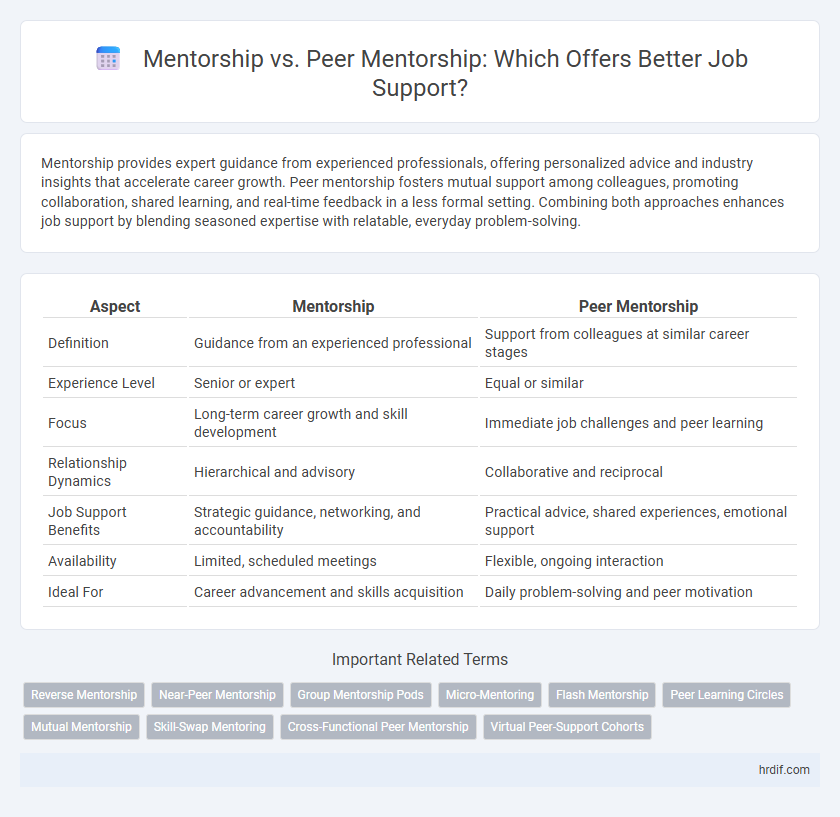
Mentorship provides expert guidance from experienced professionals, offering personalized advice and industry insights that accelerate career growth. Peer mentorship fosters mutual support among colleagues, promoting collaboration, shared learning, and real-time feedback in a less formal setting. Combining both approaches enhances job support by blending seasoned expertise with relatable, everyday problem-solving.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mentorship | Peer Mentorship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Guidance from an experienced professional | Support from colleagues at similar career stages |
| Experience Level | Senior or expert | Equal or similar |
| Focus | Long-term career growth and skill development | Immediate job challenges and peer learning |
| Relationship Dynamics | Hierarchical and advisory | Collaborative and reciprocal |
| Job Support Benefits | Strategic guidance, networking, and accountability | Practical advice, shared experiences, emotional support |
| Availability | Limited, scheduled meetings | Flexible, ongoing interaction |
| Ideal For | Career advancement and skills acquisition | Daily problem-solving and peer motivation |
Defining Mentorship and Peer Mentorship
Mentorship involves a relationship where an experienced professional provides guidance, advice, and support to advance a mentee's career development and skill growth. Peer mentorship, in contrast, is a reciprocal form of support where individuals at similar career stages share knowledge, offer feedback, and collaborate on problem-solving. Both models enhance job support by fostering learning environments, but mentorship typically emphasizes hierarchical knowledge transfer while peer mentorship focuses on mutual growth and shared experiences.
Key Differences Between Mentorship and Peer Mentorship
Mentorship typically involves a more experienced individual providing guidance, career advice, and skill development to a less experienced mentee, often in a hierarchical relationship. Peer mentorship features colleagues or individuals at similar career stages offering mutual support, shared learning, and collaborative problem-solving, fostering a more egalitarian dynamic. Key differences include the directionality of knowledge transfer, the level of experience disparity, and the mentorship goals, with traditional mentorship focusing on expertise and leadership growth, while peer mentorship emphasizes reciprocal support and networking.
Benefits of Traditional Mentorship in Career Growth
Traditional mentorship in career growth offers unparalleled personalized guidance from experienced professionals who provide strategic insights and industry-specific knowledge essential for long-term success. This form of mentorship facilitates deep professional networking, opening doors to exclusive opportunities and enhancing credibility in the job market. Additionally, mentees benefit from direct feedback and tailored advice, accelerating skill development and career advancement.
Advantages of Peer Mentorship for Job Support
Peer mentorship offers distinct advantages for job support by fostering relatable guidance through shared experiences and mutual understanding. It encourages collaborative problem-solving and continuous feedback, enhancing professional growth in real-time. Access to a diverse network within peer groups also expands opportunities for learning and career advancement.
When to Choose a Mentor Over a Peer Mentor
Choosing a mentor over a peer mentor is ideal when seeking guidance from someone with extensive industry experience and a proven track record in your career field. A mentor provides strategic insights, long-term career planning advice, and access to professional networks that peers may not offer. Opt for a mentor when aiming for personalized development and navigating complex workplace challenges beyond the scope of peer-level understanding.
How Peer Mentorship Enhances Workplace Collaboration
Peer mentorship enhances workplace collaboration by fostering open communication and trust among colleagues, which accelerates problem-solving and innovation. Unlike traditional mentorship, peer mentorship creates a reciprocal learning environment where employees share diverse perspectives and skills, leading to improved teamwork and productivity. This collaborative dynamic cultivates a supportive culture that empowers employees to engage more actively and confidently in their roles.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Mentorship Models
Traditional mentorship offers structured guidance from experienced professionals, fostering career growth through expert advice and long-term support. Peer mentorship enhances job support by promoting mutual learning and empathy, helping mentees overcome challenges through shared experiences and collaborative problem-solving. Combining both models addresses typical obstacles such as communication gaps and mismatched expectations, creating a more adaptable and effective support system.
Integrating Both Mentorship Types for Optimal Career Success
Integrating traditional mentorship with peer mentorship creates a comprehensive support network that enhances career growth by combining experienced guidance with empathetic, real-time problem-solving. Traditional mentors offer strategic insights and industry knowledge, while peer mentors provide relatable advice and emotional encouragement, fostering a balanced professional development environment. Combining both mentorship types optimizes job support by leveraging diverse perspectives, accelerating skill acquisition, and building resilience in dynamic career landscapes.
Real-World Examples: Mentorship vs Peer Mentorship Outcomes
Mentorship programs with experienced professionals often yield higher job placement rates and accelerated career growth compared to peer mentorship, according to studies from Harvard Business Review. Real-world examples include IBM's mentorship initiative, which boosted employee promotion rates by 20%, while peer mentorship at Google facilitated better teamwork but showed less impact on job advancement. Employers seeking measurable outcomes prioritize traditional mentorship for skill development and leadership readiness, whereas peer mentorship supports ongoing collaboration and problem-solving.
Tips for Maximizing Job Support Through Mentorship Programs
Mentorship programs offer personalized guidance from experienced professionals, enhancing skill development and career growth, while peer mentorship fosters collaborative learning and mutual support among colleagues facing similar challenges. To maximize job support, set clear goals, communicate regularly, and actively seek feedback within both traditional and peer mentorship relationships. Leveraging diverse perspectives ensures comprehensive learning and strengthens problem-solving abilities in the workplace.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Mentorship
Reverse mentorship leverages the unique insights of junior employees to support senior leaders, fostering innovation and adaptability in job roles. Peer mentorship promotes mutual growth among colleagues at similar career stages, but reverse mentorship specifically enhances leadership development by integrating fresh perspectives from emerging talent.
Near-Peer Mentorship
Near-peer mentorship enhances job support by pairing individuals with mentors who are slightly more experienced, fostering relatable guidance and practical advice tailored to early career challenges; this contrasts with traditional mentorship, which often involves significant experience gaps that can create less accessible communication. Leveraging near-peer mentorship models improves skill development, confidence, and workplace integration by emphasizing shared experiences and mutual growth within similar professional stages.
Group Mentorship Pods
Group mentorship pods provide a structured environment where experienced mentors guide multiple participants simultaneously, offering diverse perspectives and targeted job support. Peer mentorship encourages collaborative learning and mutual encouragement among equals, fostering a supportive community but may lack expert insights found in traditional mentorship.
Micro-Mentoring
Mentorship provides personalized guidance from experienced professionals, enhancing career growth through strategic insights, while peer mentorship fosters collaborative learning and mutual support within similar experience levels. Micro-mentoring, with its focused, brief interactions, offers efficient, targeted advice that combines the benefits of both traditional and peer mentorship for job support.
Flash Mentorship
Flash Mentorship offers targeted, time-efficient guidance from experienced professionals, providing deep industry insights and career advice unlike Peer Mentorship, which relies on mutual support and shared experiences among colleagues at similar levels. This approach accelerates skill development and decision-making in job support by connecting mentees with expert mentors for focused sessions tailored to specific challenges.
Peer Learning Circles
Peer mentorship through Peer Learning Circles fosters collaborative job support by leveraging shared experiences and collective problem-solving, enhancing skill development and professional growth more dynamically than traditional one-on-one mentorship. These circles create inclusive environments where participants exchange real-time feedback and diverse perspectives, accelerating learning outcomes and increasing workplace confidence.
Mutual Mentorship
Mutual mentorship in job support fosters reciprocal learning and growth, where both parties actively share expertise and resources to enhance skills and career development. Unlike traditional mentorship or peer mentorship, mutual mentorship emphasizes balanced collaboration, creating a dynamic exchange of feedback and support that accelerates professional progress.
Skill-Swap Mentoring
Mentorship provides structured guidance from experienced professionals, while peer mentorship fosters mutual learning through shared experiences, with skill-swap mentoring enhancing job support by enabling participants to exchange complementary skills and accelerate career growth. Leveraging skill-swap mentoring in peer mentorship creates dynamic job support networks that build diverse competencies and boost workplace confidence.
Cross-Functional Peer Mentorship
Cross-functional peer mentorship enhances job support by combining diverse expertise and fostering collaborative problem-solving across departments, leading to faster skill development and innovation. Unlike traditional mentorship, this approach encourages reciprocal learning and real-time feedback among peers, optimizing performance and adaptability in dynamic work environments.
Virtual Peer-Support Cohorts
Virtual peer-support cohorts offer collaborative mentorship where members share industry insights and problem-solving strategies, fostering real-time feedback and collective growth. Unlike traditional mentorship, peer cohorts emphasize mutual support and diverse perspectives, enhancing job readiness and professional development in a dynamic, remote environment.
Mentorship vs Peer mentorship for job support Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com