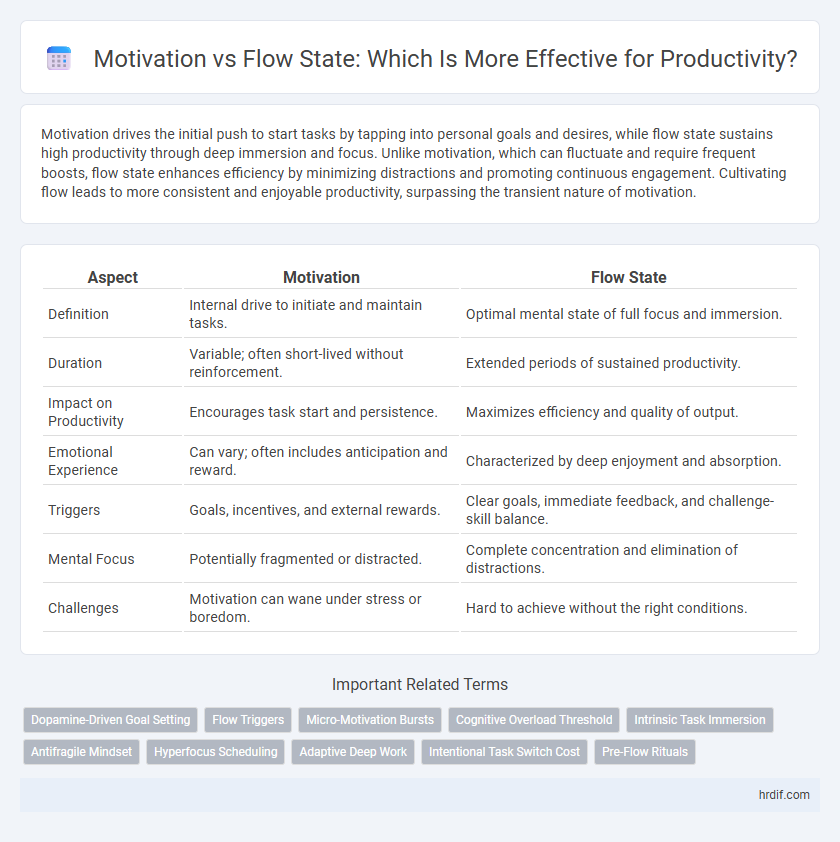
Motivation drives the initial push to start tasks by tapping into personal goals and desires, while flow state sustains high productivity through deep immersion and focus. Unlike motivation, which can fluctuate and require frequent boosts, flow state enhances efficiency by minimizing distractions and promoting continuous engagement. Cultivating flow leads to more consistent and enjoyable productivity, surpassing the transient nature of motivation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Motivation | Flow State |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internal drive to initiate and maintain tasks. | Optimal mental state of full focus and immersion. |
| Duration | Variable; often short-lived without reinforcement. | Extended periods of sustained productivity. |
| Impact on Productivity | Encourages task start and persistence. | Maximizes efficiency and quality of output. |
| Emotional Experience | Can vary; often includes anticipation and reward. | Characterized by deep enjoyment and absorption. |
| Triggers | Goals, incentives, and external rewards. | Clear goals, immediate feedback, and challenge-skill balance. |
| Mental Focus | Potentially fragmented or distracted. | Complete concentration and elimination of distractions. |
| Challenges | Motivation can wane under stress or boredom. | Hard to achieve without the right conditions. |
Understanding Motivation and Flow State in the Workplace
Motivation drives initial engagement by providing clear goals and incentives, while flow state sustains deep focus through intrinsic enjoyment and challenge balance. In the workplace, fostering autonomy, mastery, and purpose enhances motivation, but creating conditions for flow requires minimizing distractions and matching tasks to skill levels. Understanding the distinct yet complementary roles of motivation and flow state helps organizations design environments that consistently boost productivity and job satisfaction.
Key Differences Between Motivation and Flow State
Motivation drives productivity by providing the initial desire and reason to start a task, often fueled by external goals or incentives. Flow state, however, immerses individuals in deep focus and enjoyment, enabling sustained performance through intrinsic engagement and loss of self-consciousness. Key differences include motivation's reliance on reward anticipation versus flow's emphasis on seamless task absorption and optimal challenge balance.
How Motivation Drives Productivity
Motivation drives productivity by initiating goal-oriented behavior and sustaining effort toward task completion. It activates the brain's reward system, increasing focus and energy levels which enhance task engagement and performance. While flow state optimizes productivity through deep immersion, motivation is the foundational catalyst that propels individuals to start and persist in productive activities.
The Science Behind Flow State and Enhanced Performance
Flow state triggers a unique brain activity pattern characterized by increased gamma waves and synchronized neural networks, enhancing focus and cognitive performance. Motivation initiates action, but flow sustains deep immersion, resulting in higher productivity and creativity through optimal challenge-skill balance. Neurotransmitters like dopamine, norepinephrine, and endorphins surge during flow, boosting mood, alertness, and task efficiency.
Achieving Flow: Strategies for Entering the Zone
Achieving flow state significantly enhances productivity by fully immersing individuals in tasks, resulting in heightened focus and creative output. Techniques such as setting clear, challenging goals, minimizing distractions, and balancing skill level with task difficulty help trigger flow. Consistent practice of these strategies cultivates deeper engagement and sustained motivation, driving peak performance.
Motivation vs. Flow: Which is More Sustainable for Long-Term Productivity?
Flow state provides a more sustainable framework for long-term productivity by fostering deep focus and intrinsic engagement in tasks, unlike motivation which often depends on fluctuating external incentives or fleeting emotions. While motivation can initiate action, flow sustains continuous, high-quality output through seamless involvement and reduced self-consciousness. Cultivating flow enhances consistency and resilience in productivity, making it a more reliable driver than motivation over extended periods.
Combining Motivation and Flow State for Optimal Results
Combining motivation and flow state enhances productivity by harnessing the drive to initiate tasks alongside the deep focus required for sustained performance. Motivation triggers goal-oriented energy, while flow state optimizes cognitive function through immersion and effortless concentration. Integrating both elements leads to elevated creativity, efficiency, and consistent achievement of complex objectives.
Common Barriers to Motivation and Flow in Careers
Common barriers to motivation and flow in careers include unclear goals, excessive distractions, and lack of meaningful challenges, which disrupt focus and reduce productivity. Workplace environments that are overly rigid or overly chaotic hinder the ability to enter flow states, diminishing creative problem-solving and sustained engagement. Addressing these obstacles through goal-setting, minimizing interruptions, and fostering autonomy can significantly enhance career productivity.
Measuring Productivity Gains: Motivation or Flow State?
Measuring productivity gains reveals that flow state consistently outperforms motivation by fostering sustained focus and deep work, leading to higher output quality and efficiency. Motivation provides initial momentum, but flow state enables prolonged engagement, reducing cognitive fatigue and boosting task completion rates. Data from productivity studies show flow state correlates with a 30% increase in task accuracy and up to 50% faster completion times compared to motivation-driven efforts.
Practical Tips to Cultivate Both Motivation and Flow at Work
Cultivating motivation and flow at work enhances productivity by leveraging intrinsic drive and deep focus. Prioritize setting clear goals, breaking tasks into manageable steps, and minimizing distractions to trigger motivation and sustained engagement. Implement mindfulness techniques, such as short meditation breaks, and create an environment with optimal challenges to consistently enter and maintain the flow state.
Related Important Terms
Dopamine-Driven Goal Setting
Dopamine-driven goal setting enhances productivity by triggering reward pathways that increase motivation and reinforce focused effort. While motivation sparks initial action, maintaining a flow state allows sustained engagement and optimal performance through deep concentration and intrinsic satisfaction.
Flow Triggers
Flow state enhances productivity more sustainably than motivation by engaging key flow triggers such as clear goals, immediate feedback, and a balance between challenge and skill. These triggers foster deep focus and intrinsic enjoyment, leading to higher efficiency and creative output.
Micro-Motivation Bursts
Micro-motivation bursts trigger short, intense spikes of focused energy that enhance productivity by initiating and sustaining flow states. Harnessing these brief motivational surges enables seamless immersion in tasks, optimizing cognitive resources for peak performance.
Cognitive Overload Threshold
Motivation drives initial engagement in tasks, but productivity significantly improves when entering a flow state, where cognitive overload threshold is optimally balanced, allowing sustained focus without mental fatigue. Exceeding this threshold due to excessive stimuli or multitasking disrupts flow, reducing efficiency and increasing the likelihood of errors.
Intrinsic Task Immersion
Intrinsic task immersion fuels sustained productivity by engaging deep focus and minimizing distractions, unlike motivation which can fluctuate and rely on external factors. Flow state embodies this immersion, optimizing cognitive resources and enhancing task performance through seamless integration of challenge and skill.
Antifragile Mindset
An antifragile mindset leverages both motivation and flow state by embracing challenges that strengthen productivity under stress, rather than depending solely on motivation's transient energy spikes. Flow state enables deep focus and sustained performance, while antifragility transforms unpredictable obstacles into opportunities for growth and enhanced task mastery.
Hyperfocus Scheduling
Hyperfocus scheduling leverages the flow state to maximize productivity by structuring work periods around intense, distraction-free focus times, surpassing traditional motivation-based approaches that rely on fluctuating energy levels. By aligning tasks with peak cognitive performance windows, hyperfocus scheduling promotes sustained attention and deeper engagement, resulting in higher output and efficiency.
Adaptive Deep Work
Adaptive Deep Work leverages motivation by aligning task difficulty with individual skill levels, fostering a flow state that maximizes productivity through sustained focus and minimized distractions. This synergy between motivation and flow enhances cognitive performance, enabling deeper engagement and more effective problem-solving during work sessions.
Intentional Task Switch Cost
Intentional task switch cost significantly reduces productivity by disrupting flow state, which is a deep focus that enhances efficiency and creativity. Motivation alone cannot compensate for the cognitive load incurred during frequent, intentional task shifts, making sustained flow essential for optimal productivity.
Pre-Flow Rituals
Pre-flow rituals such as deep breathing, setting clear goals, and minimizing distractions prime the brain for enhanced focus, facilitating the transition into a productive flow state. These rituals increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels, bolstering motivation while seamlessly triggering sustained concentration and efficient task execution.
Motivation vs Flow State for productivity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com