Batch processing improves productivity by handling multiple tasks simultaneously in grouped sets, reducing the overhead of task switching and enabling efficient resource use. Async work enhances responsiveness and flexibility by allowing tasks to run independently without waiting for others to complete, which minimizes idle time and accelerates overall workflow. Combining batch processing with asynchronous execution can optimize productivity by balancing efficient task grouping with non-blocking operations.
Table of Comparison
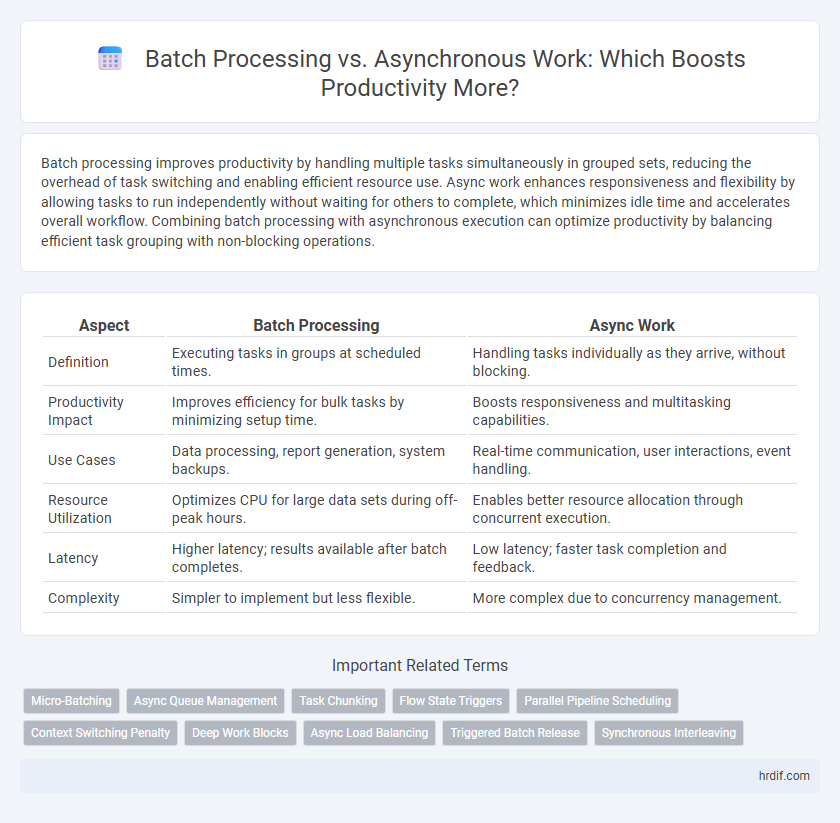
| Aspect | Batch Processing | Async Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executing tasks in groups at scheduled times. | Handling tasks individually as they arrive, without blocking. |
| Productivity Impact | Improves efficiency for bulk tasks by minimizing setup time. | Boosts responsiveness and multitasking capabilities. |
| Use Cases | Data processing, report generation, system backups. | Real-time communication, user interactions, event handling. |
| Resource Utilization | Optimizes CPU for large data sets during off-peak hours. | Enables better resource allocation through concurrent execution. |
| Latency | Higher latency; results available after batch completes. | Low latency; faster task completion and feedback. |
| Complexity | Simpler to implement but less flexible. | More complex due to concurrency management. |
Understanding Batch Processing and Asynchronous Work
Batch processing organizes tasks into groups executed sequentially to maximize efficiency by minimizing context switching and resource overhead. Asynchronous work allows tasks to run independently without waiting for others to complete, enabling faster response times and better utilization of system resources. Understanding these approaches helps optimize workflow by choosing batch processing for predictable, homogeneous tasks and asynchronous work for real-time, event-driven environments.
Key Differences Between Batch Processing and Async Work
Batch processing executes tasks in large groups at scheduled times, optimizing resource usage but potentially causing delays in task completion. Async work allows tasks to run independently and concurrently, enhancing responsiveness and reducing idle time, which boosts overall productivity. The key differences lie in execution timing, resource allocation, and task interdependence, with batch focusing on throughput and async prioritizing real-time responsiveness.
The Productivity Impact of Batch Processing
Batch processing enhances productivity by consolidating similar tasks, reducing context switching and enabling focused work sessions that increase efficiency. This method minimizes cognitive overload and streamlines workflow, leading to faster task completion compared to asynchronous work. Organizations using batch processing report significant improvements in throughput and employee performance metrics.
How Asynchronous Work Boosts Efficiency
Asynchronous work boosts efficiency by enabling parallel task execution, reducing downtime caused by waiting periods in batch processing. It allows employees to manage multiple workflows simultaneously, improving overall productivity and adaptability. Real-time communication tools and cloud platforms enhance asynchronous collaboration, accelerating project timelines and decision-making.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Batch processing enhances productivity by grouping similar tasks to minimize setup time and maximize throughput, ideal for repetitive, high-volume workflows. Async work boosts flexibility and responsiveness, allowing parallel task execution and better resource utilization in dynamic, multi-user environments. Key factors to consider include task complexity, resource availability, real-time requirements, and the need for scalability to determine the most efficient productivity approach.
Common Productivity Pitfalls in Batch and Async Methods
Batch processing often leads to productivity bottlenecks due to task accumulation and delayed feedback loops, causing slower response times and reduced workflow agility. Asynchronous work can suffer from communication gaps and coordination challenges, resulting in task misalignment and decreased overall efficiency. Both methods require careful management of task prioritization and transparency to avoid productivity losses.
Best Practices for Batch Processing in the Workplace
Best practices for batch processing in the workplace include grouping similar tasks to minimize context switching and increase focus, which enhances overall productivity. Automating repetitive workflows through software tools reduces errors and accelerates task completion. Scheduling batch processes during low-peak hours optimizes resource utilization and prevents disruption to real-time operations.
Leveraging Asynchronous Tools to Enhance Workflows
Leveraging asynchronous tools enhances productivity by allowing tasks to be processed independently without waiting for batch completion, reducing idle time and improving resource allocation. Asynchronous workflows enable continuous progress on multiple tasks simultaneously, fostering better time management and responsiveness in dynamic work environments. Integrating async communication platforms and automated task queues supports seamless collaboration and accelerates project delivery.
Case Studies: Productivity Gains from Batch and Async Work
Case studies reveal that batch processing improves productivity by minimizing task-switching and reducing cognitive load, leading to up to 40% time savings in repetitive workflows. Async work enhances focus and collaboration flexibility, with organizations reporting a 25% increase in output by enabling employees to manage tasks without constant real-time interruptions. Combining batch processing with async communication optimizes workflow efficiency, as shown in a 2023 study where teams experienced a 30% boost in project completion speed.
Making the Switch: Transitioning Teams to Optimal Work Modes
Batch processing streamlines repetitive tasks by grouping similar activities, reducing context switching and increasing efficiency. Async work empowers teams to operate independently, facilitating flexibility and reducing bottlenecks in communication. Transitioning teams to the optimal mode requires analyzing task types, prioritizing focus-intensive jobs for batching, and communication-dependent tasks for async collaboration.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Batching
Micro-batching enhances productivity by combining the efficiency of batch processing with the flexibility of asynchronous work, processing small data sets quickly to reduce latency and improve resource utilization. This method optimizes throughput in distributed systems and AI workloads by minimizing idle time and balancing load, resulting in faster task completion and smoother workflow management.
Async Queue Management
Async queue management enhances productivity by enabling non-blocking task execution and efficient resource allocation, reducing wait times and system idle periods. Unlike batch processing, asynchronous workflows support dynamic workload distribution and real-time prioritization, optimizing throughput and responsiveness in complex task environments.
Task Chunking
Batch processing consolidates similar tasks to improve focus and reduce context switching, enhancing overall productivity by enabling deep work sessions. Async work leverages task chunking by breaking projects into smaller, manageable units that can be completed independently, promoting flexibility and minimizing downtime.
Flow State Triggers
Batch processing enhances productivity by minimizing context switching and allowing deep focus during extended work sessions, which effectively triggers flow states through sustained attention and reduced cognitive load. Async work supports productivity by enabling flexible task prioritization and minimized interruptions, fostering flow through autonomy and controlled pacing aligned with individual rhythms.
Parallel Pipeline Scheduling
Parallel pipeline scheduling enhances productivity by enabling simultaneous execution of batch processing and asynchronous tasks, reducing idle times and improving resource utilization. This hybrid approach leverages concurrency to optimize workflow efficiency, minimize bottlenecks, and accelerate task completion.
Context Switching Penalty
Batch processing minimizes the context switching penalty by grouping similar tasks together, allowing deeper focus and reducing the cognitive load associated with frequent task changes. In contrast, asynchronous work often increases context switching, which can lead to significant productivity losses by fragmenting attention and increasing mental fatigue.
Deep Work Blocks
Batch processing enhances productivity by grouping similar tasks to minimize context switching and maximize focus during deep work blocks. Async work supports flexibility but can fragment attention, making batch processing more effective for sustained cognitive engagement and higher-quality output.
Async Load Balancing
Async load balancing optimizes productivity by distributing tasks dynamically across available resources, reducing bottlenecks and minimizing idle time in workflows. Batch processing processes tasks sequentially in fixed groups, which can cause delays and lower responsiveness compared to the real-time efficiency gains achieved through asynchronous load balancing.
Triggered Batch Release
Triggered batch release optimizes productivity by grouping tasks to execute simultaneously based on specific events, reducing system overhead and improving resource allocation compared to purely asynchronous work. This method enhances throughput and minimizes idle time by balancing workload peaks and enabling efficient parallel processing.
Synchronous Interleaving
Synchronous interleaving in batch processing optimizes productivity by handling multiple tasks within a fixed timeframe, reducing idle time and improving resource utilization compared to asynchronous work. This approach minimizes context switching overhead and ensures consistent workflow, boosting overall efficiency and throughput in time-sensitive environments.
Batch processing vs Async work for productivity. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com