Niche skills provide deep expertise in a specific area, allowing professionals to become highly specialized and sought-after within their field. Hybrid skills combine knowledge from multiple domains, offering versatility and the ability to adapt to diverse challenges. Balancing niche and hybrid skills in a specialization pet strategy enhances both expert credibility and cross-functional problem-solving capabilities.
Table of Comparison
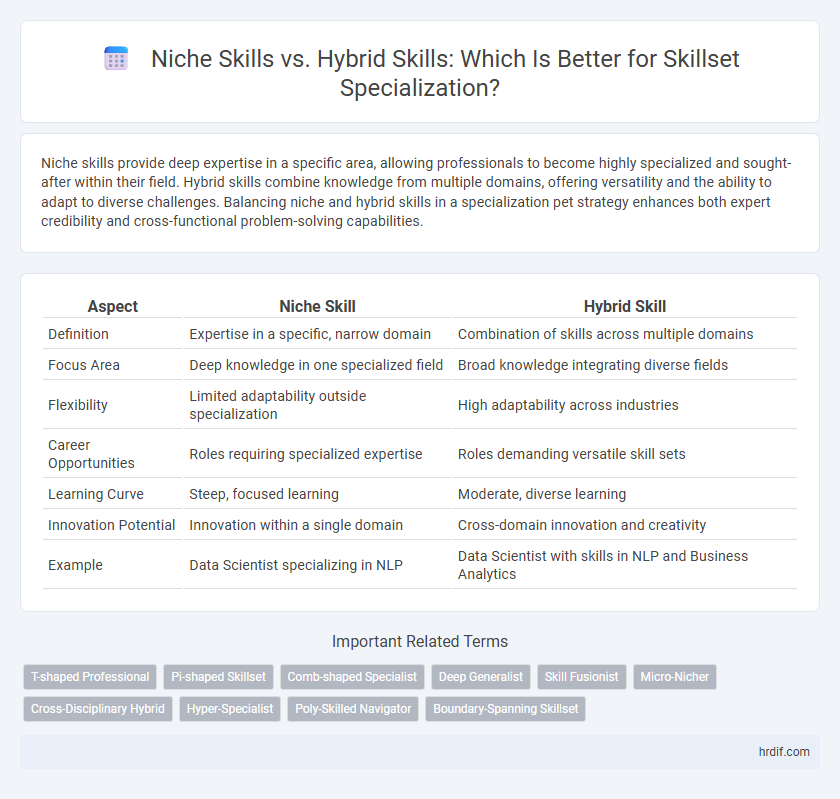
| Aspect | Niche Skill | Hybrid Skill |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expertise in a specific, narrow domain | Combination of skills across multiple domains |
| Focus Area | Deep knowledge in one specialized field | Broad knowledge integrating diverse fields |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability outside specialization | High adaptability across industries |
| Career Opportunities | Roles requiring specialized expertise | Roles demanding versatile skill sets |
| Learning Curve | Steep, focused learning | Moderate, diverse learning |
| Innovation Potential | Innovation within a single domain | Cross-domain innovation and creativity |
| Example | Data Scientist specializing in NLP | Data Scientist with skills in NLP and Business Analytics |
Defining Niche Skills and Hybrid Skills
Niche skills refer to highly specialized abilities tailored to specific industries or tasks, such as blockchain development or forensic accounting, which provide deep expertise in a narrowly defined area. Hybrid skills combine expertise from multiple disciplines, such as data analysis paired with marketing strategy, enabling professionals to address complex challenges with a versatile approach. Defining these skill types helps organizations and individuals align talent development strategies with evolving market demands and innovation priorities.
The Rise of Specialization in the Modern Workforce
The rise of specialization in the modern workforce has intensified the debate between niche skills and hybrid skills as paths to career advancement. Niche skills offer deep expertise in a specific domain, driving innovation and problem-solving in specialized fields like artificial intelligence or cybersecurity. Hybrid skills combine complementary abilities across disciplines, such as data analysis with communication, enabling adaptability and cross-functional collaboration in dynamic business environments.
Advantages of Niche Skill Specialization
Niche skill specialization offers unparalleled depth in a specific domain, enabling professionals to become experts and command higher value in targeted markets. Mastery of specialized knowledge enhances problem-solving capabilities and fosters innovation within the niche, often leading to unique career opportunities. Companies seeking expert insights often prefer niche specialists for critical roles, driving demand and career stability in specialized fields.
Strengths of Hybrid Skillsets in Today’s Job Market
Hybrid skillsets combine expertise from multiple disciplines, enabling professionals to adapt quickly and solve complex problems in dynamic work environments. In today's job market, employers value hybrid skillsets for their versatility, innovation potential, and ability to bridge gaps between specialized teams. This adaptability enhances career resilience and opens diverse opportunities across industries like technology, healthcare, and finance.
Industry Demand: Niche vs. Hybrid Skills
Niche skills cater to specific industry demands, offering deep expertise in specialized areas such as cybersecurity or data analytics that companies urgently require for targeted roles. Hybrid skills combine knowledge from multiple disciplines, like marketing and data science, meeting the rising demand for versatile professionals who can bridge gaps between departments. Industry trends show a growing preference for hybrid skills in dynamic markets, while niche skills remain crucial for highly technical or specialized positions.
Career Growth Opportunities for Specialists
Specializing in a niche skill often opens doors to highly targeted career growth opportunities within specific industries, allowing professionals to become indispensable experts. Hybrid skills, combining multiple domains, broaden adaptability and enhance leadership potential, making specialists valuable in dynamic, cross-functional roles. Career progression for specialists depends on aligning skill development with market demand and the evolving needs of their chosen sectors.
Versatility and Flexibility with Hybrid Skills
Hybrid skills combine expertise from multiple domains, enhancing versatility and flexibility in dynamic work environments by enabling professionals to adapt quickly to changing tasks. Unlike niche skills that focus deeply on a single area, hybrid skills foster cross-functional knowledge, improving problem-solving and innovation across diverse projects. Employers increasingly value hybrid skillsets for their ability to bridge gaps between disciplines and drive collaborative success.
Risks and Challenges of Over-Specialization
Over-specialization in niche skills can lead to a limited adaptability in rapidly changing job markets, increasing vulnerability to industry disruptions and technological advancements. Hybrid skills offer a wider range of competencies but risk superficial knowledge in multiple areas rather than deep expertise. Balancing specialization with versatility is critical to mitigating risks such as skill obsolescence and reduced career mobility.
Building a Future-Proof Skillset: Which Path to Choose?
Niche skills offer deep expertise in a specific field, making professionals indispensable for specialized roles and emerging technologies. Hybrid skills combine knowledge from multiple disciplines, fostering adaptability and innovation in dynamic job markets. Building a future-proof skillset involves balancing niche mastery with hybrid versatility to maximize career resilience and growth potential.
Strategies for Balancing Niche and Hybrid Skill Development
Balancing niche and hybrid skill development requires a strategic approach that aligns specialization with adaptability. Prioritizing deep expertise in a niche skill can build authority, while integrating complementary hybrid skills enhances versatility across interdisciplinary roles. Effective strategies include continuous learning frameworks, targeted cross-training, and leveraging industry trends to maintain relevance in both focused and broad skill domains.
Related Important Terms
T-shaped Professional
Niche skills offer deep expertise in a specific area, making professionals highly valuable for specialized roles, while hybrid skills combine knowledge from multiple domains, enhancing versatility and adaptability. A T-shaped professional balances both by mastering a core niche skill vertically and possessing broad hybrid skills horizontally, enabling effective collaboration and innovative problem-solving across disciplines.
Pi-shaped Skillset
A Pi-shaped skillset combines deep expertise in two niche skills with broad interdisciplinary knowledge, enabling professionals to innovate at the intersection of specialized domains. This hybrid specialization enhances adaptability and problem-solving agility compared to a single niche skill, positioning individuals uniquely in dynamic job markets.
Comb-shaped Specialist
A comb-shaped specialist combines deep expertise in a niche skill with broad hybrid skills across related domains, optimizing versatility and targeted proficiency. This skillset specialization enhances adaptability and innovation in complex roles by integrating focused knowledge with complementary abilities.
Deep Generalist
A deep generalist combines niche skills with broad hybrid skills, enabling versatility in specialized fields while maintaining deep expertise. This blend enhances problem-solving by integrating focused knowledge with cross-disciplinary insights, driving innovation and adaptability in complex roles.
Skill Fusionist
Skill Fusionists excel by integrating niche skills and hybrid skills, creating unique, specialized competencies unmatched in traditional fields. This blend allows them to innovate and adapt, providing versatile solutions across complex, interdisciplinary challenges.
Micro-Nicher
Micro-nicher specialization leverages niche skills by focusing deeply on a highly specific area, enabling unparalleled expertise and command over unique market segments. Hybrid skills complement this approach by integrating broader abilities that enhance adaptability, yet micro-nichers prioritize precise, specialized knowledge to dominate micro-markets effectively.
Cross-Disciplinary Hybrid
Cross-disciplinary hybrid skills combine expertise from multiple domains, enabling professionals to innovate and solve complex problems beyond the scope of niche skills. This approach enhances adaptability and broadens career opportunities by integrating diverse knowledge areas into a unified skillset.
Hyper-Specialist
Hyper-specialists excel by mastering niche skills that offer deep expertise in a narrowly defined field, driving innovation and competitive advantage in specialized markets. Compared to hybrid skills, which combine generalist abilities across domains, hyper-specialist niche skills deliver unmatched precision and authority, crucial for roles demanding advanced technical knowledge or expert-level problem-solving.
Poly-Skilled Navigator
Poly-skilled navigators blend niche skills with hybrid expertise, enabling adaptability and focused problem-solving across multiple disciplines. This specialization enhances versatility by combining deep knowledge in specific areas with broad competencies to effectively manage complex, cross-functional challenges.
Boundary-Spanning Skillset
Boundary-spanning skillsets blend niche expertise with hybrid capabilities, enabling professionals to navigate diverse domains and integrate knowledge across specialized fields. This unique combination fosters innovation, enhances problem-solving, and drives value creation by bridging gaps between distinct industry sectors or disciplines.
Niche Skill vs Hybrid Skill for skillset specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com