A generalist possesses broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling adaptability to various roles, while a T-shaped professional combines deep expertise in a specific area with a broad understanding of related fields, enhancing both specialization and collaboration. Specializing as a T-shaped professional often leads to greater career growth by fostering innovation and problem-solving within a focused domain while maintaining versatility. Employers increasingly value T-shaped individuals who can bridge gaps between departments and drive cross-functional success.
Table of Comparison
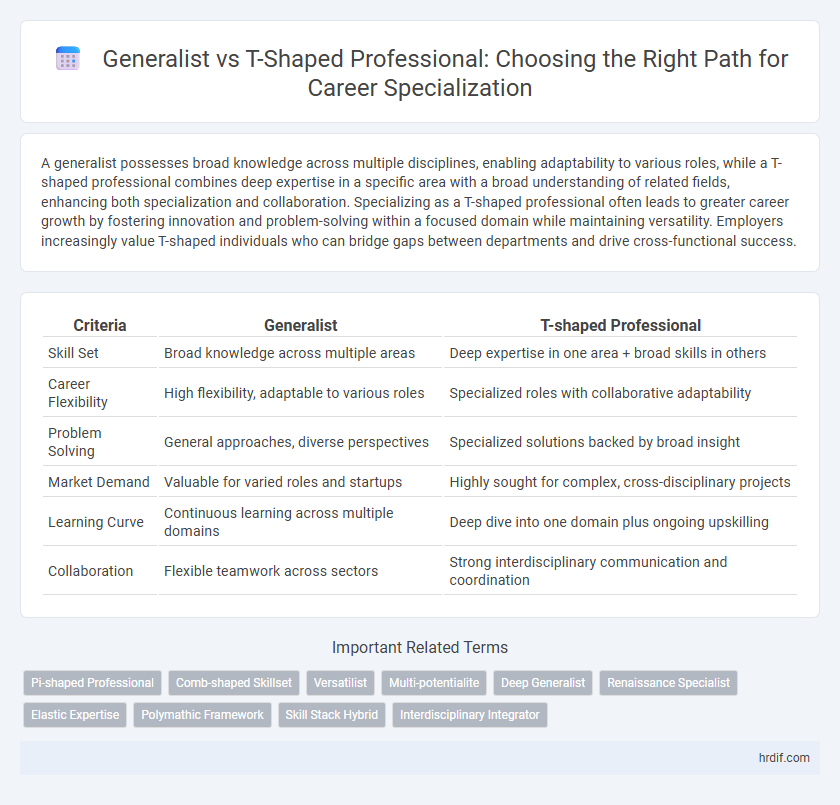
| Criteria | Generalist | T-shaped Professional |
|---|---|---|
| Skill Set | Broad knowledge across multiple areas | Deep expertise in one area + broad skills in others |
| Career Flexibility | High flexibility, adaptable to various roles | Specialized roles with collaborative adaptability |
| Problem Solving | General approaches, diverse perspectives | Specialized solutions backed by broad insight |
| Market Demand | Valuable for varied roles and startups | Highly sought for complex, cross-disciplinary projects |
| Learning Curve | Continuous learning across multiple domains | Deep dive into one domain plus ongoing upskilling |
| Collaboration | Flexible teamwork across sectors | Strong interdisciplinary communication and coordination |
Understanding Generalists and T-shaped Professionals
Understanding generalists involves recognizing professionals with broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling flexibility and adaptability in various roles. T-shaped professionals combine this broad expertise with deep specialization in one area, offering both versatility and in-depth skill sets. Employers value T-shaped professionals for their unique ability to collaborate across functions while delivering expert solutions within their specialty.
The Core Differences Between Generalists and T-shaped Specialists
Generalists possess broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling adaptability and a wide perspective in problem-solving, while T-shaped professionals combine deep expertise in a specific area with a broad understanding of related fields, promoting both specialization and collaboration. The core difference lies in the depth versus breadth of skills: generalists excel at connecting diverse concepts, whereas T-shaped specialists provide expert knowledge while maintaining cross-disciplinary communication. This blend makes T-shaped professionals highly valuable in complex projects requiring both specialized insight and integrative thinking.
Advantages of Being a Generalist in Today’s Job Market
Generalists possess a broad skill set that enables adaptability across diverse roles and industries, increasing their employability in a rapidly changing job market. Their ability to connect interdisciplinary knowledge fosters innovative problem-solving and effective collaboration on multifaceted projects. Companies value generalists for their flexibility and capacity to bridge gaps between specialized teams, making them integral to dynamic and evolving workplace environments.
Strengths of T-shaped Professionals for Career Growth
T-shaped professionals combine deep expertise in a specific field with a broad skill set across multiple disciplines, enhancing their adaptability and collaboration capabilities. This unique blend allows them to solve complex problems effectively while bridging gaps between specialized teams, driving innovation and leadership opportunities. Their versatility makes them highly valuable in dynamic work environments, accelerating career growth and long-term success.
Job Opportunities: Who Do Employers Prefer?
Employers increasingly prefer T-shaped professionals for career specialization due to their deep expertise in a core area combined with broad cross-disciplinary skills, enabling flexibility and innovation across roles. Generalists may excel in adaptability and project management but often lack the specialized knowledge that drives competitive advantage in complex industries. Data from LinkedIn and industry surveys highlight higher demand and salary premiums for T-shaped candidates, reflecting the prioritization of specialized technical proficiency integrated with collaborative capabilities.
Skill Development Strategies: Broad vs. Deep Focus
Generalists cultivate a broad skill set across multiple domains, enabling adaptability and cross-functional collaboration, while T-shaped professionals combine wide-ranging knowledge with deep expertise in a specific area, enhancing their value in specialized roles. Skill development strategies for generalists emphasize continuous learning across diverse fields, whereas T-shaped professionals prioritize mastering a core discipline alongside maintaining foundational skills in other areas. Balancing breadth and depth in skill acquisition supports career specialization by aligning expertise with evolving industry demands and job market trends.
Career Flexibility and Adaptability Compared
Generalists possess broad knowledge across multiple domains, enabling high career flexibility by easily transitioning between roles and industries. In contrast, T-shaped professionals combine deep expertise in one area with a broad understanding of adjacent fields, enhancing adaptability through specialized skills alongside versatile capabilities. This hybrid skill set allows T-shaped professionals to navigate complex challenges while maintaining the ability to collaborate across disciplines.
Industry Trends Driving the Demand for Each Type
The increasing complexity of technology and cross-functional projects drives demand for T-shaped professionals with deep expertise in one area and broad skills across disciplines, enabling innovation and agile problem-solving. Conversely, industries experiencing rapid change and requiring adaptable roles prioritize generalists who can quickly learn and integrate knowledge across diverse functions. Market trends in sectors like tech and consulting highlight a hybrid workforce where specialized T-shaped professionals lead innovation while generalists support flexible, dynamic team structures.
Challenges and Limitations: Generalists vs. T-shaped Professionals
Generalists face challenges in depth of expertise, limiting their ability to solve complex problems in specialized fields, while T-shaped professionals may struggle with breadth when required to handle diverse tasks outside their vertical expertise. Generalists often encounter difficulties in gaining recognition for specialized roles due to shallow skillsets, whereas T-shaped professionals can experience cognitive overload balancing deep knowledge with cross-disciplinary demands. Both career paths exhibit limitations in adaptability and mastery, impacting long-term career growth and specialization effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Professional Specialization
Choosing between a generalist and a T-shaped professional depends on career goals and industry demands, with generalists offering broad skills across multiple domains while T-shaped professionals combine deep expertise in one area with a wider understanding of others. Employers often prefer T-shaped professionals for their ability to integrate specialized knowledge with collaborative skills, enhancing innovation and adaptability in complex projects. Evaluating market trends, personal strengths, and long-term aspirations is essential to determine which path--broad versatility or focused depth--aligns best with professional specialization and growth.
Related Important Terms
Pi-shaped Professional
Pi-shaped professionals combine deep expertise in two distinct fields with broad skills across multiple domains, enhancing adaptability and collaboration in complex projects. Their dual specialization enables them to bridge gaps between teams, driving innovation and versatility beyond traditional generalist or T-shaped roles.
Comb-shaped Skillset
A comb-shaped skillset combines deep expertise in multiple related areas with broad knowledge across various fields, enhancing adaptability and collaboration in complex projects. This specialization approach balances the depth of a specialist with the versatility of a generalist, making it ideal for dynamic career paths.
Versatilist
A Versatilist combines deep expertise with broad skills across multiple domains, enabling adaptability and innovation in dynamic career landscapes. This specialization balances the focused knowledge of T-shaped professionals with the flexibility of generalists, driving cross-functional collaboration and problem-solving.
Multi-potentialite
Multi-potentialites leverage diverse skills across domains, offering a broad knowledge base contrasted with the depth of a T-shaped professional who combines deep expertise in one area with generalist capabilities. Embracing specialization through a T-shaped model enhances career adaptability while maintaining breadth, whereas generalists excel in versatility but may lack focused mastery critical for certain niche roles.
Deep Generalist
Deep generalists combine broad knowledge across multiple domains with specialized expertise in key areas, enabling innovative problem-solving and adaptability in complex career landscapes. Unlike T-shaped professionals, deep generalists emphasize versatile skill sets and interconnected understanding rather than focusing primarily on a single deep specialization complemented by broad skills.
Renaissance Specialist
A Renaissance Specialist combines deep expertise across multiple disciplines with broad general knowledge, embodying the T-shaped professional's balanced skill set while surpassing traditional generalist limitations. This specialization fosters innovation and adaptability, making them highly valuable in dynamic career landscapes demanding both depth and versatility.
Elastic Expertise
Elastic expertise combines the broad knowledge of a generalist with deep skills in specific areas, enabling professionals to adapt and innovate across disciplines while maintaining specialized competence. This approach enhances career specialization by balancing versatility and focused expertise, making T-shaped professionals highly valuable in dynamic industries.
Polymathic Framework
The Polymathic Framework emphasizes the value of T-shaped professionals who combine deep expertise in a specific domain with broad, interdisciplinary skills, enabling adaptability and innovative problem-solving. This approach contrasts with the generalist model, promoting specialized knowledge augmented by a wide-ranging skill set to accelerate career growth and effectiveness in complex environments.
Skill Stack Hybrid
A Skill Stack Hybrid combines the breadth of a Generalist's diverse expertise with the depth of a T-shaped professional's specialized skills, creating a versatile and competitive career profile. This blend enhances adaptability across multiple domains while fostering deep proficiency in key areas, driving innovation and problem-solving capabilities in complex work environments.
Interdisciplinary Integrator
An interdisciplinary integrator excels by combining deep expertise in a specific field with broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, embodying the T-shaped professional model that enhances innovation and problem-solving. This specialization approach contrasts with a generalist's wide but shallow skill set, positioning the integrator as a crucial asset for complex, cross-functional projects requiring versatile insights.
Generalist vs T-shaped Professional for career specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com