Mentor mentoring involves guidance from an experienced individual who provides personalized advice, skill development, and long-term support, enhancing learning efficiency and professional growth. Peer mentoring fosters mutual learning through shared experiences and collaborative problem-solving, promoting empathy and social interaction. Both methods contribute uniquely to knowledge acquisition, but mentor mentoring often delivers deeper insights due to expertise differences.
Table of Comparison
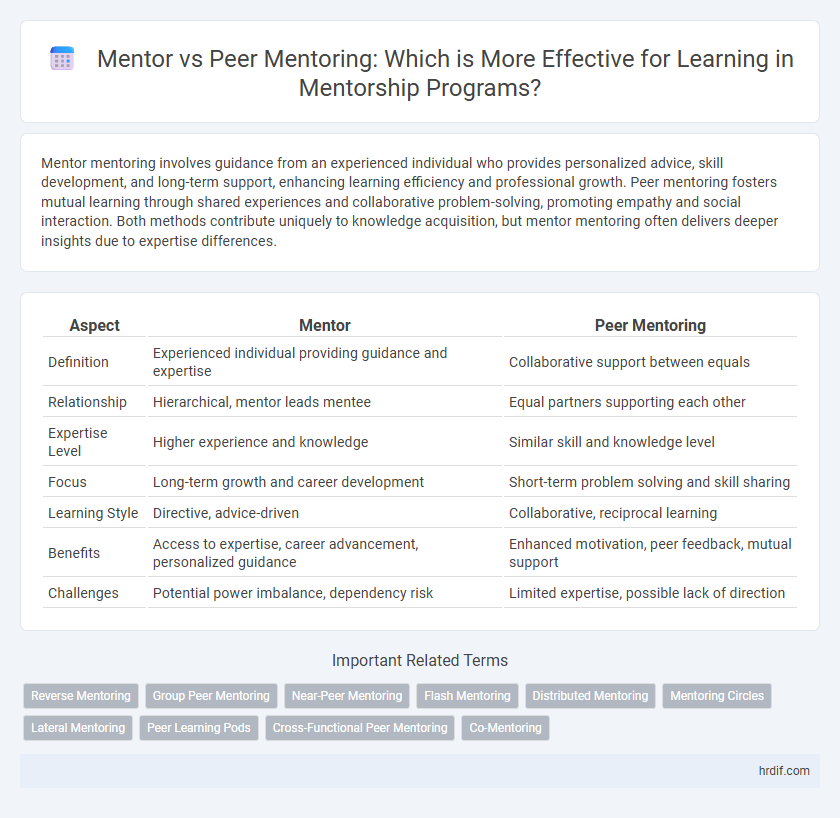
| Aspect | Mentor | Peer Mentoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Experienced individual providing guidance and expertise | Collaborative support between equals |
| Relationship | Hierarchical, mentor leads mentee | Equal partners supporting each other |
| Expertise Level | Higher experience and knowledge | Similar skill and knowledge level |
| Focus | Long-term growth and career development | Short-term problem solving and skill sharing |
| Learning Style | Directive, advice-driven | Collaborative, reciprocal learning |
| Benefits | Access to expertise, career advancement, personalized guidance | Enhanced motivation, peer feedback, mutual support |
| Challenges | Potential power imbalance, dependency risk | Limited expertise, possible lack of direction |
Defining Mentor and Peer Mentoring in Career Development
Mentor mentoring in career development involves an experienced professional guiding a less experienced individual to enhance skills, provide industry insights, and foster long-term career growth. Peer mentoring, conversely, consists of colleagues at similar career stages who exchange knowledge, share challenges, and support each other's professional development through mutual learning. Both mentor and peer mentoring play crucial roles, with mentor mentoring offering expert direction and peer mentoring promoting collaborative growth and immediate feedback.
Core Differences Between Mentor and Peer Mentoring
Mentor mentoring involves guidance from an experienced individual providing expertise, career advice, and long-term development support, while peer mentoring relies on mutual learning and shared experiences among individuals at similar skill levels. The core difference lies in the hierarchical dynamic, where mentors offer authoritative knowledge and peers promote collaborative problem-solving. Effective learning outcomes depend on the mentee's need for specialized insight versus reciprocal growth through equal partnership.
Benefits of Traditional Mentorship for Professional Growth
Traditional mentorship offers personalized guidance from experienced professionals, accelerating skill development and career advancement. Mentors provide valuable industry insights, constructive feedback, and access to expanded networks, fostering long-term professional relationships. This one-on-one dynamic enhances accountability and tailored support, which are crucial for achieving targeted growth in complex work environments.
Advantages of Peer Mentoring in Skill Acquisition
Peer mentoring enhances skill acquisition by fostering relatable communication and mutual understanding, which often accelerates practical learning. It creates a supportive environment where peers feel comfortable sharing challenges and collaboratively developing solutions. This dynamic promotes active engagement and retention of skills through continuous feedback and shared experiences.
When to Choose Mentor vs Peer Mentoring
Choose mentor mentoring when seeking expert guidance, industry-specific knowledge, and long-term career development support, as mentors provide valuable experience and strategic insights. Opt for peer mentoring during collaborative learning, skill-sharing, and mutual problem-solving, where peers offer relatable perspectives and foster a supportive learning environment. Assess goals, experience levels, and desired outcomes to determine whether authoritative mentorship or reciprocal peer interaction best suits your learning needs.
Impact on Workplace Learning and Collaboration
Mentor mentoring provides structured guidance and expert insights that accelerate professional development and foster long-term career growth, enhancing workplace learning outcomes. Peer mentoring promotes collaborative problem-solving and shared knowledge, building a culture of continuous learning and improving team cohesion. Both approaches significantly impact collaboration, with mentor mentoring driving skill mastery and peer mentoring encouraging dynamic, reciprocal learning environments.
Challenges in Mentor and Peer Mentoring Relationships
Challenges in mentor relationships often include power imbalances and communication gaps, which can hinder open dialogue and trust development. Peer mentoring faces difficulties such as lack of experience and potential role confusion, making it harder to provide effective guidance. Both models require clear boundary setting and commitment to overcome these obstacles and foster successful learning dynamics.
Success Stories: Mentorship and Peer Mentoring Outcomes
Mentorship and peer mentoring both foster significant learning outcomes, with mentor-led guidance often resulting in accelerated skill development and career advancement, as seen in numerous success stories from corporate and academic settings. Peer mentoring demonstrates strong benefits in collaborative problem-solving and emotional support, promoting engagement and retention among participants. Case studies highlight that combining mentor expertise with peer interaction creates a comprehensive learning environment that maximizes personal and professional growth.
Integrating Both Approaches for Maximum Career Growth
Combining mentor and peer mentoring leverages the unique strengths of experienced guidance and collaborative support, accelerating skill acquisition and career advancement. Mentor mentoring provides expert insights and strategic advice rooted in industry experience, while peer mentoring fosters mutual learning and real-time problem solving among colleagues. Integrating both approaches creates a holistic development environment that enhances professional growth, adaptability, and long-term success.
Best Practices for Effective Mentorship and Peer Mentoring
Effective mentorship prioritizes clear communication, goal setting, and regular feedback to foster growth and skill development, whether in traditional mentor-mentee or peer mentoring relationships. Best practices in peer mentoring emphasize mutual support, shared experiences, and collaborative problem-solving, creating an environment where both parties benefit from reciprocal learning. Structured frameworks, confidentiality, and commitment to consistent interaction enhance the impact of both mentorship types in achieving learning objectives.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Mentoring
Reverse mentoring fosters dynamic knowledge exchange by pairing less experienced employees with senior leaders, promoting fresh perspectives and digital skills transfer. Unlike traditional mentor relationships, it empowers junior mentors to influence organizational culture and innovation, enhancing learning outcomes across hierarchical levels.
Group Peer Mentoring
Group peer mentoring fosters collaborative learning by leveraging diverse perspectives and shared experiences among participants, enhancing problem-solving skills and mutual support. This approach contrasts with traditional mentor-led models by promoting egalitarian relationships and collective growth within learning communities.
Near-Peer Mentoring
Near-peer mentoring leverages the small age or experience gap between mentor and mentee, fostering relatability and increased engagement compared to traditional mentor relationships with a larger expertise gap. This approach enhances learning outcomes by promoting open communication, personalized guidance, and immediate feedback within a supportive, peer-like environment.
Flash Mentoring
Flash mentoring accelerates learning by providing concise, targeted guidance from experienced mentors, contrasting with peer mentoring which offers ongoing, reciprocal support among equals. This approach maximizes knowledge transfer in short sessions, enhancing skill development and career growth efficiently.
Distributed Mentoring
Distributed mentoring leverages both mentor and peer interactions to enhance learning by providing diverse support across multiple contexts and platforms. Unlike traditional one-on-one mentorship, this approach emphasizes collaborative feedback and real-time problem-solving through interconnected networks of experienced mentors and peers.
Mentoring Circles
Mentoring Circles leverage the benefits of both mentor and peer mentoring by creating collaborative groups where experienced mentors provide guidance while peers support collective learning and shared experiences. This hybrid approach enhances skill development, fosters diverse perspectives, and promotes continuous growth within a supportive community.
Lateral Mentoring
Lateral mentoring fosters reciprocal learning by pairing peers with comparable experience levels, enhancing knowledge exchange and collaborative problem-solving. Unlike traditional mentor-mentee relationships, lateral mentoring promotes mutual growth and a balanced power dynamic, maximizing engagement and skill development.
Peer Learning Pods
Mentor-led learning offers expert guidance and personalized feedback, while Peer Learning Pods foster collaborative knowledge exchange, critical thinking, and shared problem-solving among equals. Peer Learning Pods accelerate skill acquisition by creating a supportive environment where participants actively engage and learn from diverse perspectives.
Cross-Functional Peer Mentoring
Cross-functional peer mentoring enhances learning by enabling individuals from diverse departments to share unique expertise and perspectives, fostering innovation and collaboration. Unlike traditional mentorship, this approach leverages reciprocal knowledge exchange, accelerating skill development across various functions.
Co-Mentoring
Co-mentoring combines the expertise of a mentor with the mutual learning dynamic of peer mentoring, enhancing skill acquisition and critical thinking through collaborative dialogue. This approach fosters reciprocal growth, leveraging the strengths of both experienced mentors and peers to create a comprehensive learning environment.
Mentor vs Peer mentoring for learning Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com