining multiple skills or projects. Consider factors such as job security, income variability, industry trends, and work-life balance to make an informed decision tailored to individual professional aspirations.
Related Important Terms
Skill Stacking
Traditional roles emphasize deep specialization in a single skill or domain, fostering expertise through focused experience, while portfolio careers leverage skill stacking by combining diverse competencies across multiple fields to enhance adaptability and innovation. Skill stacking enables professionals to create unique value propositions, blending specialized knowledge with complementary skills to thrive in dynamic job markets.
Career Multipotentialite
Traditional roles emphasize deep specialization in a single field, offering stable career paths but limited flexibility, while portfolio careers enable multipotentialites to leverage diverse skills across multiple domains, fostering adaptability and continuous growth. Career multipotentialites thrive in portfolio careers by integrating varied expertise, enhancing innovation and resilience in dynamic job markets.
Slash Career
Traditional roles emphasize deep specialization within a single domain, fostering expertise and stability, while a portfolio career embraces the slash career concept, enabling professionals to combine multiple skills and roles, enhancing adaptability and diverse income streams. Slash careers redefine specialization by integrating varied talents, promoting continuous learning and flexibility in a rapidly changing job market.
Hybrid Professional
Hybrid professionals combine specialization with diverse skill sets, bridging the gap between traditional roles and portfolio careers by adapting expertise across multiple domains. This approach enhances flexibility and innovation, enabling specialists to thrive in dynamic work environments while maintaining depth in core competencies.
T-Shape Expertise
Traditional roles emphasize deep specialization in a single domain, fostering T-Shaped expertise with extensive vertical knowledge and limited horizontal skills. Portfolio careers expand this model by integrating multiple T-Shaped skill sets across diverse industries, enhancing adaptability and cross-functional innovation.
Gig-based Specialization
Gig-based specialization shifts focus from the traditional role's linear career path to a dynamic portfolio career, enabling professionals to diversify skills across multiple short-term projects. This approach maximizes adaptability and expertise in niche areas, leveraging gig platforms to build a versatile and specialized career profile.
Agile Career Path
Specializing in an Agile career path enhances adaptability and continuous learning, contrasting with the traditional role's fixed skill set that limits flexibility in evolving industries. Portfolio careers leverage diverse expertise across projects, fostering innovation and resilience in dynamic markets compared to conventional specialization focused on a single niche.
Microcredentialing
Traditional roles emphasize deep expertise in a single discipline, while portfolio careers leverage diverse microcredentials across multiple fields to showcase versatile specialization. Microcredentialing enables professionals to validate specialized skills quickly, adapting to evolving market demands beyond conventional career paths.
Polywork Portfolio
Traditional roles typically emphasize deep specialization within a single field, often limiting exposure to diverse skills, whereas a portfolio career embraces polywork by integrating multiple disciplines, fostering versatility and continuous learning. The Polywork Portfolio platform exemplifies this trend by enabling professionals to showcase varied projects and skills, highlighting multifaceted expertise beyond conventional job titles.
Adaptive Expertise
Traditional roles emphasize deep specialization within a narrow field, fostering routine expertise but limiting adaptability to new challenges. Portfolio careers promote adaptive expertise by encouraging diverse skills and cross-disciplinary knowledge, enhancing flexibility and innovation in evolving industries.
Traditional role vs Portfolio career for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com