Hierarchical leadership emphasizes a clear chain of command where decisions flow from top executives down to subordinates, ensuring control and accountability within the organization. Distributed leadership spreads decision-making authority across various levels and team members, fostering collaboration and adaptability in complex environments. Choosing between these structures depends on organizational goals, with hierarchical models benefiting stability and efficiency while distributed models enhance innovation and responsiveness.
Table of Comparison
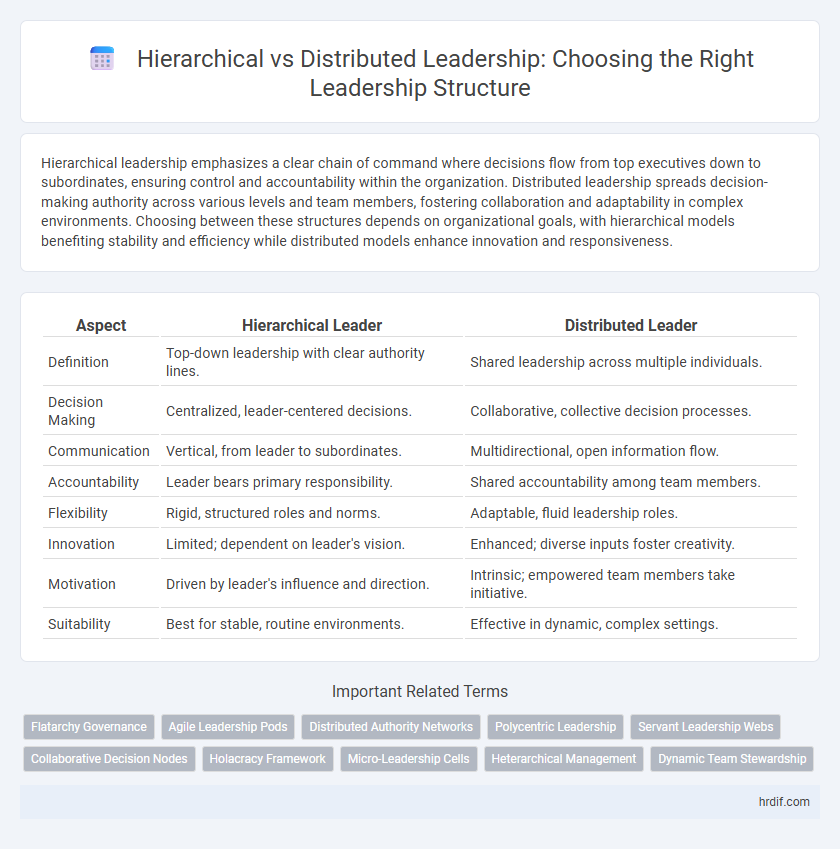
| Aspect | Hierarchical Leader | Distributed Leader |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Top-down leadership with clear authority lines. | Shared leadership across multiple individuals. |
| Decision Making | Centralized, leader-centered decisions. | Collaborative, collective decision processes. |
| Communication | Vertical, from leader to subordinates. | Multidirectional, open information flow. |
| Accountability | Leader bears primary responsibility. | Shared accountability among team members. |
| Flexibility | Rigid, structured roles and norms. | Adaptable, fluid leadership roles. |
| Innovation | Limited; dependent on leader's vision. | Enhanced; diverse inputs foster creativity. |
| Motivation | Driven by leader's influence and direction. | Intrinsic; empowered team members take initiative. |
| Suitability | Best for stable, routine environments. | Effective in dynamic, complex settings. |
Understanding Hierarchical Leadership Structures
Hierarchical leadership structures centralize decision-making authority at the top levels, creating clear lines of command and accountability within an organization. This model facilitates efficient control and coordination but may slow down responsiveness and limit innovation due to rigid formal roles. Understanding the power dynamics and communication flow in hierarchical leadership is crucial for optimizing organizational performance and employee engagement.
The Fundamentals of Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership emphasizes collaborative decision-making and shared responsibilities across team members, enhancing organizational adaptability and innovation. Unlike hierarchical leadership, where authority is centralized, distributed leadership leverages diverse expertise and fosters empowerment at multiple levels. This structure improves communication flow, encourages accountability, and drives collective problem-solving, aligning leadership efforts with dynamic organizational goals.
Key Differences Between Hierarchical and Distributed Leadership
Hierarchical leadership centralizes authority within a top-down structure where decisions flow from senior leaders to subordinates, emphasizing control and clear chains of command. Distributed leadership disperses decision-making power across multiple team members, fostering collaboration and shared responsibility to enhance innovation and adaptability. Key differences include the concentration of authority, decision-making speed, and the level of employee empowerment within each leadership model.
Pros and Cons of Hierarchical Leadership in the Workplace
Hierarchical leadership in the workplace offers clear authority lines and streamlined decision-making, enhancing accountability and consistency across teams. However, it can lead to reduced employee autonomy, slower innovation, and potential communication bottlenecks due to its rigid structure. The emphasis on top-down control may hinder adaptability and employee engagement compared to more distributed leadership models.
Benefits and Challenges of Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership fosters collaboration by empowering multiple team members to take initiative, enhancing innovation and decision-making speed. Challenges include potential role ambiguity and the need for strong communication frameworks to prevent conflicts and ensure alignment. This leadership model increases adaptability in complex organizations but requires ongoing trust-building and accountability mechanisms.
Impact on Decision-Making: Hierarchical vs Distributed Leaders
Hierarchical leaders centralize decision-making authority, resulting in faster but potentially less diverse outcomes due to limited input from lower levels. Distributed leaders promote collaborative decision-making, leveraging diverse perspectives to enhance innovation and adaptability, though this process may require more time to reach consensus. Organizations benefit from distributed leadership by fostering empowerment and improving problem-solving capabilities across teams.
Influence on Team Collaboration and Innovation
Hierarchical leaders often centralize decision-making power, which can limit team collaboration and slow innovation due to restricted input from lower-level members. Distributed leadership fosters a shared responsibility model, enhancing team collaboration by encouraging diverse perspectives and collective problem-solving. This inclusive approach accelerates innovation by leveraging the full potential of team members' skills and creativity.
Adapting Leadership Styles for Organizational Growth
Hierarchical leaders maintain clear, top-down authority, which streamlines decision-making and enforces consistency in established organizations. Distributed leaders share responsibility across teams, fostering innovation and agility essential for dynamic, growth-oriented environments. Adapting leadership styles by integrating hierarchical clarity with distributed collaboration enhances organizational resilience and scalability.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Each Structure
Hierarchical leadership structures have proven effective in organizations like the military, where clear authority and decision-making streamline operations during crises. Distributed leadership models excel in innovative companies such as Google, fostering collaboration and creativity across teams. Case studies reveal hierarchical leadership enhances control and efficiency, while distributed leadership drives engagement and adaptability.
Choosing the Right Leadership Structure for Your Organization
Selecting the right leadership structure hinges on organizational goals, culture, and scale. Hierarchical leaders provide clear authority lines, ideal for environments requiring consistent decision-making and accountability, while distributed leaders foster collaboration and adaptability, suiting dynamic, innovative settings. Evaluating the complexity of tasks, employee expertise, and the need for agility guides the choice between these models to maximize efficiency and drive sustainable success.
Related Important Terms
Flatarchy Governance
Flatarchy governance blends hierarchical leader clarity with distributed leader flexibility, fostering agility and innovation within organizations. This structure reduces traditional layers, empowering teams to collaborate dynamically while maintaining strategic oversight.
Agile Leadership Pods
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making power within a clear chain of command, which can slow innovation in Agile Leadership Pods by limiting team autonomy and adaptability. Distributed leadership empowers team members across Agile pods to collaboratively share responsibilities and make real-time decisions, driving greater innovation, responsiveness, and engagement.
Distributed Authority Networks
Distributed authority networks empower multiple leaders across various levels, enhancing flexibility and innovation within organizations by decentralizing decision-making processes. This leadership structure contrasts with hierarchical leadership, which consolidates power at the top, often limiting responsiveness and adaptability in dynamic environments.
Polycentric Leadership
Polycentric leadership emphasizes a distributed leadership structure where decision-making authority is shared across multiple centers rather than concentrated in a singular hierarchical leader. This approach enhances adaptability and responsiveness by empowering diverse leaders within an organization to contribute their expertise and lead initiatives collaboratively.
Servant Leadership Webs
Servant Leadership Webs emphasize the power of distributed leadership by fostering collaboration, shared responsibility, and empowerment across all organizational levels, contrasting the top-down control of hierarchical leaders. This structure enhances trust, innovation, and adaptability by connecting leaders and followers in a supportive, networked environment.
Collaborative Decision Nodes
Hierarchical leaders centralize decision-making authority at the top, creating a clear chain of command but limiting collaborative input across different levels. Distributed leaders promote collaborative decision nodes by empowering multiple stakeholders to share responsibility and contribute diverse perspectives, enhancing adaptability and innovation within the leadership structure.
Holacracy Framework
Hierarchical leaders centralize decision-making authority, often resulting in slower adaptability, whereas distributed leaders in Holacracy Framework share autonomy across roles, fostering agility and empowering self-management. Holacracy's structure replaces traditional management layers with dynamic governance circles that emphasize transparency and continuous role evolution.
Micro-Leadership Cells
Hierarchical leadership centralizes decision-making within a top-down structure, often limiting agility and innovation in Micro-Leadership Cells by restricting autonomy at lower levels. Distributed leadership empowers these cells with shared authority and collaborative problem-solving, fostering responsiveness and enhanced team engagement within the organization's leadership framework.
Heterarchical Management
Heterarchical management promotes a flexible leadership structure where decision-making authority is distributed across multiple nodes rather than concentrated in a single hierarchical leader, enhancing adaptability and collaboration. This distributed leadership model fosters innovation and responsiveness by leveraging diverse expertise and shared accountability within the organization.
Dynamic Team Stewardship
Hierarchical leaders maintain centralized authority, directing team roles and decisions to ensure clear accountability, while distributed leaders foster dynamic team stewardship by empowering members to share leadership responsibilities and adapt quickly to changing circumstances. This flexible approach enhances collaboration, innovation, and responsiveness within teams operating in complex environments.
Hierarchical Leader vs Distributed Leader for leadership structure. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com