Internships offer hands-on experience and skill-building opportunities within a company, providing practical exposure to industry roles. Fellowships focus on advanced professional development through research, mentorship, and specialized projects, often emphasizing leadership and innovation. Choosing between an internship and a fellowship depends on career goals, desired learning outcomes, and the level of expertise sought.
Table of Comparison
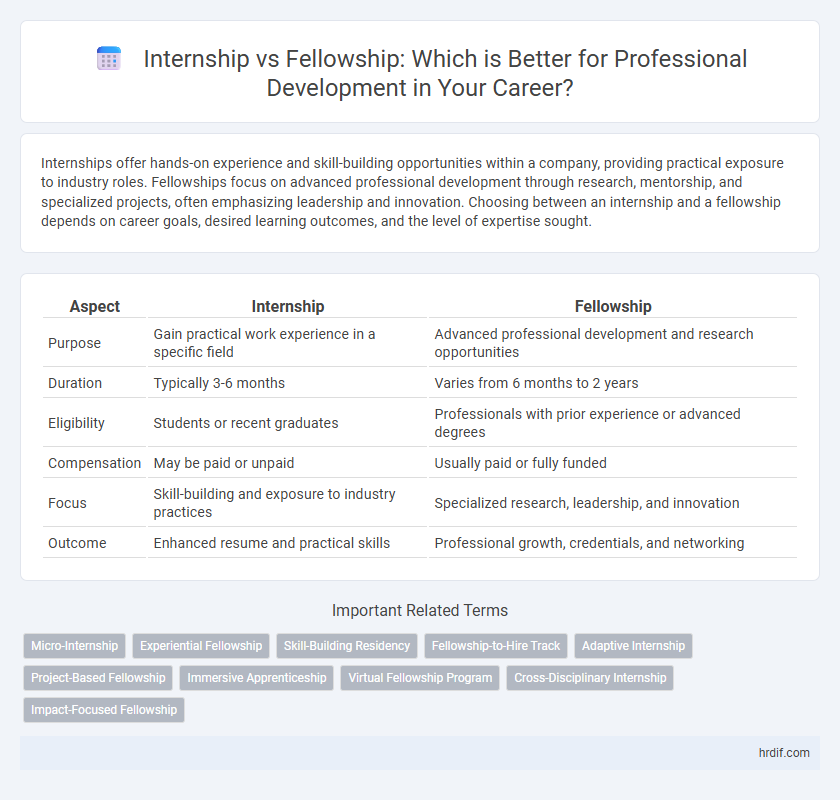
| Aspect | Internship | Fellowship |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Gain practical work experience in a specific field | Advanced professional development and research opportunities |
| Duration | Typically 3-6 months | Varies from 6 months to 2 years |
| Eligibility | Students or recent graduates | Professionals with prior experience or advanced degrees |
| Compensation | May be paid or unpaid | Usually paid or fully funded |
| Focus | Skill-building and exposure to industry practices | Specialized research, leadership, and innovation |
| Outcome | Enhanced resume and practical skills | Professional growth, credentials, and networking |
Defining Internships and Fellowships
Internships are structured work experiences designed for students or recent graduates to gain practical skills and industry exposure, typically lasting a few months. Fellowships often provide more specialized, project-based learning opportunities for professionals or scholars, focusing on research, leadership, or advanced expertise development. Both internships and fellowships contribute significantly to professional development but differ in scope, duration, and targeted participants.
Key Differences Between Internships and Fellowships
Internships typically offer short-term, practical work experience and skill development within a specific industry, targeting students or recent graduates aiming to gain hands-on exposure. Fellowships provide structured, often research-oriented professional development with mentorship and financial support, designed for individuals seeking advanced expertise and leadership growth. Key differences include the duration, scope, compensation, and focus on either practical training (internships) versus specialized, in-depth learning and career advancement (fellowships).
Eligibility Criteria for Internships vs. Fellowships
Eligibility criteria for internships typically include being a student or recent graduate seeking practical experience, often requiring enrollment in a relevant academic program or proof of recent completion. Fellowships usually demand advanced qualifications, such as a completed degree or professional experience, and may target specific fields or research objectives. Internships prioritize skill-building opportunities for early-career individuals, while fellowships emphasize specialized development and contributions to a discipline.
Learning Outcomes: Internship vs. Fellowship
Internships typically offer hands-on experience in a practical work environment, enhancing specific job-related skills and providing exposure to industry practices. Fellowships focus more on research, leadership development, and specialized knowledge acquisition, often involving mentorship and intellectual exploration. Learning outcomes from internships emphasize skill application and workplace integration, while fellowships prioritize expertise development and professional networking.
Career Advancement: Which Offers More Growth?
Internships provide hands-on experience and skill-building opportunities essential for entry-level career advancement, allowing individuals to explore industry roles and develop practical competencies. Fellowships often offer specialized, research-focused projects and networking access with industry leaders, facilitating deeper professional development and higher-level career growth. Choosing between the two depends on whether immediate skill acquisition or long-term career trajectory and leadership opportunities are prioritized for professional advancement.
Financial Compensation: Internship or Fellowship Benefits
Internships typically offer modest or unpaid financial compensation aimed at providing practical experience, while fellowships often provide substantial stipends or salaries to support advanced professional development and research. Financial benefits of fellowships include tuition coverage, living allowances, and travel grants, which are less common in internships. Choosing between internship and fellowship depends on budget needs and the level of financial support required for career advancement.
Networking Opportunities in Internships vs. Fellowships
Internships provide extensive networking opportunities by placing participants directly within industry environments where they collaborate with professionals, attend meetings, and engage in day-to-day operations. Fellowships often offer more specialized, mentorship-driven networks that connect fellows with thought leaders and experts in niche fields, fostering long-term professional relationships. Both formats are valuable, but internships usually present broader, more diverse networking experiences while fellowships focus on depth and specialized connections.
Application Process Comparison
Internship application processes generally require submitting a resume, cover letter, and sometimes academic transcripts or references, with a focus on relevant skills and experience. Fellowship applications are often more competitive and demand detailed project proposals, personal statements, and letters of recommendation, emphasizing research goals and professional impact. Timelines for fellowships tend to be longer, involving interviews and multiple review stages compared to the typically quicker internship selection.
Industry Preferences: Internship or Fellowship?
Internships are preferred by industries seeking hands-on experience and immediate contribution from candidates, often valuing skill application and workplace integration. Fellowships attract organizations focused on research, innovation, and long-term project development, providing deeper expertise and specialized knowledge. Industry preferences vary, with tech and business sectors favoring internships for talent pipeline development, while academic and nonprofit sectors lean toward fellowships.
Choosing the Right Path for Your Professional Goals
Internships offer hands-on experience and skill development in specific industries, ideal for recent graduates seeking practical exposure and entry-level opportunities. Fellowships provide specialized training, mentorship, and research opportunities, suited for professionals aiming to deepen expertise and contribute to academic or innovative projects. Selecting the right path depends on your career stage and long-term objectives, balancing immediate skill acquisition against advanced professional growth.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Internship
Micro-Internships offer short-term, project-based work experiences that provide flexible opportunities for skill development and resume building, differentiating them from fellowships which typically involve longer-term commitments with a focus on research or leadership in a specific field. These micro-internships allow professionals to gain targeted experience in diverse roles, enhancing career growth and industry exposure without the extensive time commitment of traditional fellowships.
Experiential Fellowship
Experiential fellowships offer in-depth professional development through immersive, project-based learning and mentorship, enabling participants to gain specialized expertise beyond traditional internship responsibilities. These fellowships often provide higher-level access to industry networks and leadership opportunities, accelerating career growth more effectively than standard internships.
Skill-Building Residency
Internships provide hands-on experience through practical projects and real-world tasks, fostering essential skill-building in a professional environment, while fellowships emphasize advanced research and specialized training often within a residency setting. Skill-building residencies in fellowships offer immersive opportunities for deep expertise development and networking with industry experts, accelerating career growth beyond typical internship frameworks.
Fellowship-to-Hire Track
The Fellowship-to-Hire Track offers a strategic pathway for professional development by combining immersive project experience with mentorship, often leading to direct employment opportunities. Unlike traditional internships focused on short-term learning, this model emphasizes long-term skill acquisition and organizational fit, enhancing career trajectories in competitive industries.
Adaptive Internship
Adaptive internships provide hands-on experience tailored to evolving industry needs, offering flexible learning environments that enhance skills more effectively than traditional fellowships. These programs prioritize real-world application and personalized mentorship, making them ideal for professionals seeking dynamic career growth.
Project-Based Fellowship
Project-based fellowships offer immersive professional development by engaging participants in real-world projects, fostering advanced skills and industry connections beyond the typical internship scope. Unlike internships, fellowships emphasize specialized project ownership and often provide structured mentorship, enhancing career growth and expertise in targeted fields.
Immersive Apprenticeship
Internships provide hands-on experience through short-term, immersive apprenticeships that focus on practical skill-building within a specific industry, while fellowships often offer deeper research opportunities and professional networking over a longer duration. Immersive apprenticeships within internships accelerate professional development by integrating real-world projects and mentorship, fostering industry-ready expertise more rapidly than traditional fellowships.
Virtual Fellowship Program
Virtual Fellowship Programs offer immersive, project-based experiences that enhance specialized skills and professional networks more effectively than traditional internships, which often emphasize general work exposure. These fellowships provide structured mentorship and access to industry experts, accelerating career growth in niche fields through remote collaboration and tailored learning.
Cross-Disciplinary Internship
Cross-disciplinary internships offer immersive, hands-on experience across multiple fields, fostering versatile skill sets and enhancing professional adaptability. Fellowships typically emphasize research or specialized study, while internships prioritize practical application and real-world industry exposure, crucial for holistic career development.
Impact-Focused Fellowship
Impact-focused fellowships provide immersive, project-based experiences designed to develop leadership skills and drive social change, often offering higher responsibility and networking opportunities than traditional internships. While internships primarily emphasize skill acquisition and industry exposure, fellowships prioritize measurable impact and strategic problem-solving in professional development.
Internship vs Fellowship for professional development. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com