Traditional Specialists hone deep expertise in a single pet care niche, building a strong reputation through consistent, focused practice. Portfolio Careerists diversify their skills across multiple pet-related disciplines, adapting to changing market demands and offering a broader range of services. Each approach influences career stability, client trust, and the scope of professional opportunities in the pet specialization field.
Table of Comparison
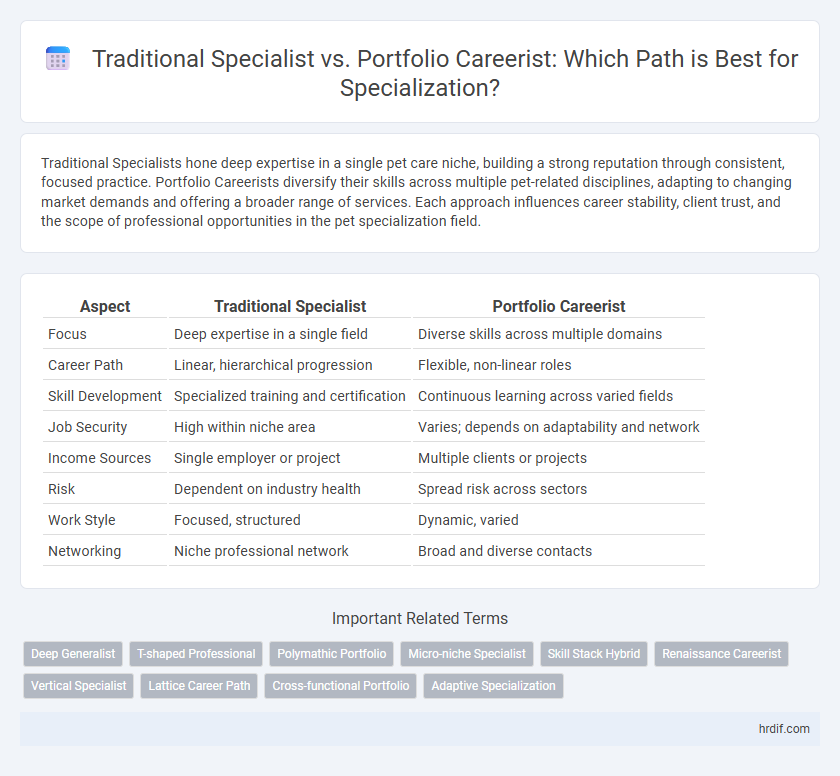
| Aspect | Traditional Specialist | Portfolio Careerist |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Deep expertise in a single field | Diverse skills across multiple domains |
| Career Path | Linear, hierarchical progression | Flexible, non-linear roles |
| Skill Development | Specialized training and certification | Continuous learning across varied fields |
| Job Security | High within niche area | Varies; depends on adaptability and network |
| Income Sources | Single employer or project | Multiple clients or projects |
| Risk | Dependent on industry health | Spread risk across sectors |
| Work Style | Focused, structured | Dynamic, varied |
| Networking | Niche professional network | Broad and diverse contacts |
Defining Traditional Specialists and Portfolio Careerists
Traditional specialists concentrate deeply on a singular field, developing expert-level skills and knowledge that make them indispensable within their niche. Portfolio careerists diversify their professional activities across various industries and roles, leveraging a broad skill set to adapt to changing market demands. The specialization of traditional specialists contrasts with the multifaceted approach of portfolio careerists, shaping distinct career trajectories and professional identities.
Core Skills: Depth vs Breadth
Traditional specialists develop core skills with deep expertise in a specific field, enabling mastery and high-value problem-solving within a narrow domain. Portfolio careerists cultivate a breadth of core skills across multiple disciplines, enhancing adaptability and innovation by connecting diverse knowledge areas. Depth in specialization supports technical excellence, while breadth fosters versatility in a rapidly evolving job market.
Career Progression Pathways
Traditional specialists follow a linear career progression pathway, advancing through hierarchical roles within a specific expertise, which often leads to deep domain knowledge and stable job positions. Portfolio careerists leverage diverse skills across multiple disciplines, creating dynamic career pathways that emphasize adaptability, continuous learning, and broad professional networks. This multifaceted approach enables portfolio careerists to pivot between industries and roles, fostering resilience in evolving job markets.
Job Security and Market Demand
Traditional specialists often benefit from higher job security due to deep expertise in a specific field, which aligns with stable market demand in industries valuing specialized skills. Portfolio careerists diversify their skill sets across multiple disciplines, increasing adaptability to fluctuating market demands but potentially facing less consistent job security. Employers increasingly seek portfolio careerists for roles requiring cross-functional capabilities, reflecting a shift toward valuing versatility alongside specialization.
Flexibility in Work Environments
Traditional specialists excel in deeply focused roles within established industries, leveraging extensive expertise to drive innovation and efficiency. Portfolio careerists prioritize flexibility in work environments by managing diverse roles across multiple fields, adapting quickly to shifting market demands and project-based opportunities. This adaptive approach allows portfolio careerists to balance variety and specialization, enhancing resilience in dynamic professional landscapes.
Personal Branding Strategies
Traditional specialists build personal branding strategies by emphasizing deep expertise and long-term reputation within a specific niche, leveraging authoritative content and industry recognition to establish credibility. Portfolio careerists develop diverse personal branding by showcasing multifaceted skills and cross-domain accomplishments, utilizing dynamic storytelling and adaptive platforms to highlight versatility and continuous learning. Both approaches require tailored communication methods to effectively position personal brands in competitive markets.
Income Stability vs Potential
Traditional specialists often experience greater income stability due to their focused expertise in a single field, ensuring consistent demand and predictable earnings. Portfolio careerists diversify their skill sets across multiple industries, potentially increasing overall income but facing fluctuations and less financial predictability. Income stability often favors traditional specialists, while portfolio careerists benefit from higher earning potential with associated risks.
Networking and Professional Relationships
Traditional specialists cultivate deep expertise within a narrow field, leveraging long-term professional relationships and established industry networks to advance their careers. Portfolio careerists build diverse connections across multiple sectors, utilizing a broad, adaptive network to access varied opportunities and cross-disciplinary collaborations. Both approaches require strategic networking to enhance reputation and unlock career growth, but the portfolio careerist's expansive relationships foster versatility in a dynamic job market.
Impact on Work-Life Balance
Traditional specialists often experience a structured work-life balance due to their focused expertise and clear career path within a single domain. Portfolio careerists, juggling multiple roles and industries, face challenges in maintaining boundaries but benefit from greater flexibility and diversified skill application. The impact on work-life balance varies significantly, with specialists enjoying predictability while portfolio careerists maximize autonomy and adaptability.
Future Trends in Career Specialization
Traditional specialists deepen expertise within a single field, ensuring high-level proficiency and stability in established roles, while portfolio careerists adapt by cultivating diverse skills across multiple domains, enhancing flexibility in dynamic job markets. Emerging trends highlight increased demand for hybrid professionals who combine deep specialization with cross-functional capabilities to navigate technological advancements and global economic shifts. Future career specialization increasingly values adaptability and continuous learning, favoring those who can integrate specialized knowledge with broad competencies to meet evolving industry needs.
Related Important Terms
Deep Generalist
Traditional specialists develop expertise in a narrowly defined field, often leading to deep but isolated knowledge, while portfolio careerists embrace a deep generalist approach by acquiring broad skills across multiple domains, enhancing adaptability and innovation. Emphasizing interdisciplinary experience, deep generalists bridge specialization gaps, increasing their value in dynamic job markets.
T-shaped Professional
Traditional specialists excel in deep, narrow expertise within a specific domain, often becoming indispensable for highly specialized roles, while portfolio careerists embody the T-shaped professional model by combining broad cross-disciplinary skills with deep knowledge in key areas to adapt in dynamic job markets. Emphasizing T-shaped skills enhances versatility and innovation, making professionals more resilient and valuable across multiple industries.
Polymathic Portfolio
Traditional specialists concentrate deeply on a single domain, developing expert-level skills and knowledge that ensure high demand within niche markets. Polymathic portfolio careerists cultivate diverse competencies across multiple fields, enabling flexibility and innovation by integrating varied expertise to adapt to evolving job landscapes.
Micro-niche Specialist
Micro-niche specialists excel by deeply mastering a highly specific segment within their field, contrasting traditional specialists who maintain a broader, singular focus. Portfolio careerists leverage diverse skills across multiple micro-niches, creating versatile expertise that adapts to evolving market demands.
Skill Stack Hybrid
Traditional specialists develop deep expertise in a single domain, relying on narrowly focused skill sets that enhance proficiency and reputation within specific industries. Portfolio careerists leverage a Skill Stack Hybrid approach, combining diverse competencies across multiple fields to create versatile expertise that adapts to dynamic job markets and evolving professional demands.
Renaissance Careerist
A Renaissance Careerist blends deep expertise across multiple disciplines, challenging the traditional specialist's narrow focus by cultivating a versatile portfolio of skills that adapt to evolving market demands. This approach leverages cross-functional knowledge and diverse experiences to drive innovation and resilience in dynamic career landscapes.
Vertical Specialist
Vertical specialists deepen expertise within a narrowly defined field, becoming indispensable for complex, industry-specific challenges that require deep knowledge, such as cybersecurity or neurosurgery. Portfolio careerists, while versatile, may lack the concentrated depth of a vertical specialist, making the latter essential for roles demanding high specialization and advanced technical proficiency.
Lattice Career Path
Traditional specialists deepen expertise within a single domain, often following a linear career progression, while portfolio careerists develop diverse skills across multiple fields, aligning with the lattice career path that emphasizes lateral moves and skill adaptability. The lattice career path facilitates specialization through varied experiences and continuous learning, enabling professionals to build a versatile portfolio aligned with evolving market demands.
Cross-functional Portfolio
Traditional specialists focus intensely on deep expertise within a single domain, often limiting their adaptability across multiple fields; portfolio careerists embrace a cross-functional portfolio by combining diverse skills and experiences from various disciplines, enabling greater flexibility and innovation in complex, interdisciplinary environments. This cross-functional approach in portfolio careers fosters specialization through breadth and integration rather than narrow depth, aligning with evolving market demands for versatile, multi-skilled professionals.
Adaptive Specialization
Adaptive specialization enables portfolio careerists to diversify skills across multiple domains, enhancing flexibility and resilience in dynamic job markets. Traditional specialists focus deeply on one niche, but adaptive specialization blends depth and breadth, optimizing career sustainability and growth opportunities.
Traditional Specialist vs Portfolio Careerist for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com