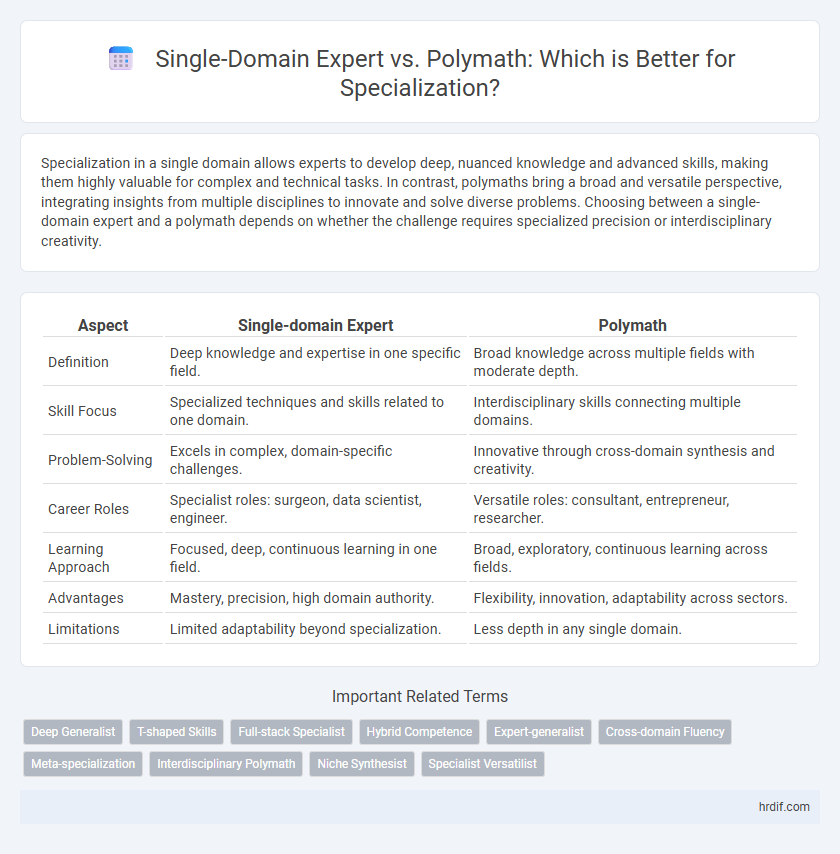
Specialization in a single domain allows experts to develop deep, nuanced knowledge and advanced skills, making them highly valuable for complex and technical tasks. In contrast, polymaths bring a broad and versatile perspective, integrating insights from multiple disciplines to innovate and solve diverse problems. Choosing between a single-domain expert and a polymath depends on whether the challenge requires specialized precision or interdisciplinary creativity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Single-domain Expert | Polymath |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deep knowledge and expertise in one specific field. | Broad knowledge across multiple fields with moderate depth. |
| Skill Focus | Specialized techniques and skills related to one domain. | Interdisciplinary skills connecting multiple domains. |
| Problem-Solving | Excels in complex, domain-specific challenges. | Innovative through cross-domain synthesis and creativity. |
| Career Roles | Specialist roles: surgeon, data scientist, engineer. | Versatile roles: consultant, entrepreneur, researcher. |
| Learning Approach | Focused, deep, continuous learning in one field. | Broad, exploratory, continuous learning across fields. |
| Advantages | Mastery, precision, high domain authority. | Flexibility, innovation, adaptability across sectors. |
| Limitations | Limited adaptability beyond specialization. | Less depth in any single domain. |
Defining Single-domain Experts and Polymaths
Single-domain experts possess deep, specialized knowledge in one specific field, enabling them to solve complex problems with precision and efficiency. Polymaths, on the other hand, have expertise across multiple domains, allowing them to integrate diverse perspectives and innovate by connecting ideas from different disciplines. This distinction highlights the trade-off between depth of knowledge and breadth of understanding in specialization.
Historical Perspectives: From Masters to Renaissance Minds
Historical perspectives reveal that single-domain experts, such as medieval masters, achieved deep mastery through focused study and practice within a narrow field, fostering innovation and authority in specific disciplines. Renaissance minds epitomized polymathic specialization by integrating diverse knowledge areas like art, science, and philosophy, driving cross-disciplinary breakthroughs that shaped modern intellectual frameworks. This evolution highlights the tension between exclusive depth and broad interdisciplinary insight, influencing how specialization is valued across eras.
Advantages of Single-domain Specialization
Single-domain specialization offers deep expertise in a specific field, enabling higher precision and mastery compared to broader knowledge scopes. Experts with focused skills can solve complex problems more efficiently and innovate within their niche, providing significant value in specialized industries such as medicine, law, or engineering. This concentrated proficiency often leads to increased credibility and career advancement opportunities in highly technical or specialized domains.
Strengths of Polymathic Careers
Polymathic careers excel in adaptability and innovation by integrating knowledge across multiple domains, fostering creative problem-solving and unique insights. This broad expertise enables polymaths to connect disparate ideas, enhancing strategic thinking and driving breakthroughs in complex, interdisciplinary challenges. Employers value polymaths for their versatility and ability to thrive in dynamic environments requiring diverse skill sets.
Industry Demand: Who Do Employers Seek?
Employers in rapidly evolving industries prioritize single-domain experts with deep, specialized skills to address complex, niche challenges efficiently. However, sectors driven by innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration increasingly seek polymaths capable of integrating diverse knowledge areas for creative problem-solving and strategic advantage. Market trends show a growing demand for hybrid profiles combining domain expertise with broad cognitive flexibility to adapt to dynamic business environments.
Navigating Career Growth: Depth vs Breadth
Single-domain experts excel by developing deep, specialized knowledge within one field, enabling them to solve complex problems and become industry leaders. Polymaths leverage breadth across multiple disciplines, fostering innovation through interdisciplinary connections and adaptability in evolving markets. Career growth hinges on aligning personal strengths with market demands, where depth offers mastery and authority, while breadth supports agility and cross-functional opportunities.
Innovation and Problem-solving Perspectives
Single-domain experts provide deep, specialized knowledge that accelerates innovation within niche fields by leveraging extensive experience and technical skills. Polymaths contribute diverse perspectives and cross-disciplinary approaches, fostering innovative problem-solving through the integration of varied concepts and methodologies. Combining focused expertise with broad knowledge enhances creativity and drives complex problem resolution in specialized domains.
Adaptability in a Rapidly Changing Job Market
Single-domain experts possess deep knowledge and skills in one field, offering high proficiency but limited flexibility in evolving industries. Polymaths adapt more readily to rapid job market changes by integrating insights across diverse domains, enabling innovative problem-solving and resilience. Employers increasingly value adaptability, making polymathic specialization a strategic advantage in dynamic economic landscapes.
Building Your Path: Choosing Specialization Strategies
Single-domain experts develop deep knowledge and skills within a narrow field, enabling high proficiency and recognition in specialized industries like medicine or law. Polymaths leverage cross-disciplinary insights, connecting concepts from multiple domains to drive innovative problem-solving in areas such as technology or entrepreneurship. Choosing specialization strategies depends on career goals, with single-domain expertise suited for roles requiring technical mastery and polymath approaches ideal for dynamic environments demanding versatile, integrative thinking.
Future-proofing Careers: Hybrid Approaches to Specialization
Future-proofing careers requires balancing deep single-domain expertise with broad polymath skills to adapt to rapidly changing industries. Hybrid specialization fosters innovation by integrating focused knowledge with interdisciplinary problem-solving, enhancing resilience against automation and market shifts. Cultivating both specialized depth and versatile breadth ensures sustainable career growth in evolving job landscapes.
Related Important Terms
Deep Generalist
A deep generalist combines extensive expertise in a primary domain with broad knowledge across multiple fields, enabling innovative problem-solving that single-domain experts might miss. This approach strategically balances depth and breadth, fostering adaptability and cross-disciplinary insight compared to the narrow focus of single-domain specialization or the generalized scope of polymaths.
T-shaped Skills
Single-domain experts possess deep knowledge and skills within a narrow field, enhancing proficiency and efficiency in specialized tasks, while polymaths leverage broad expertise across multiple domains to foster innovation and adaptability. Emphasizing T-shaped skills, professionals develop deep vertical expertise complemented by a horizontal ability to collaborate across disciplines, optimizing problem-solving capabilities in complex environments.
Full-stack Specialist
A Full-stack Specialist embodies single-domain expertise by mastering front-end, back-end, and database technologies within software development, enabling comprehensive project execution with deep technical proficiency. Unlike polymaths who leverage broad multidisciplinary knowledge, full-stack specialists deliver optimized solutions through focused specialization in interconnected web technologies.
Hybrid Competence
Hybrid competence combines the deep knowledge of a single-domain expert with the broad skills of a polymath, enabling professionals to innovate by applying specialized insights across multiple fields. This interdisciplinary approach enhances problem-solving capabilities and adaptability, fostering expertise that balances focused proficiency with versatile understanding.
Expert-generalist
A single-domain expert possesses in-depth knowledge and advanced skills within one specialized field, enabling precision and mastery that drive innovation and problem-solving in complex scenarios. In contrast, an expert-generalist blends deep expertise with interdisciplinary understanding, fostering adaptive thinking and the ability to integrate diverse perspectives for holistic solutions.
Cross-domain Fluency
Single-domain experts excel through deep knowledge in a specific field, while polymaths leverage cross-domain fluency to integrate diverse insights and innovate more adaptively. Cross-domain fluency enhances problem-solving by enabling connections between unrelated disciplines, fostering creativity beyond traditional specialization boundaries.
Meta-specialization
Meta-specialization integrates the depth of a single-domain expert with the breadth of a polymath, enabling advanced problem-solving by applying specialized knowledge across multiple fields. This approach enhances innovation and adaptability, surpassing traditional specialization through interdisciplinary expertise and cross-domain insights.
Interdisciplinary Polymath
Interdisciplinary polymaths leverage expertise across multiple domains to innovate by connecting concepts that single-domain experts often overlook, fostering creative problem-solving and comprehensive analysis. Their ability to synthesize knowledge from diverse fields enhances adaptability and drives breakthroughs in complex, multifaceted challenges.
Niche Synthesist
A niche synthesist combines deep single-domain expertise with cross-disciplinary insights, enabling innovative problem-solving and specialized knowledge application. This specialization strategy leverages the strengths of a polymath while maintaining focused authority in a specific domain, optimizing both depth and breadth.
Specialist Versatilist
A Specialist Versatilist combines deep expertise in a single domain with the ability to apply skills across multiple fields, bridging the gap between single-domain experts and polymaths. This hybrid specialization approach enhances adaptability and innovation by integrating focused knowledge with broad problem-solving capabilities.
Single-domain Expert vs Polymath for specialization. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com