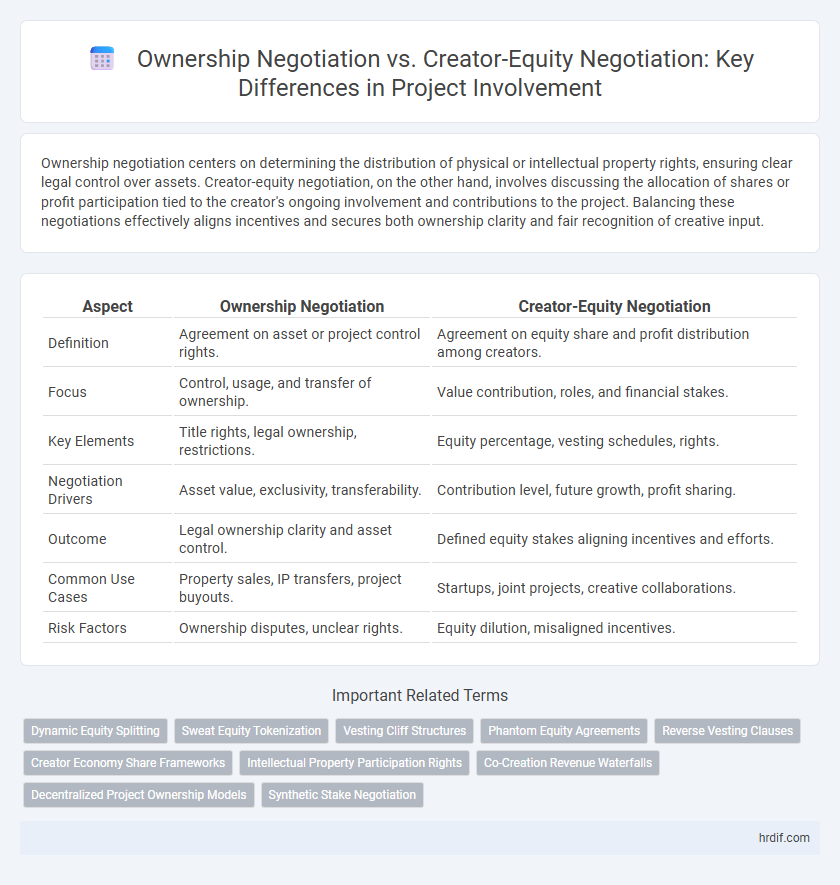
Ownership negotiation centers on determining the distribution of physical or intellectual property rights, ensuring clear legal control over assets. Creator-equity negotiation, on the other hand, involves discussing the allocation of shares or profit participation tied to the creator's ongoing involvement and contributions to the project. Balancing these negotiations effectively aligns incentives and secures both ownership clarity and fair recognition of creative input.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ownership Negotiation | Creator-Equity Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Agreement on asset or project control rights. | Agreement on equity share and profit distribution among creators. |
| Focus | Control, usage, and transfer of ownership. | Value contribution, roles, and financial stakes. |
| Key Elements | Title rights, legal ownership, restrictions. | Equity percentage, vesting schedules, rights. |
| Negotiation Drivers | Asset value, exclusivity, transferability. | Contribution level, future growth, profit sharing. |
| Outcome | Legal ownership clarity and asset control. | Defined equity stakes aligning incentives and efforts. |
| Common Use Cases | Property sales, IP transfers, project buyouts. | Startups, joint projects, creative collaborations. |
| Risk Factors | Ownership disputes, unclear rights. | Equity dilution, misaligned incentives. |
Defining Ownership Negotiation in Project Roles
Ownership negotiation in project roles involves defining clear rights and responsibilities regarding decision-making authority and asset control among stakeholders. This process establishes who holds formal ownership of project outputs versus those contributing through creative input or intellectual property, ensuring alignment on influence and accountability. Distinguishing ownership negotiation from creator-equity negotiation clarifies the distribution of tangible stakes versus recognition and benefits linked to creative contributions.
Understanding Creator-Equity Negotiation Dynamics
Creator-equity negotiation centers on aligning project stakeholders' contributions with proportional ownership stakes, emphasizing long-term value creation and incentive alignment. Unlike ownership negotiation, which often focuses on fixed asset distribution, creator-equity discussions require clear valuation of intellectual property and ongoing creative input. Understanding these dynamics ensures equitable recognition of risk, effort, and future rewards in collaborative ventures.
Key Differences Between Ownership and Creator-Equity Negotiations
Ownership negotiations primarily determine legal rights and control over project assets, emphasizing decision-making authority and asset distribution. Creator-equity negotiations focus on defining the percentage of profit-sharing and long-term financial benefits tied to the creator's contribution and involvement. Key differences lie in ownership granting tangible control, while creator-equity emphasizes incentivizing ongoing participation and aligning interests with project success.
Motivations for Seeking Ownership vs. Equity
Ownership negotiation often centers on motivating stakeholders through control and decision-making power directly tied to tangible assets, fostering a sense of security and responsibility. Creator-equity negotiation emphasizes aligning incentives with project success, where equity offers potential financial rewards and long-term value appreciation, appealing to contributors driven by growth and shared outcomes. Understanding these motivations helps tailor negotiation strategies to balance immediate authority with future gains, optimizing engagement and commitment from involved parties.
Legal Implications of Ownership and Equity Agreements
Ownership negotiation establishes clear legal rights and responsibilities regarding asset control and transfer, often requiring formal documentation like titles or patents to prevent disputes. Creator-equity negotiation involves granting a stake in the project's future profits and decision-making, necessitating detailed shareholder or partnership agreements to address dilution, exit strategies, and compliance with securities laws. Both require careful legal structuring to safeguard intellectual property, ensure enforceability, and minimize risks of conflicts or litigation.
Impact on Long-term Career Growth and Recognition
Ownership negotiation emphasizes securing control and decision-making authority, which can directly influence long-term career growth by establishing a foundation of leadership and accountability. Creator-equity negotiation, however, prioritizes profit-sharing and reflects recognition of intellectual contributions, enhancing reputation and potential financial rewards over time. Balancing both elements ensures sustained professional development and acknowledgment within the industry.
Risk and Reward: Evaluating Negotiation Outcomes
Ownership negotiation often centers on securing legal rights and control over a project, directly impacting long-term asset value and decision-making authority. Creator-equity negotiation balances the distribution of profit shares and creative input, aligning incentives while mitigating financial and reputational risks for all parties involved. Evaluating negotiation outcomes requires assessing both the tangible rewards of ownership and the strategic risks embedded in creator equity arrangements.
Best Practices for Structuring Project Involvement Deals
Ownership negotiation typically centers on defining clear rights and responsibilities related to asset control, ensuring all parties understand their stakes and limitations. Creator-equity negotiation emphasizes distributing value based on individual contributions, aligning incentives to foster collaboration and long-term project commitment. Structuring project involvement deals optimally requires transparent communication, precise documentation of roles, and adaptable terms that accommodate evolving project dynamics while protecting all stakeholders' interests.
Common Pitfalls in Ownership and Equity Negotiations
Common pitfalls in ownership and equity negotiations include unclear definitions of roles, ambiguous valuation of contributions, and misaligned expectations on control and profit distribution. Failing to establish explicit terms leads to disputes over decision-making authority and future equity adjustments. Addressing these issues early with transparent communication and documented agreements is essential for equitable project involvement.
Real-world Case Studies: Successes and Lessons Learned
Ownership negotiation often centers on revenue shares and intellectual property rights, while creator-equity negotiation emphasizes long-term stake and influence in project outcomes; real-world case studies reveal that transparent communication and clearly defined roles enhance collaboration and minimize conflicts. Successful negotiations leverage detailed term sheets and align incentives with project milestones, ensuring both creators and stakeholders feel valued. Lessons learned highlight the importance of flexibility and ongoing dialogue to adapt equity arrangements as projects evolve.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Equity Splitting
Dynamic equity splitting offers a flexible framework for ownership negotiation by allocating shares based on real-time contributions rather than fixed stakes, ensuring fair compensation aligned with each creator's effort and value addition. This approach contrasts with traditional creator-equity negotiation, which often relies on predetermined roles and static equity, potentially misrepresenting individual impact and risking disputes over project involvement.
Sweat Equity Tokenization
Ownership negotiation centers on defining stakes and control percentages, while creator-equity negotiation emphasizes fair compensation tied to individual contributions. Sweat equity tokenization transforms labor input into digital assets, enabling transparent valuation and equitable distribution of project ownership among creators.
Vesting Cliff Structures
Vesting cliff structures in ownership negotiation typically grant full equity after a set period, incentivizing long-term commitment but risking loss of partial contributions if participants leave early. Creator-equity negotiations often employ tailored cliff schedules that align vesting milestones with creative input and project milestones, ensuring fair recognition of individual contributions over time.
Phantom Equity Agreements
Ownership negotiation centers on transferring actual equity or shares in a company, granting full rights and responsibilities, while creator-equity negotiation often involves Phantom Equity Agreements, which provide economic benefits tied to company performance without granting true ownership. Phantom Equity Agreements align project creators' incentives with company success through cash bonuses or profit-sharing that mimic shareholder returns without diluting ownership.
Reverse Vesting Clauses
Reverse vesting clauses protect founders' ownership by subjecting equity to repurchase rights if they leave the project prematurely, aligning incentives with long-term commitment. Ownership negotiation centers on immediate equity distribution, whereas creator-equity negotiation integrating reverse vesting ensures gradual ownership accrual contingent on continued contribution.
Creator Economy Share Frameworks
Ownership negotiation centers on the division of existing assets and rights, emphasizing legal control and intellectual property stakes within a project, while creator-equity negotiation in the Creator Economy Share Frameworks prioritizes dynamic participation, value contribution, and profit-sharing models that align creator incentives with project growth. These frameworks enable transparent, flexible equity distribution tailored to creators' varying roles and ongoing input, fostering collaborative ecosystems that balance individual recognition with collective success.
Intellectual Property Participation Rights
Ownership negotiation centers on defining legal title and control over intellectual property, ensuring clear assignment of rights and responsibilities. Creator-equity negotiation emphasizes proportional participation in project benefits and decision-making, aligning intellectual property participation rights with contributions rather than mere ownership titles.
Co-Creation Revenue Waterfalls
Ownership negotiation centers on defining control and legal rights over project assets, while creator-equity negotiation emphasizes fair distribution of project value based on individual contributions; Co-Creation Revenue Waterfalls systematically allocate revenue streams, reflecting negotiated equity stakes and ensuring transparent financial returns aligned with creative input. Carefully structured waterfalls optimize stakeholder incentives by linking revenue distribution directly to co-creation roles and ownership proportions.
Decentralized Project Ownership Models
Decentralized project ownership models emphasize equitable creator-equity negotiation, aligning incentives through tokenized shares or stakeholding rather than traditional ownership transfers. This approach fosters transparent value distribution and collective governance, enhancing commitment and reducing conflicts often seen in conventional ownership negotiation frameworks.
Synthetic Stake Negotiation
Synthetic stake negotiation leverages predefined valuation models to allocate ownership percentages without directly dividing equity or control, enabling collaborators to quantify project involvement more flexibly. This approach contrasts with creator-equity negotiation, which ties ownership strictly to equity shares, often complicating incentives and diluting founder control in early-stage projects.
ownership negotiation vs creator-equity negotiation for project involvement Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com