Internships typically offer comprehensive project work that spans several weeks or months, providing in-depth industry experience and opportunities for skill development. Micro-internships focus on short-term, specific projects that allow students to gain quick exposure and contribute tangible results without long-term commitment. Both formats provide valuable hands-on experience, but micro-internships suit those seeking flexibility and immediate application, while traditional internships cater to immersive learning and career exploration.
Table of Comparison
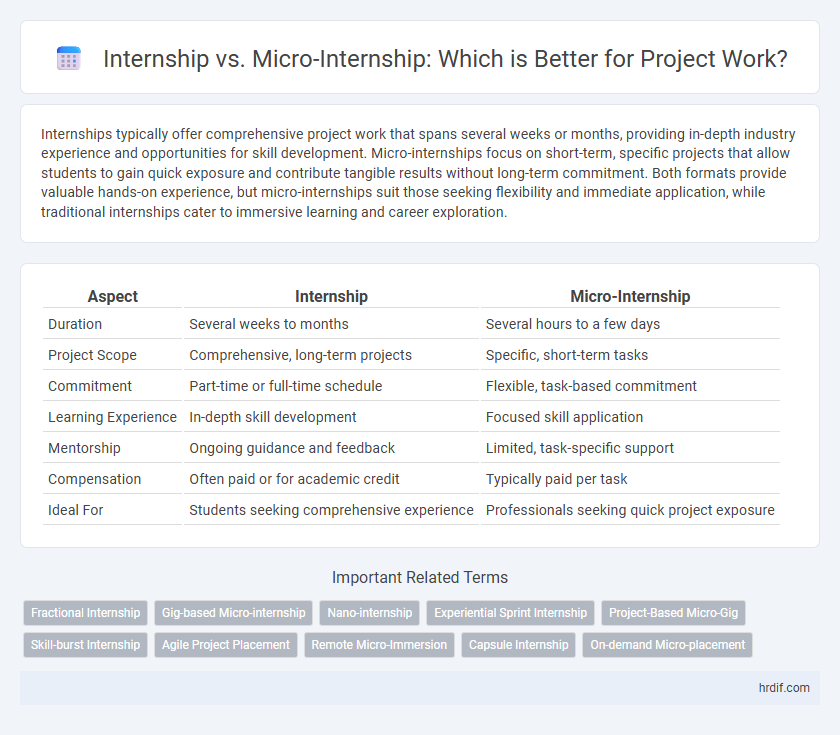
| Aspect | Internship | Micro-Internship |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Several weeks to months | Several hours to a few days |
| Project Scope | Comprehensive, long-term projects | Specific, short-term tasks |
| Commitment | Part-time or full-time schedule | Flexible, task-based commitment |
| Learning Experience | In-depth skill development | Focused skill application |
| Mentorship | Ongoing guidance and feedback | Limited, task-specific support |
| Compensation | Often paid or for academic credit | Typically paid per task |
| Ideal For | Students seeking comprehensive experience | Professionals seeking quick project exposure |
Understanding Internships and Micro-internships
Internships typically involve longer-term commitments, ranging from several weeks to months, allowing interns to gain in-depth experience through comprehensive project work and consistent mentorship. Micro-internships are short-term, project-based assignments lasting from a few hours to a few weeks, designed for quick skill application and immediate results in specific tasks. Both formats offer valuable learning opportunities, with internships fostering broader professional development and micro-internships providing flexible, targeted experiences.
Key Differences Between Internships and Micro-internships
Internships typically span several months, offering in-depth project involvement, while micro-internships are short-term engagements lasting a few days to weeks, focusing on specific, well-defined tasks. Internships often require a greater time commitment and provide broader learning opportunities with mentorship, whereas micro-internships emphasize flexibility and quick, outcome-oriented contributions. Compensation varies, with traditional internships sometimes unpaid or modestly paid, while many micro-internships offer clear, upfront payment for discrete projects.
Duration and Commitment: What to Expect
Internships typically require a longer duration, ranging from several weeks to months, demanding consistent, full-time or part-time commitment which fosters in-depth project involvement and skill development. Micro-internships offer shorter, flexible assignments often lasting a few days to a couple of weeks, designed for quick, focused project contributions with minimal commitment. The choice between the two depends on the desired level of engagement and the project timeline.
Types of Project Work in Internships vs Micro-internships
Internships typically involve long-term projects allowing interns to engage in comprehensive tasks such as research, product development, and strategic planning, which provide in-depth industry experience. Micro-internships focus on short-term, skill-specific projects like data analysis, content creation, or market research, enabling rapid completion and immediate impact. These micro-projects emphasize agility and specific skill application, contrasting with the broader scope and extended timelines found in traditional internships.
Skill Development Opportunities
Internships provide comprehensive skill development opportunities through extended project work, enabling in-depth learning and mentorship in real-world settings. Micro-internships offer concentrated, short-term projects that help build specific skills quickly, ideal for gaining targeted experience in a flexible timeframe. Both formats enhance professional growth, but internships foster broader competencies while micro-internships focus on immediate, task-oriented expertise.
Networking Prospects in Both Models
Internships provide extensive networking opportunities through prolonged interaction with industry professionals, fostering deeper connections and mentorship possibilities. Micro-internships offer concise, task-specific engagements that enable rapid exposure to diverse companies and professionals, accelerating portfolio development and contact expansion. Choosing between these models depends on whether sustained relationship-building or varied, short-term professional interactions align better with career goals.
Compensation and Incentives Comparison
Micro-internships typically offer payment on a per-project basis, providing immediate compensation aligned with short-term deliverables, while traditional internships often include a fixed stipend or hourly wage, which may be unpaid in some cases. Incentives for micro-internships frequently emphasize portfolio-building and flexible scheduling, appealing to students seeking specific skill acquisition without long-term commitment. In contrast, traditional internships may provide broader career development opportunities, networking, and potential for full-time employment but can vary significantly in financial rewards and benefits.
Ideal Candidates for Internships vs Micro-internships
Internships are ideal for candidates seeking comprehensive, long-term project involvement and skill development within a specific industry, often requiring a significant time commitment and offering in-depth mentorship. Micro-internships suit individuals looking for short-term, flexible project work that provides targeted experience and opportunities to showcase specific skills without extended engagements. Candidates pursuing internships typically aim for holistic career growth, whereas those choosing micro-internships prioritize diverse, rapid exposure to various tasks and industries.
Impact on Career Growth and Resume Value
Internships provide comprehensive project experience and deeper skill development, significantly enhancing long-term career growth and resume credibility. Micro-internships offer targeted, short-term project work that can quickly showcase specialized skills and adaptability, adding concise value to resumes for immediate job market relevance. Employers increasingly recognize micro-internships as proof of practical abilities, while full internships demonstrate sustained commitment and advanced professional growth.
Choosing the Right Experience for Your Career Goals
Traditional internships provide comprehensive, long-term project involvement that fosters in-depth skill development and professional networking, ideal for building a strong foundation in your career field. Micro-internships offer short-term, task-specific projects that allow quick skill acquisition and flexibility, making them suitable for exploring diverse industries or supplementing existing experience. Selecting between these options depends on your career goals, time availability, and the level of exposure needed to enhance your resume effectively.
Related Important Terms
Fractional Internship
Fractional internships offer a flexible alternative to traditional internships by allowing students to engage in project-based work for shorter, defined periods, often focusing on specific skills or tasks. Unlike micro-internships, fractional internships provide more substantial involvement in projects, fostering deeper learning and professional growth within a limited timeframe.
Gig-based Micro-internship
Gig-based micro-internships offer flexible, short-term project work allowing interns to gain hands-on experience without long-term commitments, contrasting traditional internships that often require extended periods and fixed schedules. This model enables students to build diverse portfolios rapidly while companies access specialized skills on-demand for specific projects.
Nano-internship
Nano-internships offer short-term, project-based work experiences that typically last from a few hours to a few days, providing immediate skill development and flexibility compared to traditional internships that extend over several months. These micro-internships enable students and professionals to engage in diverse projects across industries, accelerating practical learning while allowing companies to assess talent efficiently with minimal commitment.
Experiential Sprint Internship
Experiential Sprint Internships offer focused, short-term project work providing in-depth hands-on experience unlike Micro-internships, which are brief and task-oriented with limited scope. These sprints enable interns to develop specialized skills and deliver substantial project outcomes within a condensed timeframe, enhancing their practical expertise significantly.
Project-Based Micro-Gig
Project-based micro-gigs offer a flexible alternative to traditional internships by allowing students to complete short-term, skill-specific tasks that build real-world experience in a condensed timeframe. These micro-internships enable focused contributions to project work, often remote and paid, enhancing portfolio development and accelerating career readiness without long-term commitments.
Skill-burst Internship
Skill-burst internships offer short-term, focused project work that enhances specific skills quickly, making them ideal for candidates seeking targeted experience without long-term commitment. Unlike traditional internships, micro-internships provide flexible, bite-sized task opportunities that allow interns to build diverse portfolios through real-world project exposure.
Agile Project Placement
Micro-internships offer agile project placement by providing short-term, focused tasks that allow interns to gain practical experience and deliver immediate value without long-term commitments. Traditional internships typically involve extended durations with broader responsibilities, making them less adaptable to dynamic, fast-paced project environments.
Remote Micro-Immersion
Remote micro-internships offer flexible, short-term project work that allows students to gain specific skills and real-world experience without the extended commitment of traditional internships. These micro-immersions leverage digital platforms to connect interns with employers worldwide, enhancing accessibility and diversity in professional development.
Capsule Internship
Capsule Internship offers a streamlined alternative to traditional internships by delivering focused, project-based micro-internships that prioritize skill development and real-world application within shorter timeframes. This approach enhances flexibility for both interns and employers, enabling targeted experiential learning and efficient talent evaluation.
On-demand Micro-placement
On-demand micro-placement offers flexible, short-term project work tailored to specific skills, providing immediate value and focused experience compared to traditional internships that demand longer commitments. These micro-internships enable companies to quickly address project needs while giving interns diverse, real-world exposure in a condensed timeframe.
Internship vs Micro-internship for project work. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com