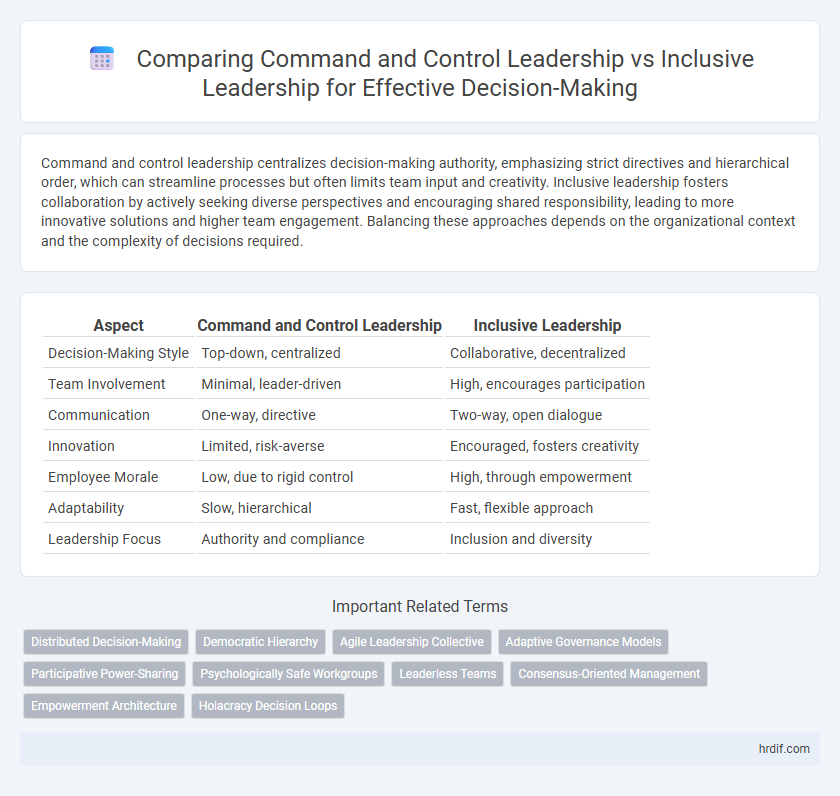
Command and control leadership centralizes decision-making authority, emphasizing strict directives and hierarchical order, which can streamline processes but often limits team input and creativity. Inclusive leadership fosters collaboration by actively seeking diverse perspectives and encouraging shared responsibility, leading to more innovative solutions and higher team engagement. Balancing these approaches depends on the organizational context and the complexity of decisions required.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Command and Control Leadership | Inclusive Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making Style | Top-down, centralized | Collaborative, decentralized |
| Team Involvement | Minimal, leader-driven | High, encourages participation |
| Communication | One-way, directive | Two-way, open dialogue |
| Innovation | Limited, risk-averse | Encouraged, fosters creativity |
| Employee Morale | Low, due to rigid control | High, through empowerment |
| Adaptability | Slow, hierarchical | Fast, flexible approach |
| Leadership Focus | Authority and compliance | Inclusion and diversity |
Understanding Command and Control Leadership in Decision-Making
Command and control leadership centralizes decision-making authority, emphasizing hierarchical structure and directive communication to enforce compliance and maintain order. This approach prioritizes swift, top-down decisions, often at the expense of team input and adaptability. While efficient in crisis situations, it risks stifling innovation and employee engagement by limiting diverse perspectives in the decision-making process.
Inclusive Leadership: Definition and Core Principles
Inclusive leadership promotes diverse perspectives and collaborative decision-making by valuing each team member's unique contributions. Core principles include empathy, active listening, transparency, and fostering psychological safety to encourage open dialogue and innovation. This approach enhances team engagement and drives better outcomes through shared ownership and trust.
Historical Evolution of Leadership Styles
The historical evolution of leadership styles reveals a shift from rigid Command and Control approaches, characterized by top-down decision-making and hierarchical authority, towards Inclusive Leadership that values collaboration, diverse perspectives, and shared decision-making power. Early industrial-age leadership emphasized efficiency and obedience, while contemporary leadership theories prioritize emotional intelligence, empowerment, and stakeholder engagement. This transformation reflects broader social changes and advances in organizational psychology, highlighting the effectiveness of inclusive practices in adaptive and innovative decision-making.
Key Differences Between Command and Control and Inclusive Leadership
Command and Control leadership relies on centralized decision-making where authority is exercised top-down, often limiting team input and flexibility. Inclusive Leadership emphasizes collaboration, valuing diverse perspectives and fostering open communication to enhance decision quality. Key differences include the distribution of power, engagement levels, and adaptability in dynamic environments.
Impact of Leadership Style on Team Morale and Engagement
Command and Control leadership often results in lower team morale and engagement due to limited autonomy and restricted communication, leading to decreased motivation and creativity. Inclusive leadership fosters collaboration and values diverse perspectives, significantly enhancing team commitment and satisfaction. Research shows teams under inclusive leaders report higher productivity and psychological safety, driving sustained organizational success.
Decision-Making Speed vs. Quality: A Comparative Analysis
Command and control leadership accelerates decision-making speed by centralizing authority but risks compromising quality due to limited input from team members. Inclusive leadership enhances decision quality through diverse perspectives and collaborative problem-solving, though it may slow down the process. Balancing rapid decisions with thorough analysis requires integrating elements of both styles depending on situational demands.
Inclusivity as a Driver for Innovation in Organizations
Inclusive leadership fosters a culture where diverse perspectives contribute to decision-making, enhancing creativity and innovation within organizations. Embracing inclusivity enables leaders to tap into a broader range of ideas, driving adaptive solutions and sustaining competitive advantage. Organizations that prioritize inclusive decision-making report higher employee engagement and improved problem-solving outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Leadership Approach
Command and Control leadership often faces challenges such as limited employee engagement and reduced innovation due to its top-down decision-making structure. Inclusive Leadership, while fostering collaboration and diverse perspectives, may encounter difficulties in achieving swift decisions and managing conflicting input from team members. Both approaches present limitations in balancing control with flexibility, impacting organizational responsiveness and team morale.
Adapting Leadership Style to Organizational Culture
Adapting leadership style to an organization's culture directly impacts decision-making efficacy, where Command and Control suits hierarchical, risk-averse environments requiring clear directives and accountability. Inclusive leadership thrives in collaborative, innovative cultures, promoting diverse input and shared ownership to enhance creativity and employee engagement. Understanding these dynamics enables leaders to balance authority with empowerment, aligning strategies with cultural values for optimal organizational performance.
Selecting the Right Leadership Model for Effective Decision-Making
Effective decision-making hinges on selecting the appropriate leadership model tailored to the organizational context and goals. Command and control leadership excels in high-pressure situations requiring quick decisions and clear authority, while inclusive leadership fosters diverse perspectives and collective input, enhancing creativity and long-term commitment. Organizations benefit from integrating situational awareness to balance directive guidance with participative engagement, optimizing outcomes through adaptive leadership strategies.
Related Important Terms
Distributed Decision-Making
Distributed decision-making empowers teams by dispersing authority across various levels, fostering agility and responsiveness beyond the rigid Command and Control hierarchy. Inclusive leadership cultivates collaboration and diverse input, enhancing problem-solving effectiveness through shared responsibility and collective intelligence.
Democratic Hierarchy
Democratic hierarchy in leadership balances command and control with inclusive decision-making by encouraging participation from all levels while maintaining clear accountability structures. This approach enhances organizational agility and innovation by integrating diverse perspectives within a structured framework.
Agile Leadership Collective
Agile Leadership Collective emphasizes Inclusive Leadership over traditional Command and Control by fostering collaborative decision-making that enhances team agility and innovation. This approach drives faster problem-solving and higher engagement by valuing diverse perspectives within adaptive, transparent processes.
Adaptive Governance Models
Adaptive governance models emphasize inclusive leadership by integrating diverse stakeholder input and fostering collaboration, enhancing decision-making flexibility in complex environments. Command and control structures limit adaptability through rigid hierarchies, whereas inclusive leadership promotes responsiveness and innovation essential for dynamic governance challenges.
Participative Power-Sharing
Participative power-sharing in leadership fosters collaborative decision-making by distributing authority among team members, enhancing engagement and innovation compared to the centralized command and control model that concentrates decision-making with top leaders. Inclusive leadership emphasizes transparency, collective input, and shared responsibility, resulting in improved trust, adaptability, and overall organizational performance.
Psychologically Safe Workgroups
Command and Control leadership often limits psychological safety by discouraging open dialogue and fostering fear of mistakes, whereas Inclusive Leadership promotes trust and collaboration, enabling diverse perspectives to inform decision-making. Psychologically safe workgroups under Inclusive Leadership experience higher engagement, creativity, and resilience, driving more effective and adaptive organizational outcomes.
Leaderless Teams
Command and control decision-making centralizes authority, often limiting the adaptive capacity and innovation of leaderless teams by restricting input and collaboration. Inclusive leadership empowers these teams through distributed decision-making, enhancing engagement, diverse problem-solving, and collective ownership of outcomes.
Consensus-Oriented Management
Consensus-oriented management fosters inclusive leadership by integrating diverse perspectives in decision-making, enhancing collaboration and team commitment. Unlike command and control styles that rely on unilateral directives, this approach emphasizes shared ownership and collective problem-solving to drive sustainable organizational success.
Empowerment Architecture
Command and Control leadership centralizes decision-making authority, limiting team autonomy and often stifling innovation, whereas Inclusive Leadership fosters an Empowerment Architecture that distributes authority, encourages diverse input, and enhances collaborative decision-making. Empowerment Architecture within Inclusive Leadership promotes trust, accountability, and agility by enabling team members to take ownership and contribute meaningfully to organizational goals.
Holacracy Decision Loops
Command and Control decision-making centralizes authority, often leading to slower responses and reduced adaptability, whereas Inclusive Leadership embraces Holacracy Decision Loops, promoting distributed authority and faster, more transparent decision cycles. Holacracy's iterative governance processes empower teams to self-organize, increasing agility and collective intelligence in complex organizational environments.
Command and Control vs Inclusive Leadership for decision-making. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com