Specialists develop deep expertise in a narrow field, allowing them to solve complex problems with precision and efficiency. Polymaths, with their broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, excel at connecting ideas and innovating at interdisciplinary intersections. Choosing between specialist and polymath depends on whether depth or breadth of knowledge better suits your goals and the demands of your specialization.
Table of Comparison
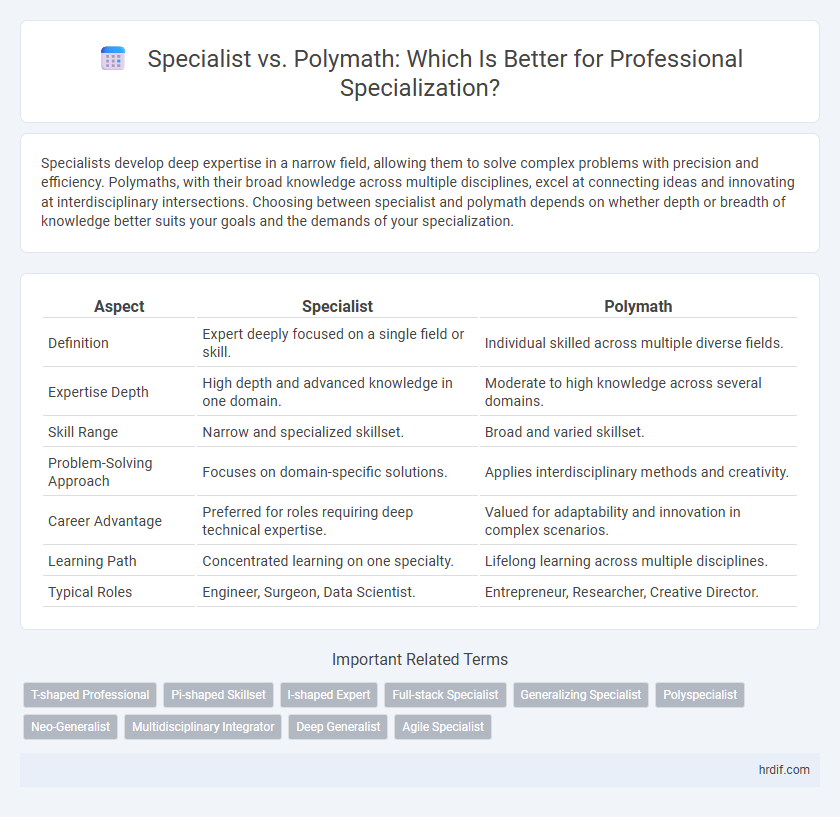
| Aspect | Specialist | Polymath |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expert deeply focused on a single field or skill. | Individual skilled across multiple diverse fields. |
| Expertise Depth | High depth and advanced knowledge in one domain. | Moderate to high knowledge across several domains. |
| Skill Range | Narrow and specialized skillset. | Broad and varied skillset. |
| Problem-Solving Approach | Focuses on domain-specific solutions. | Applies interdisciplinary methods and creativity. |
| Career Advantage | Preferred for roles requiring deep technical expertise. | Valued for adaptability and innovation in complex scenarios. |
| Learning Path | Concentrated learning on one specialty. | Lifelong learning across multiple disciplines. |
| Typical Roles | Engineer, Surgeon, Data Scientist. | Entrepreneur, Researcher, Creative Director. |
Introduction: The Specialist vs Polymath Debate
The debate between specialists and polymaths centers on depth versus breadth of knowledge, where specialists develop expertise in a single domain while polymaths acquire skills across multiple disciplines. Specialists often drive innovation through focused mastery and deep problem-solving abilities, whereas polymaths foster creativity by integrating diverse perspectives and cross-disciplinary insights. Understanding this contrast is essential for organizations aiming to balance expert precision with adaptive versatility in a rapidly evolving knowledge economy.
Defining Specialist and Polymath in Career Contexts
A specialist in career contexts possesses deep expertise and skills concentrated in a specific field, enabling mastery and high efficiency in niche roles. A polymath integrates knowledge across multiple domains, leveraging diverse skills to innovate and adapt broadly in complex work environments. Both approaches shape career trajectories, with specialists excelling in focused problem-solving and polymaths thriving in interdisciplinary challenges.
Core Advantages of Specialization
Specialization enhances expertise by allowing individuals to develop deep knowledge and skills in a specific field, resulting in higher efficiency and superior problem-solving capabilities. Specialists benefit from targeted experience, which often leads to increased innovation and professional recognition within their niche. This focused mastery enables quicker adaptation to complex challenges and contributes to advancing industry standards.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Being a Polymath
Being a polymath offers the benefit of interdisciplinary knowledge, enabling innovative problem-solving by connecting diverse fields such as science, art, and technology. However, the drawback lies in the potential lack of deep expertise compared to specialists, which may limit opportunities in highly specialized industries that demand focused skills. Polymaths often excel in adaptability and creativity but might face challenges in achieving mastery or recognition within niche domains.
Industry Demand: Specialists vs. Polymaths
Industry demand favors specialists for roles requiring deep expertise in areas such as cybersecurity, data science, and artificial intelligence, where precise skills and certifications are critical. Polymaths, however, are increasingly valued in innovation-driven sectors like technology startups and product development for their ability to integrate diverse knowledge areas and solve complex, interdisciplinary problems. Hiring trends indicate companies prioritize specialists for technical roles and polymaths for strategic, creative, and leadership positions that benefit from broad, adaptable expertise.
Skills Development: Deep Focus vs. Broad Knowledge
Specialists develop deep expertise in a specific skill set, enabling high proficiency and mastery in targeted areas. Polymaths cultivate a broad knowledge base across multiple domains, fostering adaptability and innovative problem-solving. Balancing deep focus with diverse skills enhances both precision and creativity in professional growth.
Career Growth Trajectories for Specialists and Polymaths
Specialists often experience rapid career growth within niche fields due to deep expertise and targeted skills, making them invaluable for highly technical or industry-specific roles. Polymaths possess diverse knowledge across multiple domains, enabling flexible career trajectories and adaptability to interdisciplinary opportunities, which can lead to leadership positions that require broad problem-solving abilities. Organizations valuing innovation and versatility may favor polymaths, while sectors demanding precision and depth typically prioritize specialists for advancement.
Adaptability in a Changing Job Market
Specialists offer deep expertise in a specific field, making them highly valuable for roles requiring advanced technical skills or niche knowledge. Polymaths excel at adaptability, applying diverse skills across multiple domains to navigate the rapidly evolving job market effectively. Emphasizing flexibility and continuous learning empowers both specialists and polymaths to thrive amid industry disruptions and technological advancements.
How to Choose: Factors Influencing Specialization Paths
Choosing between a specialist and a polymath career path depends on factors like industry demands, personal learning styles, and long-term goals. Specialists thrive in fields requiring deep expertise, such as medicine or engineering, while polymaths excel in dynamic environments valuing cross-disciplinary innovation. Evaluating market trends, skill adaptability, and passion for focused or broad knowledge helps optimize specialization decisions.
Conclusion: Navigating Your Path Between Specialist and Polymath
Choosing between becoming a specialist or a polymath depends on your career goals and industry demands. Specialists provide deep expertise crucial for roles requiring advanced skills, while polymaths offer versatility and innovation by integrating knowledge across fields. Balancing depth with breadth allows you to adapt and excel in an evolving job market.
Related Important Terms
T-shaped Professional
A T-shaped professional combines deep expertise in a single domain with broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, bridging the gap between specialists and polymaths. This hybrid skill set enhances collaboration and innovation by applying specialized insights while adapting to diverse challenges.
Pi-shaped Skillset
The Pi-shaped skillset combines deep expertise in two core areas with broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, balancing the focused depth of a specialist with the versatility of a polymath. This approach enables professionals to innovate by bridging specialized domains while maintaining adaptability in rapidly evolving industries.
I-shaped Expert
An I-shaped expert embodies deep specialization in a single domain, providing highly focused expertise essential for solving complex, niche problems. Unlike polymaths who possess broad, multidisciplinary knowledge, specialists contribute intense, in-depth skills that drive innovation and mastery within their specific field.
Full-stack Specialist
A Full-stack Specialist combines deep expertise across front-end and back-end technologies, enabling seamless development of comprehensive applications with optimized performance and scalability. This focused specialization often leads to higher proficiency and efficiency compared to polymaths who spread their skills across multiple unrelated domains.
Generalizing Specialist
Generalizing specialists combine deep expertise in a specific field with broad knowledge across multiple disciplines, enabling them to adapt and innovate more effectively than traditional specialists or polymaths. This unique blend accelerates problem-solving by integrating specialized skills with a wide-ranging perspective.
Polyspecialist
A polyspecialist combines deep expertise across multiple disciplines, enabling innovative problem-solving and adaptive thinking beyond the narrow focus of a specialist. This diverse knowledge spectrum fosters cross-disciplinary insights that drive creativity and strategic flexibility in complex environments.
Neo-Generalist
Neo-generalists combine deep specialization with broad interdisciplinary knowledge, enabling them to adapt and innovate across multiple fields. Unlike traditional specialists who focus narrowly, neo-generalists leverage polymathic skills to solve complex problems by integrating diverse expertise efficiently.
Multidisciplinary Integrator
A multidisciplinary integrator combines expertise across multiple fields, leveraging diverse knowledge to create innovative solutions beyond the scope of a single specialization. This approach enhances problem-solving capabilities by synthesizing specialist insights with broad, interdisciplinary understanding.
Deep Generalist
A deep generalist combines the broad knowledge of a polymath with the focused expertise of a specialist, enabling innovation across multiple domains by applying specialized skills in diverse contexts. This specialization approach fosters adaptability and creative problem-solving, bridging the gap between narrow focus and wide-ranging competence.
Agile Specialist
An Agile Specialist leverages deep expertise in Agile methodologies to optimize team collaboration and project delivery, contrasting with polymaths who apply broad, cross-disciplinary knowledge but may lack focused mastery in Agile practices. Specialization in Agile frameworks enhances adaptability and efficiency within iterative workflows, driving sustained organizational agility.
Specialist vs Polymath for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com