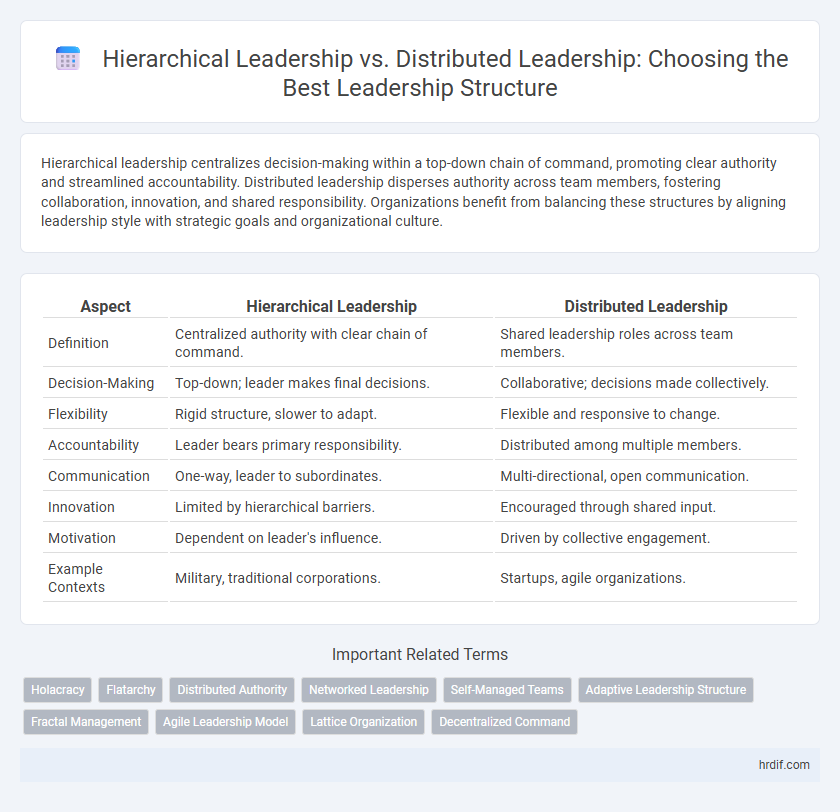
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making within a top-down chain of command, promoting clear authority and streamlined accountability. Distributed leadership disperses authority across team members, fostering collaboration, innovation, and shared responsibility. Organizations benefit from balancing these structures by aligning leadership style with strategic goals and organizational culture.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hierarchical Leadership | Distributed Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized authority with clear chain of command. | Shared leadership roles across team members. |
| Decision-Making | Top-down; leader makes final decisions. | Collaborative; decisions made collectively. |
| Flexibility | Rigid structure, slower to adapt. | Flexible and responsive to change. |
| Accountability | Leader bears primary responsibility. | Distributed among multiple members. |
| Communication | One-way, leader to subordinates. | Multi-directional, open communication. |
| Innovation | Limited by hierarchical barriers. | Encouraged through shared input. |
| Motivation | Dependent on leader's influence. | Driven by collective engagement. |
| Example Contexts | Military, traditional corporations. | Startups, agile organizations. |
Understanding Hierarchical Leadership
Hierarchical Leadership centers on a clear chain of command where authority flows from top-level executives down to lower-level employees, ensuring structured decision-making and accountability. This leadership style promotes efficiency through defined roles and responsibilities, enabling swift implementation of directives. Understanding Hierarchical Leadership reveals its strength in maintaining order and control within large organizations, though it may limit flexibility and employee empowerment.
Defining Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership emphasizes shared responsibility across multiple team members rather than centralized control by a single leader. This approach fosters collaboration, encourages diverse input, and enhances adaptability by leveraging the strengths and expertise of various individuals within the organization. Unlike hierarchical leadership, distributed leadership promotes a more flexible and inclusive decision-making process that can improve organizational performance and innovation.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Distributed Leadership
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making within a defined chain of command, emphasizing clear authority and top-down control, while distributed leadership disperses responsibilities across multiple team members, fostering collaboration and shared accountability. Hierarchical structures often ensure uniformity and clear guidance but may reduce flexibility and innovation compared to distributed leadership, which encourages diverse input and adaptive problem-solving. Key differences include the flow of communication, decision-making scope, and empowerment levels, with hierarchical leadership favoring formal roles and distributed leadership promoting dynamic, inclusive participation.
Advantages of Hierarchical Leadership Structures
Hierarchical leadership structures provide clear authority lines and defined roles that enhance decision-making efficiency and accountability within organizations. This structure supports a well-established chain of command, facilitating straightforward communication and consistent enforcement of policies. By centralizing control, hierarchical leadership often simplifies coordination and accelerates responses in complex or large-scale environments.
Benefits of Distributed Leadership Models
Distributed leadership models enhance organizational agility by empowering multiple team members to take ownership and make decisions, fostering innovation and faster problem-solving. This approach promotes collaboration and leverages diverse expertise, increasing overall effectiveness and employee engagement. By decentralizing authority, distributed leadership reduces bottlenecks common in hierarchical structures and supports continuous learning and adaptability.
Challenges Faced in Hierarchical Leadership
Hierarchical leadership often encounters challenges such as limited communication flow, slow decision-making processes, and reduced employee empowerment. These structures can create bottlenecks where information must pass through multiple layers, hindering agility and innovation. Resistance to change and a lack of flexibility in adapting to dynamic environments further exacerbate these issues, impacting overall organizational performance.
Obstacles to Implementing Distributed Leadership
Obstacles to implementing distributed leadership often include resistance to change from middle management accustomed to hierarchical control, unclear role definitions leading to confusion and inefficiency, and insufficient trust among team members to delegate authority effectively. Organizations entrenched in hierarchical leadership structures may struggle with relinquishing power, hindering collaboration and innovation. Successful transition requires overcoming cultural barriers and establishing clear communication channels to support shared decision-making.
Impact on Employee Engagement and Productivity
Hierarchical leadership often creates clear roles and accountability, which can streamline decision-making but may suppress employee autonomy, leading to lower engagement and productivity. Distributed leadership empowers team members by sharing responsibility and encouraging collaboration, significantly boosting employee motivation and innovation. Studies show organizations adopting distributed leadership report up to 30% higher employee engagement and improved overall productivity metrics.
Organizational Suitability: Which Structure Fits Your Team?
Hierarchical leadership suits organizations with clear authority lines and routine tasks, providing stability and quick decision-making in structured environments. Distributed leadership thrives in dynamic, collaborative teams, promoting shared responsibility and innovation through diverse input. Assess your organization's complexity, team expertise, and adaptability needs to determine which leadership structure enhances productivity and team cohesion.
Transitioning from Hierarchical to Distributed Leadership
Transitioning from hierarchical leadership to distributed leadership involves shifting decision-making authority from a centralized figure to multiple team members, fostering collaboration and empowerment. This change enhances organizational agility and innovation by leveraging diverse expertise and encouraging accountability across all levels. Effective communication and trust-building are essential to successfully implement distributed leadership and ensure alignment with strategic goals.
Related Important Terms
Holacracy
Holacracy represents a shift from hierarchical leadership to distributed leadership by decentralizing decision-making authority and embedding roles within self-managing teams. This organizational structure enhances agility and transparency by replacing traditional top-down control with dynamic governance processes that empower employees at all levels.
Flatarchy
Flatarchy combines elements of hierarchical leadership and distributed leadership by maintaining clear authority while promoting collaboration and innovation across teams. This hybrid structure enables faster decision-making and greater adaptability by empowering employees at various levels to contribute ideas and take initiative.
Distributed Authority
Distributed leadership promotes shared decision-making authority across various organizational levels, enhancing innovation and responsiveness by empowering multiple leaders rather than centralizing control. Unlike hierarchical leadership, which consolidates power at the top, distributed authority fosters collaboration, accountability, and adaptability within teams, driving improved performance and employee engagement.
Networked Leadership
Networked leadership integrates hierarchical and distributed leadership by fostering collaboration across various organizational levels to enhance agility and innovation. This approach leverages interconnected relationships and shared decision-making, enabling adaptive responses in complex environments.
Self-Managed Teams
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making authority within a defined chain of command, often limiting autonomy in self-managed teams, whereas distributed leadership empowers team members to share responsibilities and make collaborative decisions, significantly enhancing adaptability and innovation. Self-managed teams thrive under distributed leadership structures by fostering accountability, mutual trust, and dynamic problem-solving without relying on top-down directives.
Adaptive Leadership Structure
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making authority within a defined chain of command, enabling clear accountability but often limiting flexibility in dynamic environments. Distributed leadership disperses responsibility across team members, fostering adaptive capacity and collaborative problem-solving essential for responding effectively to complex challenges.
Fractal Management
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making authority within a top-down structure, often limiting adaptability and rapid response in complex environments. Distributed leadership, particularly through fractal management, decentralizes leadership roles by embedding self-similar decision-making units across organizational layers, enhancing scalability, agility, and collaborative problem-solving.
Agile Leadership Model
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making power within defined authority levels, often slowing adaptability, whereas distributed leadership disperses responsibilities across team members, fostering agility and responsiveness critical to the Agile leadership model. Agile leadership emphasizes collaboration, empowerment, and iterative problem-solving, aligning closely with distributed leadership to enhance innovation and organizational flexibility.
Lattice Organization
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making within a rigid chain of command, often slowing adaptability, whereas distributed leadership in lattice organizations promotes a flexible, collaborative framework where authority is shared across multiple levels. This decentralized structure enhances innovation and responsiveness by empowering team members to contribute dynamically to organizational goals.
Decentralized Command
Decentralized command in distributed leadership empowers team members by delegating decision-making authority closer to the operational level, enhancing agility and responsiveness. In contrast, hierarchical leadership centralizes control, potentially slowing innovation and reducing adaptability in dynamic environments.
Hierarchical Leadership vs Distributed Leadership for leadership structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com