Micromanagers limit project success by controlling every detail, which stifles team creativity and slows progress. Agile leaders empower their teams, fostering collaboration and adaptability to navigate complex challenges efficiently. This leadership approach enhances innovation and drives better project outcomes through trust and flexibility.
Table of Comparison
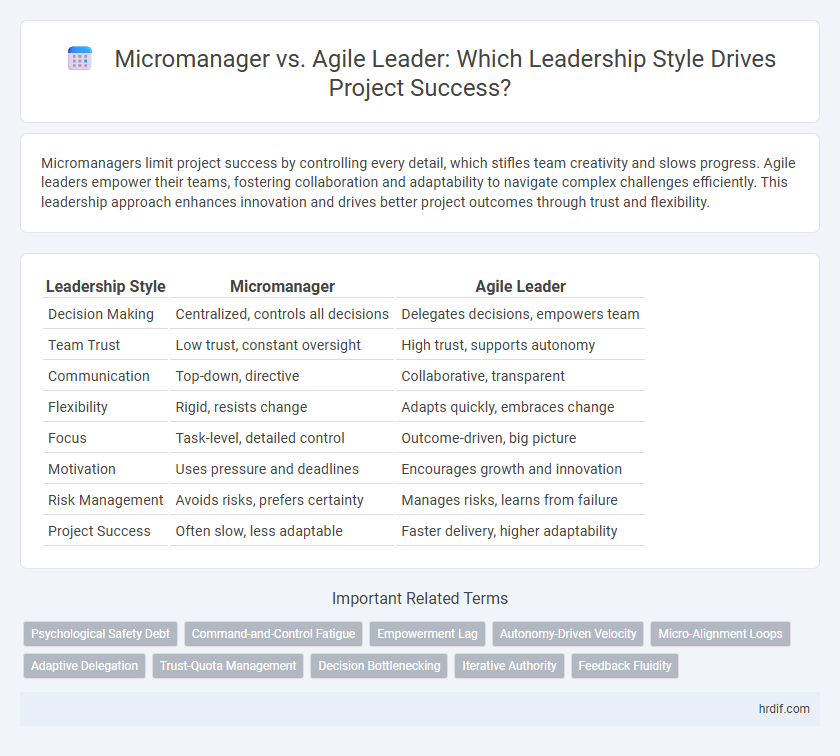
| Leadership Style | Micromanager | Agile Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Centralized, controls all decisions | Delegates decisions, empowers team |
| Team Trust | Low trust, constant oversight | High trust, supports autonomy |
| Communication | Top-down, directive | Collaborative, transparent |
| Flexibility | Rigid, resists change | Adapts quickly, embraces change |
| Focus | Task-level, detailed control | Outcome-driven, big picture |
| Motivation | Uses pressure and deadlines | Encourages growth and innovation |
| Risk Management | Avoids risks, prefers certainty | Manages risks, learns from failure |
| Project Success | Often slow, less adaptable | Faster delivery, higher adaptability |
Defining the Micromanager and Agile Leader
A micromanager closely supervises every detail of a project, often restricting team autonomy and stifling creativity, which can lead to reduced employee morale and productivity. An agile leader, by contrast, empowers teams through trust, flexibility, and adaptive planning, fostering collaboration and innovation in dynamic project environments. Effective project leadership favors agile principles, promoting responsiveness and continuous improvement over rigid control.
Key Traits: Micromanagement vs Agile Leadership
Micromanagers exhibit control-oriented behavior, closely overseeing every project detail, which often stifles team creativity and delays decision-making. Agile leaders emphasize adaptability, empower teams through trust, and foster collaboration to accelerate innovation and responsiveness. This contrast in leadership traits critically impacts project outcomes, with agile leadership promoting higher engagement and productivity.
Communication Styles: Directive vs Collaborative
Micromanagers rely on directive communication, issuing explicit instructions and closely controlling team tasks, which can stifle creativity and reduce morale. Agile leaders embrace collaborative communication, encouraging open dialogue and feedback to foster trust, adaptability, and team empowerment. This shift from control to collaboration enhances project flexibility and drives innovative problem-solving.
Impact on Team Motivation and Engagement
Micromanagers often stifle team motivation by controlling every detail and limiting employee autonomy, leading to decreased engagement and creativity. Agile leaders foster an environment of trust and collaboration, empowering team members to take ownership and contribute innovative solutions. This approach significantly enhances team morale, productivity, and sustained commitment to project goals.
Decision-Making Approaches Compared
Micromanagers maintain tight control over every project detail, often making decisions unilaterally and slowing progress by stifling team autonomy. Agile leaders prioritize collaborative decision-making, empowering team members to contribute ideas and adapt swiftly to changing project dynamics. This approach enhances innovation, responsiveness, and overall project success by leveraging diverse perspectives and promoting trust.
Handling Change: Rigidity vs Adaptability
Micromanagers struggle with handling change due to their rigid control and resistance to shifting project dynamics, often leading to stalled progress and low team morale. Agile leaders embrace adaptability, encouraging flexible responses to evolving challenges and fostering a collaborative environment that drives innovation. This contrast in handling change directly impacts project outcomes, with agile leadership significantly enhancing resilience and success rates.
Trust and Autonomy in Project Teams
Micromanagers often diminish trust by overseeing every detail, which stifles autonomy and hampers team creativity in project leadership. Agile leaders foster trust by empowering project teams with decision-making autonomy, promoting accountability and innovation. This approach enhances collaboration, accelerates problem-solving, and drives project success through shared ownership.
Productivity and Project Outcomes
Micromanagers hinder productivity by enforcing excessive control and limiting team autonomy, often leading to reduced innovation and delayed project outcomes. Agile leaders empower teams through trust and adaptive planning, boosting collaboration and accelerating delivery timelines. This shift from rigid oversight to fluid leadership enhances overall project success and employee engagement.
Employee Growth and Talent Retention
Micromanagers often stifle employee growth by controlling every task, leading to decreased motivation and higher turnover rates. Agile leaders empower teams through trust and autonomy, fostering continuous learning and adaptability that boost talent retention. Prioritizing employee development and open communication creates a resilient workforce committed to long-term project success.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style for Project Success
Micromanagers often hinder project progress by controlling every detail, leading to reduced team motivation and slower decision-making. Agile leaders empower teams with flexibility, fostering collaboration and rapid adaptation to changing project requirements. Selecting an Agile leadership style enhances project success through increased innovation, accountability, and responsiveness.
Related Important Terms
Psychological Safety Debt
Micromanagers accumulate psychological safety debt by fostering an environment of constant scrutiny and fear, which stifles creativity and reduces team morale. Agile leaders prioritize trust and autonomy, cultivating psychological safety that empowers teams to innovate and take ownership of projects.
Command-and-Control Fatigue
Micromanagers often impose excessive oversight and rigid control, leading to Command-and-Control Fatigue characterized by reduced employee autonomy, burnout, and decreased project innovation. Agile leaders foster trust and flexibility, empowering teams to make decisions and adapt rapidly, which mitigates fatigue and enhances productivity in dynamic project environments.
Empowerment Lag
Micromanagers create an empowerment lag by controlling every decision and stifling team autonomy, which slows project momentum and reduces innovation. Agile leaders minimize this lag by delegating authority, fostering trust, and enabling teams to respond quickly to change and deliver results efficiently.
Autonomy-Driven Velocity
Micromanagers restrict team autonomy by closely controlling every task, which stifles innovation and slows project velocity. Agile leaders empower teams with decision-making freedom, fostering autonomy-driven velocity that accelerates delivery and adapts rapidly to change.
Micro-Alignment Loops
Micromanagers rely heavily on Micro-Alignment Loops, frequently checking and controlling every project detail, which often stifles team autonomy and slows progress. Agile Leaders implement Micro-Alignment Loops strategically to ensure clear communication and swift adjustments while empowering teams to innovate and take ownership.
Adaptive Delegation
Micromanagers exert excessive control over project details, hindering team autonomy and innovation, while Agile Leaders practice adaptive delegation by empowering team members to make decisions and adjust tasks based on evolving project needs. This approach enhances flexibility, boosts morale, and drives successful project outcomes through trust and dynamic collaboration.
Trust-Quota Management
Micromanagers often undermine Trust-Quota by excessively controlling tasks and limiting team autonomy, leading to decreased motivation and innovation. Agile Leaders cultivate high Trust-Quota through empowerment and transparent communication, fostering collaboration and adaptive project success.
Decision Bottlenecking
Micromanagers create decision bottlenecks by controlling every detail, slowing project progress and stifling team autonomy, whereas agile leaders delegate authority, enabling faster decision-making and fostering innovation. Efficient project leadership thrives when decision-making is distributed, reducing delays and empowering teams to adapt quickly to changing conditions.
Iterative Authority
Micromanagers exert tight, centralized control over every project task, often stifling creativity and slowing progress, whereas Agile Leaders distribute iterative authority, empowering teams to make decisions and adapt swiftly throughout project cycles. This iterative approach enhances responsiveness, fosters collaboration, and drives continuous improvement in dynamic project environments.
Feedback Fluidity
Micromanagers stifle feedback fluidity by controlling every task and limiting open communication, which hampers team innovation and adaptability. Agile leaders promote continuous, transparent feedback loops, fostering trust and rapid adjustment to project challenges for enhanced team performance.
Micromanager vs Agile Leader for project leadership. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com