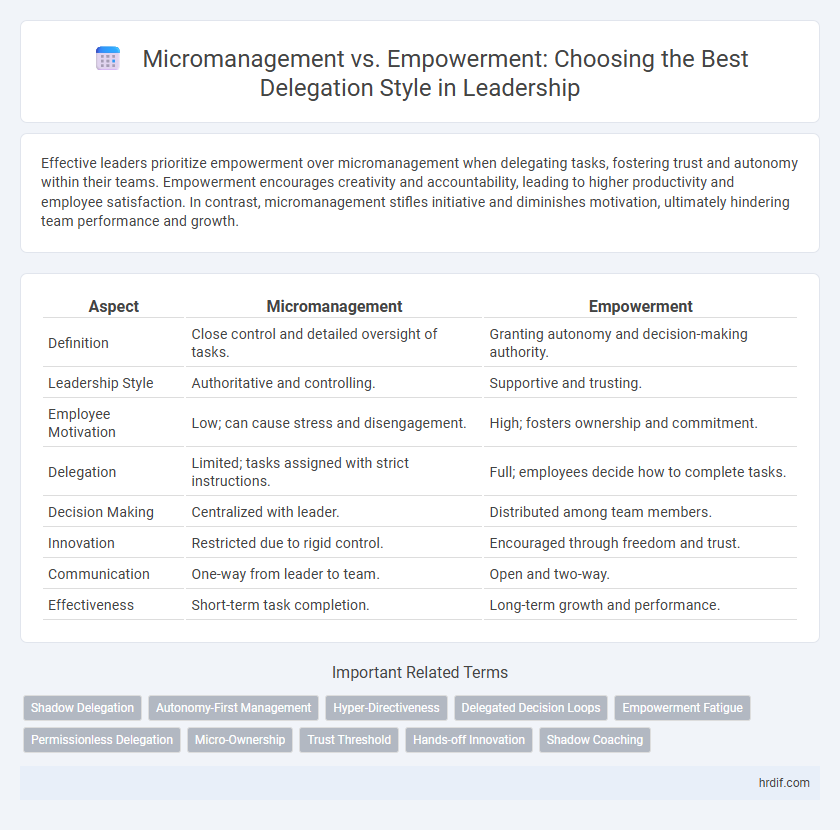
Effective leaders prioritize empowerment over micromanagement when delegating tasks, fostering trust and autonomy within their teams. Empowerment encourages creativity and accountability, leading to higher productivity and employee satisfaction. In contrast, micromanagement stifles initiative and diminishes motivation, ultimately hindering team performance and growth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Micromanagement | Empowerment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Close control and detailed oversight of tasks. | Granting autonomy and decision-making authority. |
| Leadership Style | Authoritative and controlling. | Supportive and trusting. |
| Employee Motivation | Low; can cause stress and disengagement. | High; fosters ownership and commitment. |
| Delegation | Limited; tasks assigned with strict instructions. | Full; employees decide how to complete tasks. |
| Decision Making | Centralized with leader. | Distributed among team members. |
| Innovation | Restricted due to rigid control. | Encouraged through freedom and trust. |
| Communication | One-way from leader to team. | Open and two-way. |
| Effectiveness | Short-term task completion. | Long-term growth and performance. |
Understanding Delegation in Leadership
Effective delegation in leadership hinges on balancing control and autonomy, where micromanagement restricts team creativity and slows progress, while empowerment fosters trust and accelerates achievement. Leaders who empower their teams delegate authority, encouraging decision-making that drives ownership and accountability. Understanding this balance enhances productivity and cultivates a motivated, high-performing workforce.
The Spectrum: Micromanagement vs Empowerment
The spectrum of delegation style ranges from micromanagement, where leaders closely control every task detail, to empowerment, which encourages autonomy and trust in team members. Effective leadership balances these approaches by adapting the level of oversight based on team skills, task complexity, and organizational goals. Shifting towards empowerment promotes innovation, accountability, and employee engagement, while excessive micromanagement often stifles creativity and reduces morale.
Key Traits of Micromanagement
Micromanagement is characterized by excessive control, constant oversight, and a lack of trust in employees' capabilities, which stifles creativity and reduces productivity. Leaders exhibiting micromanagement often engage in detailed task supervision, frequent intervention, and limited delegation, undermining team autonomy. This style contrasts sharply with empowerment, which encourages independence, fosters innovation, and enhances employee motivation through trust and accountability.
Hallmarks of Empowerment in Leadership
Empowerment in leadership is characterized by trust, autonomy, and active support, enabling team members to make decisions and take ownership of their tasks. Leaders who practice empowerment prioritize developing skills, encouraging innovation, and fostering a collaborative environment that drives accountability and motivation. Unlike micromanagement, empowerment enhances employee engagement and productivity by promoting confidence and responsibility within the team.
Impacts on Team Performance and Morale
Micromanagement stifles team creativity and reduces morale by creating a culture of constant oversight, leading to decreased productivity and increased employee turnover. Empowerment fosters trust and autonomy, enhancing motivation, innovation, and overall team performance through shared responsibility. Leaders who delegate with empowerment see improved engagement, higher job satisfaction, and accelerated skill development among team members.
Delegation Styles: Choosing the Right Approach
Effective delegation style directly influences team productivity and morale. Micromanagement, characterized by excessive control and oversight, often leads to reduced autonomy and stifled innovation, while empowerment fosters trust, promotes accountability, and enhances employee engagement. Selecting the appropriate delegation style depends on task complexity, team experience, and organizational goals, balancing guidance with autonomy to optimize performance.
Recognizing When Micromanagement Occurs
Micromanagement occurs when leaders excessively control or monitor team members' tasks, stifling creativity and reducing motivation. Common signs include frequent check-ins, reluctance to delegate meaningful responsibilities, and corrective feedback on minor details. Recognizing these behaviors enables leaders to shift toward empowerment, fostering trust and enhancing team productivity.
Fostering a Culture of Empowerment
Fostering a culture of empowerment enhances team performance by encouraging autonomy and accountability, which contrasts sharply with micromanagement's control-driven approach that stifles creativity and motivation. Leaders who delegate with trust and provide clear goals enable employees to develop problem-solving skills and take ownership of their tasks, resulting in increased innovation and job satisfaction. Empowerment-driven delegation cultivates resilience and adaptive leadership within organizations, essential for sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Overcoming the Challenges of Letting Go
Overcoming the challenges of letting go involves shifting from micromanagement to empowerment, fostering trust and autonomy among team members. Effective delegation requires leaders to clearly define goals while allowing employees the freedom to innovate and take ownership of their tasks. This approach enhances motivation, boosts productivity, and cultivates a culture of accountability.
Building Trust Through Effective Delegation
Effective delegation that fosters empowerment over micromanagement significantly builds trust within teams by promoting autonomy and accountability. Leaders who delegate with clear expectations and provide support without excessive control encourage employee growth and innovation. This trust-based approach enhances team morale, productivity, and long-term organizational success.
Related Important Terms
Shadow Delegation
Shadow delegation, a micromanagement pitfall, occurs when leaders ostensibly delegate tasks but retain control over decisions, stifling team autonomy and innovation. Empowerment-driven delegation contrasts this by entrusting employees with full responsibility and decision-making authority, fostering ownership and enhancing organizational performance.
Autonomy-First Management
Autonomy-first management prioritizes empowering employees by granting decision-making authority, fostering innovation, and increasing job satisfaction, contrasting sharply with micromanagement's restrictive oversight that stifles creativity and reduces productivity. Research shows that teams with higher autonomy outperform those under micromanagement, demonstrating enhanced accountability and stronger leadership development.
Hyper-Directiveness
Hyper-directiveness in micromanagement stifles employee autonomy, leading to decreased motivation and productivity. Empowerment through delegation fosters trust and innovation, enabling leaders to unlock their team's full potential.
Delegated Decision Loops
Micromanagement restricts delegated decision loops by imposing tight control and requiring constant approval, which stifles employee autonomy and slows project momentum. Empowerment enhances delegated decision loops by granting team members authority to make decisions independently, fostering innovation, accountability, and faster problem-solving.
Empowerment Fatigue
Empowerment fatigue occurs when leaders consistently delegate tasks without providing adequate support, leading employees to feel overwhelmed despite increased autonomy. Balancing delegation with clear guidance and resources helps sustain motivation and prevents burnout associated with excessive empowerment.
Permissionless Delegation
Permissionless delegation empowers team members to make decisions autonomously without waiting for explicit approval, enhancing agility and innovation by reducing bottlenecks caused by micromanagement. This leadership style fosters trust, accelerates project timelines, and cultivates ownership, significantly improving overall organizational performance.
Micro-Ownership
Micromanagement stifles team innovation by controlling every detail, while empowerment fosters micro-ownership, encouraging employees to take responsibility and initiative within delegated tasks. Emphasizing micro-ownership enhances accountability and drives higher engagement, leading to improved performance and sustainable leadership success.
Trust Threshold
Micromanagement lowers the trust threshold by restricting autonomy and increasing oversight, which can stifle innovation and reduce employee morale. Empowerment raises the trust threshold by granting decision-making authority, fostering accountability and motivating teams to achieve higher productivity and engagement.
Hands-off Innovation
Empowerment as a delegation style fosters hands-off innovation by granting teams autonomy to experiment and develop creative solutions without constant oversight. This approach contrasts with micromanagement, which stifles innovation by imposing rigid controls and limiting employees' decision-making authority.
Shadow Coaching
Shadow coaching enhances empowerment by fostering trust and autonomy in delegation, allowing leaders to guide without micromanaging. This method develops employee skills and accountability while minimizing intrusive oversight, promoting sustainable leadership growth and performance.
Micromanagement vs Empowerment for delegation style. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com