Salaried work offers consistent routines and stable income, which can enhance productivity through structured schedules and clear expectations. Gig economy participation provides flexibility and variety, allowing individuals to tailor tasks to peak performance times and maintain motivation. Balancing the stability of salaried roles with the adaptability of gig work can optimize productivity by leveraging the strengths of both employment models.
Table of Comparison
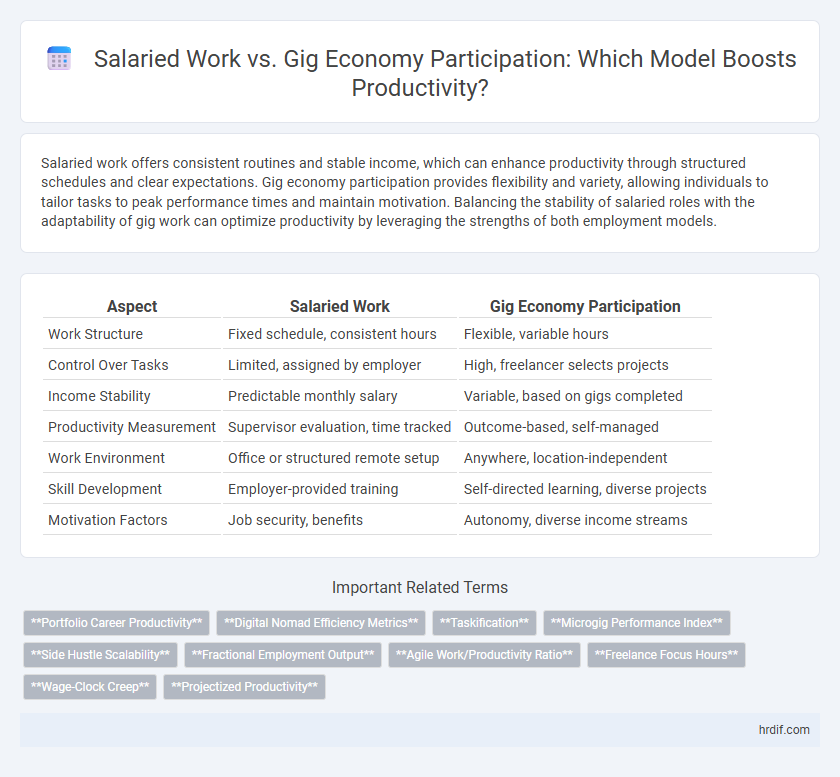
| Aspect | Salaried Work | Gig Economy Participation |
|---|---|---|
| Work Structure | Fixed schedule, consistent hours | Flexible, variable hours |
| Control Over Tasks | Limited, assigned by employer | High, freelancer selects projects |
| Income Stability | Predictable monthly salary | Variable, based on gigs completed |
| Productivity Measurement | Supervisor evaluation, time tracked | Outcome-based, self-managed |
| Work Environment | Office or structured remote setup | Anywhere, location-independent |
| Skill Development | Employer-provided training | Self-directed learning, diverse projects |
| Motivation Factors | Job security, benefits | Autonomy, diverse income streams |
Defining Salaried Employment and the Gig Economy
Salaried employment involves a fixed income with consistent hours, offering stability and predictable productivity outcomes through structured work environments and defined roles. The gig economy, characterized by freelance, contract, or temporary jobs, provides flexibility and autonomy, enabling workers to manage multiple projects and potentially increase productivity through varied skill application. Understanding these employment types helps evaluate their distinct impacts on individual productivity and workforce efficiency.
Productivity Metrics in Traditional Salaried Roles
Productivity metrics in traditional salaried roles typically emphasize consistent output, time management, and adherence to predefined goals within structured work hours. These metrics often include quantitative performance indicators such as project completion rates, quality assessments, and attendance records. Organizations rely on these standardized measures to evaluate employee efficiency and overall contribution to sustained business objectives.
Measuring Productivity in Gig Economy Work
Measuring productivity in gig economy work requires tracking output based on task completion rates, time spent per gig, and client satisfaction metrics to capture the variability of freelance assignments. Unlike salaried roles with fixed hours, gig work productivity hinges on efficiency and quality across diverse projects, necessitating flexible performance indicators. Data analytics and real-time feedback systems enhance accuracy in assessing gig worker contributions, ensuring alignment with overall productivity goals.
Flexibility and Its Impact on Output
Flexibility in gig economy participation allows workers to tailor their schedules, often leading to increased productivity by aligning tasks with peak performance times. Salaried work typically involves fixed hours, which can limit adaptability but may provide structure that supports consistent output. Balancing autonomy and routine is crucial, as gig workers benefit from customizable work patterns, while salaried employees rely on steady workflows to maintain efficiency.
Job Security: Influence on Worker Performance
Job security in salaried work creates a stable environment that enhances worker performance by reducing stress and promoting long-term commitment. In contrast, gig economy participation often lacks consistent income and benefits, which can lead to fluctuating motivation and diminished productivity. Research shows that employees with secure jobs are more likely to invest effort and improve skills, directly boosting overall productivity levels.
Autonomy and Personal Accountability in Both Models
Salaried work offers structured autonomy with clear role definitions, promoting consistent productivity through accountability to employers. Gig economy participation provides heightened personal accountability as workers self-manage tasks, driving productivity via flexible schedules and self-motivation. Both models leverage autonomy differently, impacting productivity by balancing external oversight and individual responsibility.
Work-Life Balance: Productivity Implications
Salaried work typically offers structured hours and stable income, promoting consistent productivity through routine and predictable work-life balance. Gig economy participation provides flexibility, enabling individuals to tailor work schedules around personal life, which can enhance productivity by reducing burnout and increasing motivation. However, inconsistent income and variable hours in gig roles may challenge sustained productivity due to potential stress and work-life imbalance.
Financial Stability and Its Effect on Efficiency
Financial stability in salaried work provides consistent income, reducing stress and enabling employees to focus fully on tasks, thereby enhancing productivity. In contrast, gig economy participation often entails income variability, which can lead to financial insecurity and distraction, negatively impacting efficiency. Stable earnings foster better time management and sustained effort, key drivers of high productivity.
Technological Tools Enhancing Productivity
Technological tools such as project management software, time-tracking apps, and cloud collaboration platforms significantly increase productivity in both salaried work and gig economy participation. These tools facilitate efficient task organization, real-time communication, and seamless remote work, enabling workers to manage multiple projects effectively. Access to advanced technology empowers gig workers to compete with salaried employees by optimizing workflows and reducing downtime.
Comparing Long-Term Career Growth and Productivity
Salaried work offers structured career progression with consistent productivity improvements through skill development and organizational support, fostering long-term growth. Gig economy participation provides flexibility and diverse project experience, but often lacks stability and clear advancement pathways, which may limit sustained productivity gains. Evaluating productivity, salaried positions typically yield higher cumulative output over time due to predictable workloads and performance incentives.
Related Important Terms
Portfolio Career Productivity
Portfolio career productivity thrives by balancing salaried work's stability with the gig economy's flexibility, allowing professionals to diversify skills and income streams efficiently. This hybrid approach enhances time management and fosters continuous learning, driving higher overall output and job satisfaction.
Digital Nomad Efficiency Metrics
Digital nomad efficiency metrics reveal that gig economy participation often enhances productivity through flexible work hours and diverse project engagement, contrasting with the predictable but sometimes rigid structure of salaried work. Metrics such as task completion rate, time utilization, and adaptive skill application consistently show increased output and innovation among digital nomads navigating gig platforms.
Taskification
Taskification in salaried work streamlines productivity through structured roles and consistent workflows, whereas gig economy participation relies on discrete, often fragmented tasks that require rapid adaptation and multitasking efficiency. This shift to task-based engagements influences time management and output quality, creating distinct productivity dynamics between stable employment and gig assignments.
Microgig Performance Index
The Microgig Performance Index reveals that gig economy participation often boosts productivity by enabling flexible task management and skill diversity, whereas salaried work provides steady output through structured schedules and consistent resources. Analysis of the index highlights how microgigs leverage short-term, high-impact assignments that optimize time efficiency, compared to traditional salaried roles focused on long-term project continuity.
Side Hustle Scalability
Side hustle scalability in the gig economy offers salaried workers the opportunity to boost productivity by diversifying income streams without sacrificing core job performance. Leveraging flexible platforms enables efficient time management and skill expansion, which enhances overall work output and career growth potential.
Fractional Employment Output
Fractional employment output in gig economy participation often surpasses traditional salaried work by enabling flexible task allocation and time management, leading to increased productivity per hour worked. This model leverages diverse skill sets across multiple projects simultaneously, optimizing resource utilization and enhancing overall workforce efficiency.
Agile Work/Productivity Ratio
The Agile Work/Productivity Ratio demonstrates higher efficiency in gig economy participation by enabling flexible task management and rapid adaptation to project changes, often surpassing traditional salaried work constraints. Gig workers leverage autonomous scheduling and diversified skill application, optimizing productivity through agile methodologies better than fixed-hour salaried roles.
Freelance Focus Hours
Freelance Focus Hours typically enhance productivity by allowing workers to tailor their schedules based on peak efficiency and workload demands, contrasting salaried employees' fixed hours that may include less productive time. Data shows gig economy participants optimize 20-30% more focus hours weekly, leveraging autonomy to prioritize high-impact tasks and reduce burnout.
Wage-Clock Creep
Wage-clock creep, the gradual extension of paid work hours without proportional productivity gains, disproportionately affects salaried employees compared to gig economy participants who often set flexible schedules. This phenomenon reduces overall efficiency in traditional employment while gig workers leverage autonomy to optimize output within self-managed time frames.
Projectized Productivity
Projectized productivity in salaried work often benefits from structured timelines and clearly defined deliverables, enabling efficient resource allocation and consistent output quality. In contrast, gig economy participation fosters flexibility and diverse project exposure, enhancing adaptive skills but may challenge sustained focus and long-term productivity metrics.
Salaried Work vs Gig Economy Participation for productivity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com