Achievement motivation drives individuals to excel by setting and reaching personal or professional goals, often fueled by external rewards and recognition. Meaningful work, however, sustains motivation through a sense of purpose and alignment with personal values, fostering deeper engagement and long-term satisfaction. Balancing achievement motivation with meaningful work creates a powerful synergy that enhances overall productivity and fulfillment.
Table of Comparison
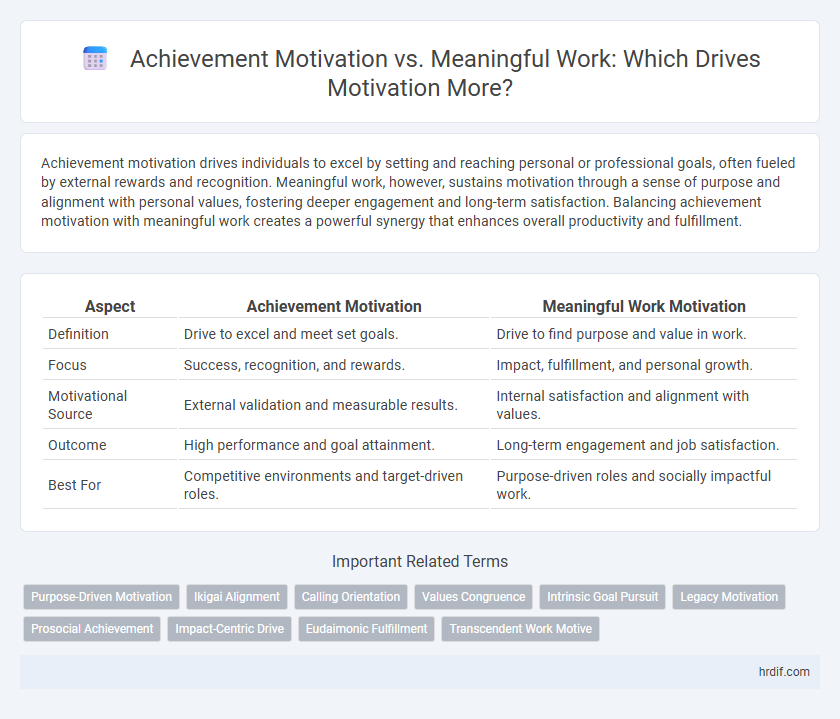
| Aspect | Achievement Motivation | Meaningful Work Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Drive to excel and meet set goals. | Drive to find purpose and value in work. |
| Focus | Success, recognition, and rewards. | Impact, fulfillment, and personal growth. |
| Motivational Source | External validation and measurable results. | Internal satisfaction and alignment with values. |
| Outcome | High performance and goal attainment. | Long-term engagement and job satisfaction. |
| Best For | Competitive environments and target-driven roles. | Purpose-driven roles and socially impactful work. |
Defining Achievement Motivation in the Workplace
Achievement motivation in the workplace refers to an individual's drive to accomplish goals, excel in tasks, and attain measurable success, often fueled by personal ambition and external recognition. This type of motivation focuses on setting challenging objectives, overcoming obstacles, and receiving feedback that reinforces a sense of competence and progress. Unlike meaningful work motivation, which emphasizes purpose and fulfillment, achievement motivation prioritizes tangible results and performance outcomes within professional settings.
What Makes Work Meaningful?
Work becomes meaningful when it aligns with personal values and contributes to a greater purpose beyond mere achievement motivation. Meaningful work fosters intrinsic motivation by fulfilling psychological needs for autonomy, competence, and relatedness, leading to sustained engagement and satisfaction. Unlike achievement motivation, which focuses on external rewards and status, meaningful work emphasizes the impact and significance of tasks on individuals and society.
Key Differences Between Achievement Motivation and Meaningful Work
Achievement motivation centers on individuals' drive to attain specific goals, measurable success, and external recognition, emphasizing performance and rewards. Meaningful work motivation arises from personal values, purpose, and the intrinsic satisfaction derived from tasks that contribute to a larger cause, fostering long-term commitment. The key difference lies in achievement motivation's focus on outcomes and validation, while meaningful work prioritizes alignment with personal significance and enduring fulfillment.
Psychological Theories Behind Workplace Motivation
Achievement motivation, rooted in McClelland's theory of needs, emphasizes the drive to excel and attain measurable success, often linked to intrinsic rewards such as personal growth and competence. Meaningful work motivation aligns with self-determination theory, highlighting autonomy, purpose, and connection as critical factors that foster sustained engagement and well-being. Psychological theories suggest integrating both achievement goals and meaningfulness can enhance workplace motivation by addressing employees' diverse psychological needs for competence, relatedness, and purpose.
Benefits of Achievement Motivation for Career Growth
Achievement motivation drives individuals to set and accomplish challenging goals, fostering continuous personal and professional development. This intrinsic drive enhances productivity, increases resilience, and cultivates a results-oriented mindset essential for career advancement. Emphasizing measurable accomplishments positions professionals favorably for promotions, leadership roles, and industry recognition.
The Impact of Meaningful Work on Job Satisfaction
Meaningful work significantly enhances job satisfaction by fulfilling employees' intrinsic needs for purpose and personal growth, leading to higher levels of engagement and commitment. Unlike achievement motivation, which focuses on external goals and performance outcomes, meaningful work fosters deeper emotional connections and a sense of belonging within the organization. Research indicates that employees who perceive their work as meaningful report greater well-being, increased productivity, and lower turnover rates.
Challenges of Relying Solely on Achievement Motivation
Relying solely on achievement motivation can lead to burnout and decreased job satisfaction as individuals chase external rewards without deeper fulfillment. This approach often overlooks the intrinsic value found in meaningful work, which fosters long-term engagement and resilience. Without meaningful work, motivation may become short-lived, hindering sustained performance and personal growth.
Strategies to Cultivate Meaningful Work Environments
Cultivating meaningful work environments involves aligning individual values with organizational goals to enhance intrinsic motivation and job satisfaction. Implementing strategies such as fostering autonomy, encouraging mastery through continuous learning opportunities, and promoting a sense of purpose can significantly boost employees' engagement and achievement motivation. Creating a culture of recognition and support further solidifies meaningful work experiences, driving sustained motivation and productivity.
Balancing Achievement Goals with Purpose-Driven Work
Balancing achievement goals with purpose-driven work enhances long-term motivation by aligning personal success with meaningful contributions. Research shows that individuals motivated by meaningful work experience higher job satisfaction, sustained engagement, and resilience against burnout compared to those solely focused on achievement. Integrating goal-setting theories with purpose-oriented frameworks fosters motivation that supports both performance outcomes and psychological well-being.
Choosing the Right Motivation Path for Career Success
Achievement motivation drives individuals to excel through goal-setting and measurable success, fostering competitive performance and tangible career milestones. Meaningful work enhances intrinsic motivation by aligning tasks with personal values and purpose, leading to sustained engagement and job satisfaction. Balancing achievement motivation with meaningful work creates a holistic approach to career success, combining external accomplishments with internal fulfillment.
Related Important Terms
Purpose-Driven Motivation
Purpose-driven motivation stems from engaging in meaningful work that aligns with personal values, fostering deeper commitment and sustained achievement motivation. Employees driven by a strong sense of purpose exhibit higher productivity, greater resilience, and enhanced job satisfaction compared to those motivated solely by external rewards or achievement goals.
Ikigai Alignment
Achievement motivation drives individuals to meet specific goals and gain external recognition, while meaningful work fosters intrinsic fulfillment by aligning tasks with personal values. Ikigai alignment integrates both by encouraging pursuit of passion, mission, profession, and vocation, enhancing sustained motivation through a balanced sense of purpose and accomplishment.
Calling Orientation
Achievement motivation centers on attaining specific goals and external recognition, driving individuals through success and tangible rewards, while meaningful work tied to calling orientation fosters intrinsic motivation by aligning tasks with personal values and a sense of purpose. Employees with a strong calling orientation experience higher engagement and satisfaction as their motivation stems from contributing to something greater beyond individual accomplishments.
Values Congruence
Achievement motivation drives individuals to excel through measurable success and goal attainment, while meaningful work fosters motivation by aligning tasks with personal values and a sense of purpose. Values congruence between personal beliefs and organizational mission enhances intrinsic motivation, leading to sustained engagement and higher job satisfaction.
Intrinsic Goal Pursuit
Intrinsic goal pursuit in achievement motivation drives individuals to seek personal growth and mastery, fueling sustained engagement and resilience. Meaningful work enhances intrinsic motivation by aligning tasks with core values, fostering a deeper sense of purpose and fulfillment beyond external rewards.
Legacy Motivation
Legacy motivation, a subset of achievement motivation, drives individuals to pursue meaningful work that transcends personal success by impacting future generations. This form of motivation emphasizes leaving a lasting contribution, blending intrinsic satisfaction with a commitment to purpose beyond immediate accomplishments.
Prosocial Achievement
Prosocial achievement motivation drives individuals to excel by contributing to societal well-being and fostering positive social impact, which enhances intrinsic motivation and job satisfaction. Meaningful work complements this by providing a sense of purpose and alignment with personal values, reinforcing sustained engagement and commitment in prosocial roles.
Impact-Centric Drive
Achievement motivation centers on accomplishing goals and gaining recognition, while meaningful work emphasizes purposeful contributions and personal fulfillment; an impact-centric drive merges both by motivating individuals through the tangible effects their efforts have on others and society. This fusion enhances engagement and sustains motivation by aligning personal success with broader social impact.
Eudaimonic Fulfillment
Achievement motivation drives individuals to reach specific goals and garner external rewards, whereas meaningful work fosters eudaimonic fulfillment by aligning tasks with personal values and intrinsic purpose. Eudaimonic fulfillment enhances long-term motivation through a deep sense of contribution and self-realization beyond mere accomplishment.
Transcendent Work Motive
Achievement motivation drives individuals by the pursuit of personal success and measurable goals, whereas the transcendent work motive emphasizes engaging in meaningful work that contributes to a greater good beyond the self. Research indicates that employees motivated by transcendent goals experience higher job satisfaction and sustained commitment, linking purpose-driven work with enhanced intrinsic motivation and long-term performance.
Achievement motivation vs Meaningful work for motivation. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com