Salary-based motivation offers immediate financial security and clear tangible rewards that can drive career decisions, but it often lacks deeper personal fulfillment. Ikigai-driven motivation, rooted in finding purpose and passion, fosters long-term satisfaction and resilience by aligning work with one's values and strengths. Balancing monetary incentives with intrinsic meaning creates a sustainable and rewarding career path.
Table of Comparison
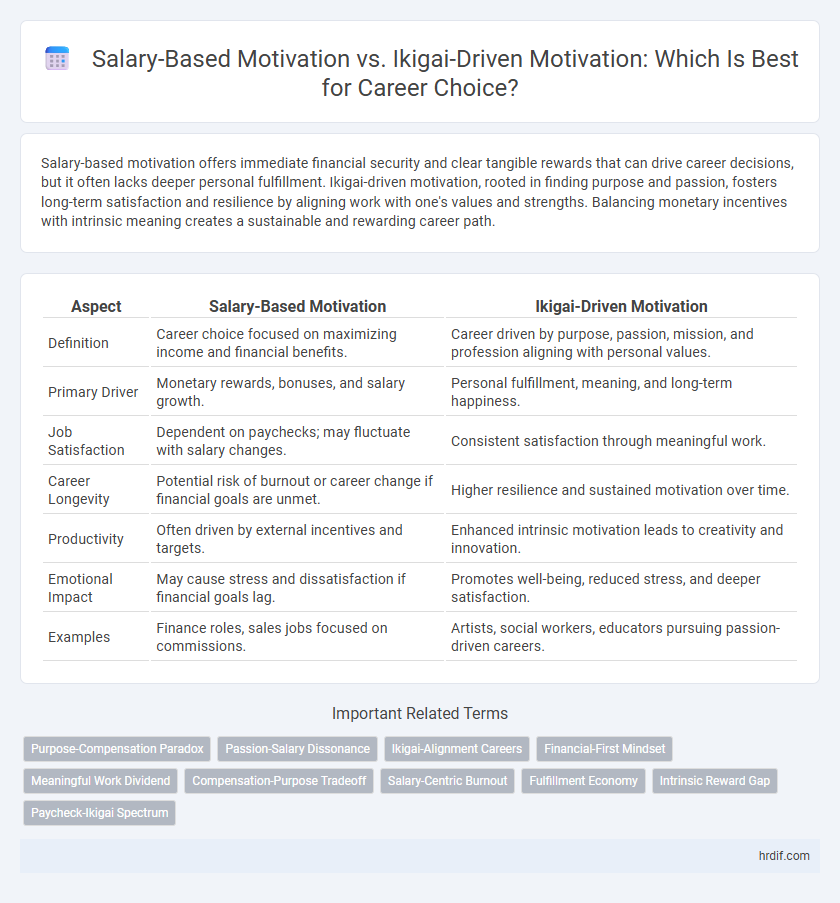
| Aspect | Salary-Based Motivation | Ikigai-Driven Motivation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Career choice focused on maximizing income and financial benefits. | Career driven by purpose, passion, mission, and profession aligning with personal values. |
| Primary Driver | Monetary rewards, bonuses, and salary growth. | Personal fulfillment, meaning, and long-term happiness. |
| Job Satisfaction | Dependent on paychecks; may fluctuate with salary changes. | Consistent satisfaction through meaningful work. |
| Career Longevity | Potential risk of burnout or career change if financial goals are unmet. | Higher resilience and sustained motivation over time. |
| Productivity | Often driven by external incentives and targets. | Enhanced intrinsic motivation leads to creativity and innovation. |
| Emotional Impact | May cause stress and dissatisfaction if financial goals lag. | Promotes well-being, reduced stress, and deeper satisfaction. |
| Examples | Finance roles, sales jobs focused on commissions. | Artists, social workers, educators pursuing passion-driven careers. |
Salary vs Ikigai: Understanding Two Main Career Motivators
Salary-based motivation prioritizes immediate financial rewards and job security, often driving individuals to choose careers with higher paychecks regardless of personal passion or fulfillment. Ikigai-driven motivation centers on finding a career that aligns with one's values, purpose, and passions, fostering long-term satisfaction and intrinsic happiness. Understanding the balance between salary and ikigai helps professionals make career choices that support both economic stability and meaningful engagement.
The Financial Allure: Why Salary Still Matters in Career Choices
Salary remains a critical factor in career decisions due to its direct impact on financial stability, lifestyle, and future planning. High earnings can alleviate stress related to basic needs and enable investment in personal growth and family support. While Ikigai-driven motivation fosters passion and purpose, the financial allure of a substantial salary ensures security and practical well-being, making it a powerful motivator in many professional choices.
What is Ikigai? Exploring Purpose-Driven Career Motivation
Ikigai is a Japanese concept meaning "reason for being," combining passion, mission, vocation, and profession to create purposeful living and career fulfillment. Unlike salary-based motivation that emphasizes financial rewards, Ikigai-driven motivation focuses on intrinsic satisfaction, personal growth, and meaningful contributions. This purpose-driven approach to career choice fosters long-term engagement, resilience, and holistic well-being beyond monetary incentives.
Comparing Short-Term Gains and Long-Term Fulfillment
Salary-based motivation offers immediate financial rewards that satisfy short-term needs and enhance living standards, often leading to quicker job acceptance and stability. Ikigai-driven motivation, rooted in finding purpose and passion, fosters enduring career fulfillment, resilience, and intrinsic satisfaction despite potential initial financial sacrifices. Balancing both approaches can optimize career decisions by addressing essential monetary requirements while nurturing long-term personal and professional growth.
Benefits of Salary-Based Career Decisions
Salary-based career decisions provide financial stability and security, enabling individuals to meet essential needs and plan for the future confidently. Higher salaries often correlate with better access to healthcare, education, and retirement benefits, contributing to overall well-being. This approach also allows for greater flexibility in lifestyle choices and reduces stress related to financial uncertainty.
The Emotional Rewards of Ikigai-Driven Careers
Ikigai-driven careers provide profound emotional rewards by aligning work with personal purpose, fostering a deep sense of fulfillment and meaning beyond monetary compensation. Employees motivated by ikigai often experience increased intrinsic motivation, resilience, and long-term satisfaction. Unlike salary-based motivation, which primarily addresses external incentives, ikigai taps into core values and passions, enhancing overall well-being and mental health in the workplace.
Challenges of Prioritizing Money Over Meaning
Prioritizing salary over ikigai in career choices often leads to decreased job satisfaction and increased burnout due to misalignment with personal values and passions. High income may provide short-term rewards but fails to sustain long-term motivation and engagement, resulting in reduced productivity and mental well-being. Employees driven solely by financial gain face challenges such as lack of purpose, diminished creativity, and higher turnover rates, impacting overall career fulfillment.
Navigating Societal Pressure: Prestige, Pay, and Personal Purpose
Navigating societal pressure often forces individuals to choose between salary-based motivation, which emphasizes financial prestige and external validation, and Ikigai-driven motivation that centers on personal purpose and fulfillment. While high pay can satisfy immediate social expectations and status, Ikigai encourages long-term career satisfaction through aligning work with intrinsic values and passions. Balancing these motivations helps professionals make sustainable career choices that honor both economic needs and deeper personal meaning.
Finding Balance: Integrating Salary and Ikigai in Career Planning
Balancing salary-based motivation with Ikigai-driven motivation creates a sustainable career path that fulfills both financial needs and personal purpose. Integrating competitive compensation with meaningful work enhances job satisfaction, productivity, and long-term engagement. Prioritizing career strategies that align income goals with intrinsic passion fosters holistic professional fulfillment and resilience.
Choosing Wisely: Strategies for Aligning Career With Both Wealth and Purpose
Choosing a career that balances salary-based motivation with ikigai-driven motivation enhances long-term satisfaction and financial stability. Research shows professionals aligned with their ikigai experience higher engagement and resilience, while salary considerations ensure material comfort and security. Integrating both strategies through self-assessment and market analysis promotes a holistic approach to career fulfillment and wealth accumulation.
Related Important Terms
Purpose-Compensation Paradox
Salary-based motivation emphasizes financial rewards as the primary driver of career choice, often leading to higher short-term gains but potential long-term dissatisfaction. Ikigai-driven motivation integrates purpose with profession, balancing personal fulfillment and compensation, highlighting the Purpose-Compensation Paradox where optimal career decisions require aligning meaningful work with sustainable income.
Passion-Salary Dissonance
Passion-salary dissonance occurs when individuals prioritize high-paying jobs over their true interests, leading to decreased long-term motivation and job satisfaction. Studies show that ikigai-driven motivation, which aligns career choices with personal purpose and passion, often results in higher engagement and sustained productivity despite initially lower salaries.
Ikigai-Alignment Careers
Ikigai-alignment careers foster intrinsic motivation by harmonizing personal passion, mission, vocation, and profession, resulting in sustained job satisfaction and overall well-being. Unlike salary-based motivation that emphasizes external rewards, Ikigai-driven motivation enhances long-term engagement and purpose, leading to higher productivity and reduced burnout.
Financial-First Mindset
A financial-first mindset prioritizes salary-based motivation, driving career choices by emphasizing immediate monetary rewards and job security over personal fulfillment. While this approach ensures financial stability, it may overlook long-term satisfaction derived from ikigai-driven motivation, which aligns work with passion and purpose.
Meaningful Work Dividend
Salary-based motivation often prioritizes immediate financial rewards but may lead to lower long-term job satisfaction and engagement. Ikigai-driven motivation integrates personal purpose and passion with professional goals, generating a Meaningful Work Dividend that enhances well-being, creativity, and sustained career fulfillment.
Compensation-Purpose Tradeoff
Salary-based motivation often leads professionals to prioritize immediate financial rewards, potentially causing a tradeoff between compensation and long-term career satisfaction; Ikigai-driven motivation emphasizes aligning work with personal purpose, which can result in sustained engagement despite lower initial pay. Research indicates that balancing monetary incentives with intrinsic purpose enhances overall job performance and employee retention in competitive markets.
Salary-Centric Burnout
Salary-based motivation often leads to burnout due to repetitive dissatisfaction and the relentless pursuit of higher income without personal fulfillment. Ikigai-driven motivation fosters long-term career satisfaction by aligning work with intrinsic passion and purpose, reducing stress and emotional exhaustion.
Fulfillment Economy
Salary-based motivation centers on immediate financial rewards, often driving career choices toward high-paying roles but risking long-term dissatisfaction, while Ikigai-driven motivation aligns work with personal purpose and values, fostering sustained fulfillment and engagement. In the Fulfillment Economy, prioritizing Ikigai cultivates intrinsic motivation and well-being, leading to enhanced productivity and meaningful contributions beyond mere income.
Intrinsic Reward Gap
Salary-based motivation prioritizes financial compensation, often leading to job satisfaction tied to extrinsic rewards, while Ikigai-driven motivation emphasizes purpose and personal fulfillment, bridging the intrinsic reward gap. Research indicates that careers aligned with Ikigai promote higher long-term engagement and well-being compared to roles chosen primarily for salary, as intrinsic satisfaction fuels sustained motivation and productivity.
Paycheck-Ikigai Spectrum
Salary-based motivation centers on financial rewards as the primary driver for career decisions, emphasizing immediate economic benefits and job security. In contrast, Ikigai-driven motivation integrates personal passion, mission, vocation, and profession, fostering long-term fulfillment and purpose beyond the paycheck, creating a holistic approach along the Paycheck-Ikigai Spectrum.
Salary-based motivation vs Ikigai-driven motivation for career choice. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com