Top-down leaders rely on hierarchical decision-making, emphasizing authority and control, which can limit flexibility and slow response times in dynamic environments. Network leaders foster collaboration across teams, encouraging decentralized input and adaptive problem-solving that drives innovation. Modern leadership structures benefit from blending these approaches to balance clear direction with agility and collective intelligence.
Table of Comparison
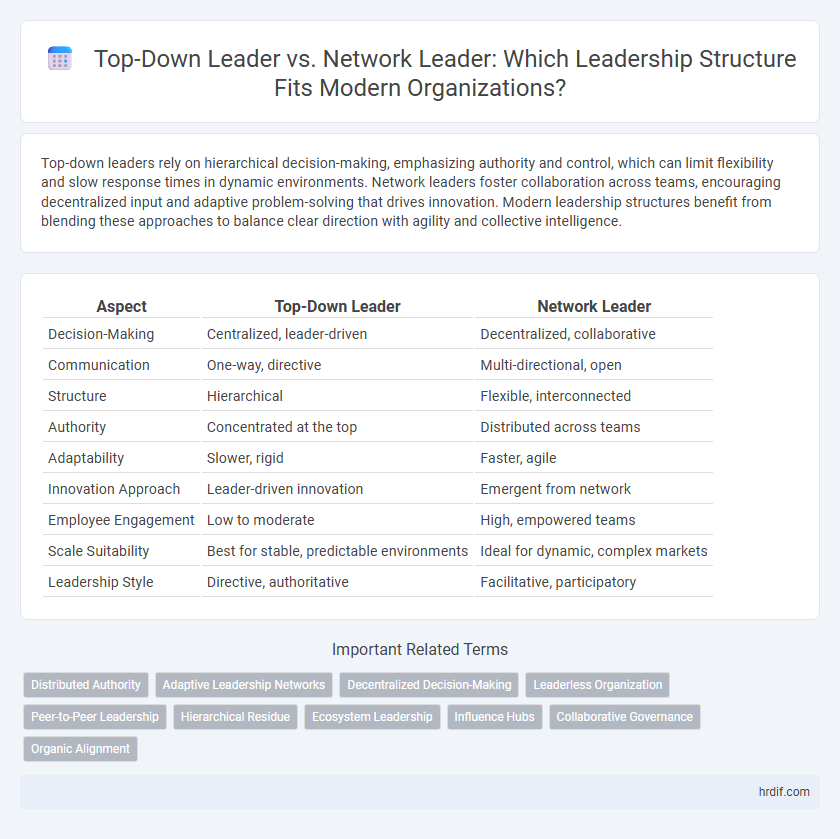
| Aspect | Top-Down Leader | Network Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized, leader-driven | Decentralized, collaborative |
| Communication | One-way, directive | Multi-directional, open |
| Structure | Hierarchical | Flexible, interconnected |
| Authority | Concentrated at the top | Distributed across teams |
| Adaptability | Slower, rigid | Faster, agile |
| Innovation Approach | Leader-driven innovation | Emergent from network |
| Employee Engagement | Low to moderate | High, empowered teams |
| Scale Suitability | Best for stable, predictable environments | Ideal for dynamic, complex markets |
| Leadership Style | Directive, authoritative | Facilitative, participatory |
Defining Top-Down Leadership and Network Leadership
Top-down leadership is characterized by a hierarchical structure where decisions and directives flow from senior leaders to subordinates, emphasizing clear authority and control. Network leadership operates through decentralized, interconnected relationships promoting collaboration, flexibility, and shared decision-making across teams. Modern leadership structures increasingly favor network leadership for its adaptability and empowerment, contrasting with the rigid command and control model of top-down leadership.
Historical Evolution of Leadership Structures
The historical evolution of leadership structures reveals a shift from traditional top-down leaders, who exercised hierarchical control and centralized decision-making, to network leaders fostering collaboration and decentralized influence. Modern organizations increasingly emphasize network leadership to adapt to complex, dynamic environments by leveraging diverse expertise and promoting agile communication. This transition reflects the growing recognition that effective leadership depends on connectivity and shared vision rather than rigid authority.
Core Principles of Top-Down Leadership
Top-down leadership is characterized by clear hierarchies, centralized decision-making, and well-defined roles, emphasizing authority and accountability within organizations. Core principles include directive communication, a focus on control and order, and the delegation of tasks from leaders to subordinates to ensure alignment with strategic goals. This leadership style suits environments requiring quick decision-making and consistent execution but may limit innovation and employee empowerment.
Key Characteristics of Network Leadership
Network leaders prioritize collaboration, empowering team members across hierarchical levels to enhance innovation and agility. They leverage transparent communication, decentralized decision-making, and strong relationship-building to foster trust and adaptability within dynamic organizational environments. This leadership style contrasts with the rigid control of top-down leaders, promoting resilience through interconnected networks rather than command chains.
Decision-Making: Centralized vs Distributed Approaches
Top-down leaders centralize decision-making authority, enabling swift, unified directives crucial for urgent or highly controlled environments. Network leaders distribute decision-making across connected individuals or teams, fostering innovation and adaptability through collaborative input and shared responsibility. Modern leadership increasingly favors distributed approaches, leveraging diverse perspectives to navigate complex, dynamic challenges effectively.
Impact on Organizational Innovation and Agility
A Top-Down Leader often centralizes decision-making, which can limit organizational innovation and slow agility due to slower feedback loops and reduced empowerment at lower levels. In contrast, a Network Leader fosters decentralized communication and collaboration, enabling faster adaptation and increased creative problem-solving across teams. This distributed leadership structure enhances both innovation capacity and organizational responsiveness in dynamic markets.
Employee Engagement and Motivation in Each Model
Top-down leaders drive employee engagement through clear directives and structured accountability, but this often limits autonomy and intrinsic motivation. Network leaders foster collaboration and empowerment, increasing motivation by valuing employee input and creating a sense of ownership. Modern leadership benefits from combining top-down clarity with networked flexibility to maximize engagement and sustain motivation.
Suitability for Different Industries and Business Sizes
Top-down leadership excels in industries with hierarchical structures such as manufacturing and finance, where clear authority and streamlined decision-making are crucial. Network leadership thrives in dynamic, innovation-driven sectors like technology and creative industries, enabling agility and collaborative problem-solving. Small to medium businesses benefit from network leadership through enhanced flexibility, while large corporations often maintain top-down approaches for consistent control and accountability.
Challenges and Pitfalls of Each Leadership Structure
Top-down leadership often faces challenges such as limited adaptability and reduced employee engagement due to its hierarchical decision-making process. Network leadership can struggle with coordination complexity and slower decision-making as it relies on decentralized communication and collaboration among diverse teams. Both structures risk inefficiencies: top-down from rigidity and network leadership from potential ambiguity in authority and accountability.
Choosing the Right Leadership Model for the Future
Top-down leadership centralizes decision-making within a hierarchical framework, enabling quick, authoritative actions often suited to crisis management and established organizational cultures. Network leadership fosters collaboration, agility, and distributed power, promoting innovation and responsiveness in complex, rapidly changing environments. Selecting the optimal leadership model depends on the organization's size, industry dynamics, and strategic priorities, with modern enterprises increasingly favoring network leadership for sustainable growth and employee engagement.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Authority
Top-Down Leaders centralize decision-making power, creating hierarchical structures that may limit agility in dynamic environments, whereas Network Leaders distribute authority across teams to enhance collaboration and rapid innovation. Emphasizing distributed authority fosters empowerment and resilience, enabling organizations to respond effectively to complex challenges in modern leadership frameworks.
Adaptive Leadership Networks
Top-Down Leaders typically rely on hierarchical decision-making, which can limit agility in complex environments, whereas Network Leaders foster Adaptive Leadership Networks that leverage collaboration and shared intelligence to navigate uncertainty effectively. Emphasizing decentralized authority and real-time communication, Network Leaders enhance organizational resilience and innovation in dynamic markets.
Decentralized Decision-Making
Top-down leaders centralize decision-making authority, often resulting in slower responses and limited employee autonomy, while network leaders promote decentralized decision-making by empowering teams throughout the organization, driving agility and innovation. Emphasizing decentralized decision-making in modern leadership structures enhances collaboration, accelerates problem-solving, and adapts more effectively to complex, rapidly changing environments.
Leaderless Organization
Top-down leaders rely on hierarchical control and centralized decision-making, often limiting adaptability in fast-changing environments, whereas network leaders foster collaboration and distributed authority, enabling more innovative and resilient leaderless organizations. Emphasizing shared responsibility and decentralized communication, network leadership structures align with modern demands for agility and employee empowerment.
Peer-to-Peer Leadership
Top-Down Leadership relies on hierarchical authority and centralized decision-making, often slowing responsiveness and innovation in dynamic markets. Network Leaders foster Peer-to-Peer Leadership by empowering distributed teams, enhancing collaboration, agility, and adaptability in modern organizational environments.
Hierarchical Residue
Top-Down Leaders often struggle with hierarchical residue, where outdated authority structures hinder agility and innovation within organizations. Network Leaders bypass these rigid chains of command by fostering decentralized decision-making and collaborative influence, driving adaptability in modern leadership structures.
Ecosystem Leadership
Top-down leaders centralize decision-making and control within hierarchical structures, often limiting adaptability in dynamic business ecosystems. Network leaders foster collaborative relationships across diverse stakeholders, leveraging interconnected resources and collective intelligence to drive innovation and resilience in complex environments.
Influence Hubs
Top-Down Leaders rely on hierarchical authority to direct decision-making, often limiting organizational adaptability and innovation. In contrast, Network Leaders leverage Influence Hubs--strategic nodes within informal networks--to facilitate collaboration, agility, and decentralized influence essential for modern leadership structures.
Collaborative Governance
Top-Down Leadership relies on hierarchical decision-making where authority flows from executives to subordinates, often slowing responsiveness and limiting innovation. Network Leadership fosters Collaborative Governance by promoting decentralized decision-making, enabling diverse teams to co-create solutions and adapt swiftly to complex, dynamic environments.
Organic Alignment
Top-down leaders emphasize centralized decision-making with clear hierarchical control, often leading to rigid structures that may hinder rapid adaptation. Network leaders foster organic alignment by promoting decentralized collaboration, empowering teams to innovate and respond dynamically within modern leadership frameworks.
Top-Down Leader vs Network Leader for modern leadership structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com