Autocratic leaders drive team decisions through centralized authority, often leading to faster execution but reduced employee morale and limited engagement. Inclusive leaders promote open communication and participation, fostering a sense of belonging that significantly boosts team motivation and collaboration. Prioritizing inclusivity in leadership enhances overall team performance by valuing diverse perspectives and empowering members.
Table of Comparison
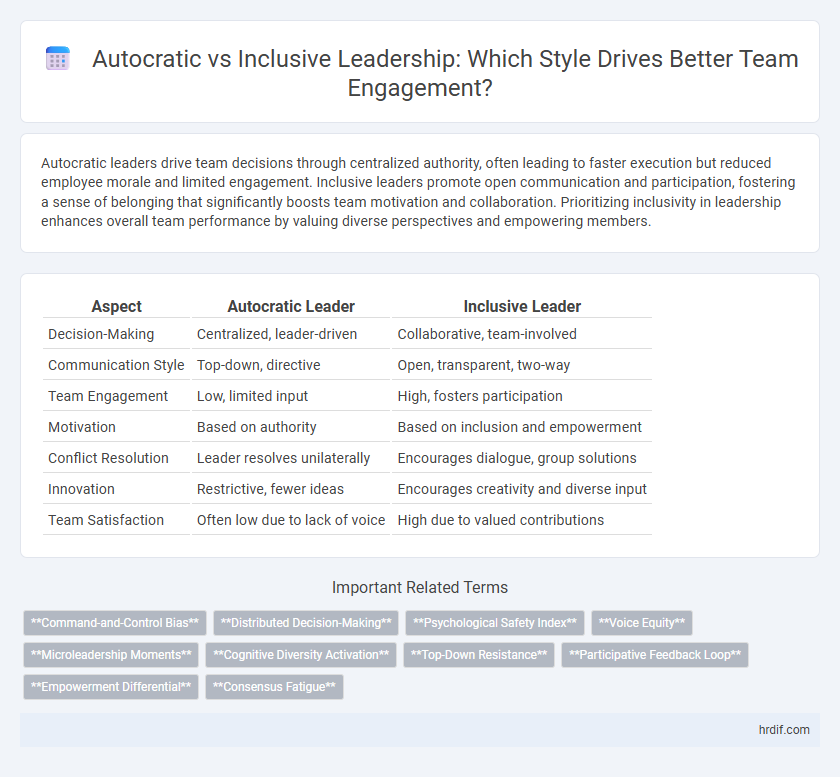
| Aspect | Autocratic Leader | Inclusive Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized, leader-driven | Collaborative, team-involved |
| Communication Style | Top-down, directive | Open, transparent, two-way |
| Team Engagement | Low, limited input | High, fosters participation |
| Motivation | Based on authority | Based on inclusion and empowerment |
| Conflict Resolution | Leader resolves unilaterally | Encourages dialogue, group solutions |
| Innovation | Restrictive, fewer ideas | Encourages creativity and diverse input |
| Team Satisfaction | Often low due to lack of voice | High due to valued contributions |
Understanding Autocratic and Inclusive Leadership Styles
Autocratic leaders make decisions unilaterally, prioritizing control and efficiency, which can limit team engagement and creativity. Inclusive leaders foster collaboration by actively seeking diverse perspectives, promoting psychological safety, and empowering team members to contribute. Understanding these leadership styles is essential for optimizing team dynamics, as inclusive leadership typically enhances engagement, motivation, and innovation.
Key Traits of Autocratic Leaders
Autocratic leaders exhibit decisive decision-making, centralized control, and clear directives that drive quick execution and maintain order within teams. Their authoritative approach often results in high efficiency but may suppress team creativity and reduce engagement. Effective autocratic leaders balance firmness with communication to sustain motivation despite limited collaboration.
Key Traits of Inclusive Leaders
Inclusive leaders foster team engagement by promoting open communication, valuing diverse perspectives, and encouraging collaboration, resulting in higher employee satisfaction and innovation. Unlike autocratic leaders who centralize decision-making and limit input, inclusive leaders empower team members through active listening and empathy, building trust and commitment. Key traits of inclusive leaders include emotional intelligence, cultural awareness, and a strong commitment to equity and fairness in the workplace.
Impact on Team Motivation and Morale
Autocratic leaders often decrease team motivation and morale by limiting employee autonomy and fostering a controlling environment, which can lead to disengagement and low creativity. Inclusive leaders enhance team motivation by actively involving members in decision-making, recognizing diverse contributions, and promoting psychological safety. Research shows inclusive leadership positively impacts employee satisfaction, collaboration, and long-term team performance.
Decision-Making: Top-Down vs. Collaborative
Autocratic leaders make decisions unilaterally, driving efficiency but often limiting team input and reducing engagement. Inclusive leaders foster collaborative decision-making, encouraging diverse perspectives that enhance team commitment and innovation. Studies show teams with inclusive leadership experience higher morale and productivity compared to those led autocratically.
Employee Engagement in Autocratic Teams
Autocratic leadership often results in lower employee engagement due to limited autonomy and restricted communication, causing team members to feel undervalued and disengaged. Inclusive leaders foster open dialogue and collaboration, promoting a sense of belonging and empowerment that significantly enhances employee motivation and commitment. In autocratic teams, enhancing engagement requires intentional efforts to involve employees in decision-making processes and recognize their contributions.
Employee Engagement in Inclusive Teams
Inclusive leaders foster higher employee engagement by encouraging collaboration, valuing diverse perspectives, and promoting open communication within teams. Unlike autocratic leaders who rely on top-down decision-making, inclusive leadership creates a sense of belonging and empowerment that drives motivation and productivity. Research shows that inclusive teams experience increased job satisfaction, reduced turnover, and enhanced innovation due to active participation and mutual respect.
Communication Patterns and Feedback
Autocratic leaders dominate communication with top-down directives, limiting team input and reducing engagement, while inclusive leaders foster open dialogue and value diverse perspectives, enhancing collaboration and motivation. Feedback in autocratic settings is typically one-way and critical, which can stifle creativity, whereas inclusive leaders encourage bidirectional feedback that promotes continuous improvement and trust. Research shows inclusive communication patterns correlate with higher employee satisfaction and retention compared to autocratic communication styles.
Productivity and Performance Outcomes
Autocratic leaders drive productivity through directive control and rapid decision-making, often achieving short-term performance gains but risking lower team engagement and creativity. Inclusive leaders foster collaboration and open communication, enhancing team motivation and sustained performance by leveraging diverse perspectives. Studies show inclusive leadership results in higher employee satisfaction, innovation, and long-term productivity compared to autocratic approaches.
Choosing the Right Leadership Style for Your Team
Autocratic leaders make decisions unilaterally, which can streamline processes but often diminishes team engagement and creativity in collaborative environments. Inclusive leaders actively involve team members in decision-making, fostering higher morale, stronger commitment, and innovative problem-solving. Choosing the right leadership style depends on the team's needs, task complexity, and desired level of employee empowerment for optimal engagement.
Related Important Terms
Command-and-Control Bias
Autocratic leaders exhibit a command-and-control bias that often stifles team engagement by limiting input and decision-making autonomy, resulting in reduced motivation and creativity. Inclusive leaders reverse this bias by fostering open communication and shared authority, which enhances team collaboration, trust, and overall engagement.
Distributed Decision-Making
An inclusive leader fosters team engagement through distributed decision-making, empowering members to contribute diverse perspectives and enhancing collective ownership. In contrast, an autocratic leader centralizes decisions, which can limit team involvement and reduce motivation by restricting input and autonomy.
Psychological Safety Index
Autocratic leaders often score lower on the Psychological Safety Index due to their top-down decision-making, which can inhibit open communication and reduce team engagement. Inclusive leaders foster higher psychological safety by encouraging participation and valuing diverse perspectives, resulting in enhanced trust and collaborative team dynamics.
Voice Equity
Autocratic leaders often limit voice equity by centralizing decision-making and suppressing team input, which can diminish engagement and creativity. Inclusive leaders promote voice equity by encouraging diverse perspectives and active participation, fostering higher team engagement and collaborative innovation.
Microleadership Moments
Microleadership moments under autocratic leaders often involve top-down directives that limit team input, reducing overall engagement and innovation. Inclusive leaders leverage these brief interactions to actively solicit diverse perspectives, fostering a collaborative environment that enhances team commitment and performance.
Cognitive Diversity Activation
Autocratic leaders often suppress cognitive diversity activation by enforcing uniform thinking, which limits team innovation and engagement. Inclusive leaders actively harness cognitive diversity by encouraging varied perspectives, fostering deeper collaboration and higher team engagement.
Top-Down Resistance
Autocratic leaders often face high top-down resistance due to their centralized decision-making and lack of team input, which can diminish team engagement and morale. Inclusive leaders minimize resistance by fostering open communication and involving team members in decisions, thereby boosting collaboration and commitment.
Participative Feedback Loop
Autocratic leaders often limit team engagement by controlling decision-making, which hinders the participative feedback loop essential for innovation and morale. Inclusive leaders foster continuous two-way communication, encouraging diverse input that strengthens the feedback loop and drives team collaboration and engagement.
Empowerment Differential
Autocratic leaders centralize decision-making, often limiting team members' autonomy and stifling empowerment, which can reduce overall engagement and innovation. Inclusive leaders actively distribute authority, fostering a sense of ownership and encouraging diverse contributions, thereby significantly enhancing team empowerment and engagement.
Consensus Fatigue
Autocratic leaders often diminish team engagement by enforcing decisions without input, leading to quicker exhaustion from top-down mandates, whereas inclusive leaders foster consensus-building that enhances participation but may risk consensus fatigue from prolonged decision-making processes. Balancing swift authority with collaborative involvement is essential to prevent consensus fatigue while maintaining high team morale and effectiveness.
Autocratic Leader vs Inclusive Leader for team engagement. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com