Mentor and peer mentor roles differ significantly in skill-building, with mentors offering experienced guidance and long-term development strategies, while peer mentors provide relatable support and collaborative learning opportunities. Mentors typically bring industry expertise and personalized feedback that accelerates professional growth, whereas peer mentors foster motivation and shared experiences that enhance confidence and practical application. Choosing between the two depends on the learner's need for authoritative insight versus mutual encouragement during their development journey.
Table of Comparison
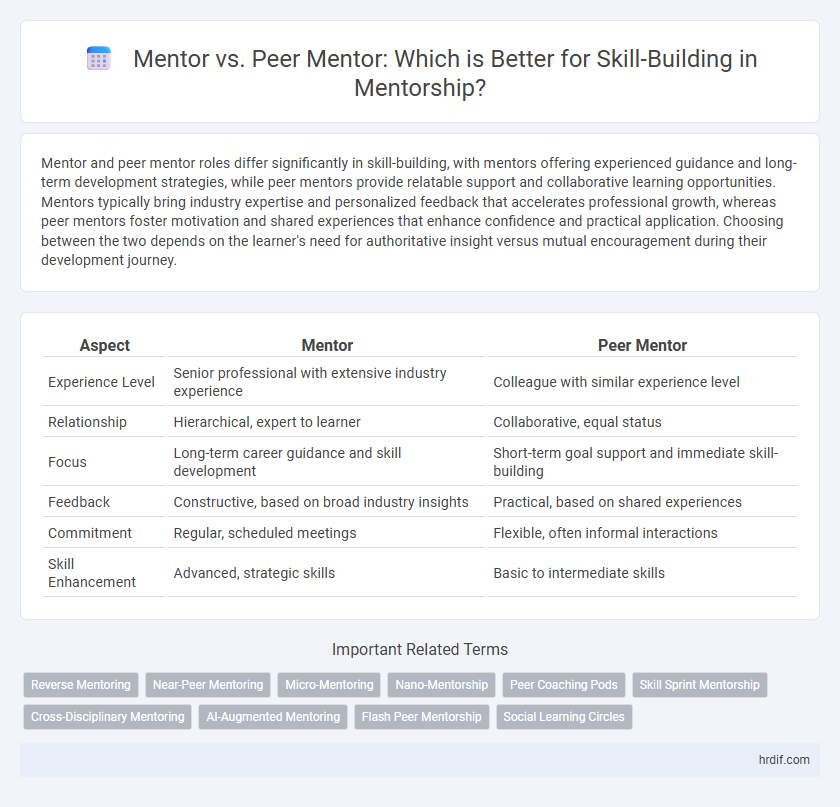
| Aspect | Mentor | Peer Mentor |
|---|---|---|
| Experience Level | Senior professional with extensive industry experience | Colleague with similar experience level |
| Relationship | Hierarchical, expert to learner | Collaborative, equal status |
| Focus | Long-term career guidance and skill development | Short-term goal support and immediate skill-building |
| Feedback | Constructive, based on broad industry insights | Practical, based on shared experiences |
| Commitment | Regular, scheduled meetings | Flexible, often informal interactions |
| Skill Enhancement | Advanced, strategic skills | Basic to intermediate skills |
Understanding Mentorship: Mentor vs Peer Mentor
Mentors are experienced professionals who provide guidance, industry insights, and long-term career advice to accelerate skill-building in specialized areas. Peer mentors offer real-time support, relatable feedback, and collaborative learning opportunities, fostering practical skill development through shared experiences. Both roles complement each other by addressing different aspects of mentorship, combining expertise with peer relatability to optimize growth.
Defining the Roles: Mentor and Peer Mentor
A mentor is an experienced professional who provides guidance, shares industry knowledge, and supports long-term career development, while a peer mentor is a colleague with similar experience who offers relatable advice and mutual skill-building support. Mentors typically have broader expertise and a more authoritative role in shaping mentee growth, whereas peer mentors focus on collaborative learning and addressing immediate challenges through shared experiences. Clearly defining these roles helps organizations optimize mentorship programs by aligning mentee needs with the appropriate type of support.
Skill-Building Approaches: Traditional vs Peer Models
Mentors provide expert guidance and structured skill-building through personalized feedback and experience-based insights, fostering accelerated learning in traditional skill development models. Peer mentors emphasize collaborative learning and mutual support, enabling skill acquisition via shared experiences and real-time problem-solving within a less hierarchical framework. Both approaches enhance skill-building, but traditional mentorship offers targeted expertise while peer mentorship promotes interactive, flexible learning environments.
Benefits of Mentorship for Professional Growth
Mentorship accelerates professional growth by providing tailored guidance, fostering industry-specific knowledge, and enhancing problem-solving skills through experienced mentors' insights. Peer mentors offer relatable support and collaborative learning opportunities that encourage skill development in a less formal, more approachable environment. Combining both mentor types maximizes skill-building by blending expert advice with shared experiences, leading to comprehensive professional advancement.
How Peer Mentors Enhance Skill Development
Peer mentors accelerate skill development by providing relatable guidance rooted in recent, relevant experiences, fostering a collaborative learning environment that encourages active problem-solving. Their proximity in skill level and shared challenges create a supportive atmosphere, promoting confidence and practical application of new skills. This dynamic interaction facilitates continuous feedback and real-time adaptation, enhancing retention and mastery more effectively than traditional mentorship.
Comparing Guidance Styles: Hierarchical vs Collaborative
Mentors typically provide hierarchical guidance, leveraging their extensive experience to direct skill development through structured advice and long-term goal setting. Peer mentors adopt a collaborative approach, engaging in mutual support and sharing real-time feedback to enhance learning in a more interactive and relatable manner. This contrast in guidance styles influences the dynamics of mentorship, where hierarchical mentorship often delivers authoritative expertise, while peer mentoring fosters a partnership centered on shared growth and immediate problem-solving.
Choosing the Right Mentor for Your Career Stage
Selecting the right mentor depends on your career stage and learning goals; traditional mentors offer deep industry experience and guidance critical for early-stage professionals seeking strategic insights. Peer mentors provide relatable, real-time support ideal for mid-career individuals focusing on skill refinement and navigating current challenges. Aligning mentorship type with your developmental needs enhances skill-building effectiveness and career progression.
Real-World Outcomes: Mentor vs Peer Mentor Impact
Mentors typically offer extensive industry experience and strategic guidance, leading to accelerated professional growth and higher job placement rates. Peer mentors provide relatable, ongoing support that fosters skill reinforcement and confidence through shared experiences, enhancing day-to-day learning retention. Real-world outcomes show that combining both mentorship types significantly improves skill acquisition and long-term career success.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Mentorship Relationships
Mentors provide experienced guidance, helping mentees navigate complex skill-building obstacles with customized strategies tailored to individual goals. Peer mentors foster collaborative learning environments, encouraging mutual support and accountability to overcome skill gaps through shared experiences. Both roles address challenges such as communication barriers and motivation lapses, enhancing resilience and confidence in mentees.
Building an Effective Mentorship Strategy
A mentor brings industry experience and strategic guidance that accelerates skill-building by providing personalized feedback and long-term career insights. Peer mentors enhance learning through relatable, real-time problem-solving and collaborative skill development within similar experience levels. Combining structured mentorship with peer support fosters a comprehensive strategy that addresses both foundational knowledge and practical application.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Mentoring
Reverse mentoring leverages the expertise of younger or less experienced individuals to enhance the skills of senior mentors, fostering a dynamic exchange that accelerates learning and innovation. This approach contrasts with traditional mentorship by promoting mutual growth and breaking hierarchical barriers, making skill-building more collaborative and inclusive.
Near-Peer Mentoring
Near-peer mentoring accelerates skill-building by pairing individuals with mentors who are only slightly more experienced, fostering relatable guidance and practical advice. Unlike traditional mentors, near-peer mentors provide immediate, context-specific support that enhances learning through shared recent experiences.
Micro-Mentoring
Mentors offer expert guidance and industry insights critical for advanced skill-building, while peer mentors provide relatable support and collaborative learning opportunities ideal for Micro-Mentoring sessions. Micro-Mentoring leverages brief, focused interactions, making peer mentorship highly effective for immediate skill application and continuous improvement.
Nano-Mentorship
Nano-mentorship accelerates skill-building by pairing individuals with experienced mentors who provide targeted guidance and personalized feedback, unlike peer mentors who offer mutual support but lack advanced expertise. This focused approach in nano-mentorship enhances learning efficiency, particularly for complex skills requiring industry-specific knowledge.
Peer Coaching Pods
Peer Mentor programs, especially Peer Coaching Pods, enhance skill-building by enabling collaborative learning and real-time feedback among equals, fostering mutual growth and accountability. Unlike traditional Mentor roles, Peer Coaching Pods create interactive environments where participants actively engage in problem-solving and skill development together, accelerating professional competency.
Skill Sprint Mentorship
Skill Sprint Mentorship leverages the expertise of mentors who provide targeted guidance and industry insights, accelerating skill acquisition and professional growth. Peer mentors offer collaborative learning environments, fostering mutual feedback and real-time problem-solving, which complements formal mentorship by enhancing practical application and confidence.
Cross-Disciplinary Mentoring
Mentors provide expert guidance tailored to specific domains, while peer mentors facilitate collaborative learning through shared experiences, enhancing skill-building across disciplines by combining specialized knowledge with relatable insights. Cross-disciplinary mentoring bridges gaps between fields, fostering innovation and adaptable skill development by leveraging diverse perspectives from both mentors and peer mentors.
AI-Augmented Mentoring
Mentors offer expert-guided skill-building with deep experience and strategic insights, while peer mentors provide collaborative learning and real-time feedback in AI-augmented mentoring environments. AI tools enhance both roles by personalizing development plans, tracking progress, and facilitating adaptive communication, optimizing skill acquisition through tailored support.
Flash Peer Mentorship
Flash Peer Mentorship accelerates skill-building by leveraging real-time, focused interactions between peers, contrasting traditional mentorship where a more experienced mentor guides over a longer term. This approach fosters rapid knowledge exchange, collaborative problem-solving, and immediate feedback, making it highly effective for developing practical skills in dynamic environments.
Social Learning Circles
Mentors provide expert guidance and personalized feedback, accelerating skill-building through structured knowledge transfer, while peer mentors foster collaborative learning and mutual support within Social Learning Circles, enhancing communication and critical thinking skills. Social Learning Circles leverage the dynamic interaction of peer mentors to create a supportive environment that encourages shared problem-solving and continuous skill development.
Mentor vs Peer Mentor for skill-building. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com