Internships provide hands-on experience and practical skills essential for early career development, allowing individuals to explore specific industries and build professional networks. Fellowships often offer more specialized training, mentorship, and research opportunities that deepen expertise in a particular field. Choosing between an internship and a fellowship depends on career goals, with internships emphasizing skill-building and exposure, while fellowships focus on advanced development and leadership potential.
Table of Comparison
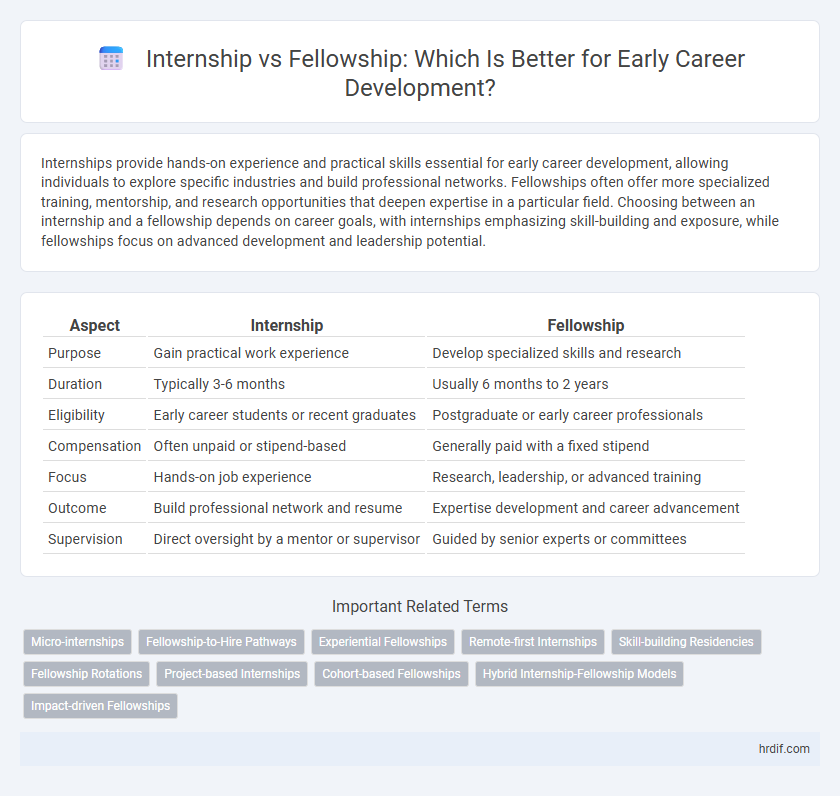
| Aspect | Internship | Fellowship |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Gain practical work experience | Develop specialized skills and research |
| Duration | Typically 3-6 months | Usually 6 months to 2 years |
| Eligibility | Early career students or recent graduates | Postgraduate or early career professionals |
| Compensation | Often unpaid or stipend-based | Generally paid with a fixed stipend |
| Focus | Hands-on job experience | Research, leadership, or advanced training |
| Outcome | Build professional network and resume | Expertise development and career advancement |
| Supervision | Direct oversight by a mentor or supervisor | Guided by senior experts or committees |
Understanding Internships and Fellowships
Internships provide hands-on work experience and practical skills within a specific industry, offering early career professionals opportunities to apply academic knowledge in real-world settings. Fellowships usually emphasize research, leadership development, or specialized training, often involving a stipend and a structured mentoring program. Both internships and fellowships enhance resumes, but internships focus more on skill acquisition and workplace exposure, while fellowships prioritize professional growth and networking in a specialized field.
Key Differences Between Internships and Fellowships
Internships typically offer hands-on work experience and skill development within companies or organizations over a short-term period, often ranging from a few weeks to several months. Fellowships are usually more specialized, long-term programs focused on research, professional growth, or leadership development, often including mentorship and stipends. The key differences lie in duration, focus, and structure, with internships emphasizing practical experience and fellowships prioritizing deeper expertise and career advancement in specific fields.
Eligibility Criteria for Internships vs Fellowships
Internships typically require candidates to be current students or recent graduates seeking practical experience in their field, often without stringent prior qualifications. Fellowships demand a more advanced level of education, such as a completed degree, and focus on specialized research or professional development for early-career individuals. Eligibility for internships emphasizes foundational skills and learning potential, whereas fellowships prioritize demonstrated expertise and a clear career trajectory.
Duration and Structure: Internship vs Fellowship
Internships typically last from a few weeks to several months and offer structured, hands-on experience within a specific department or project, ideal for gaining practical skills quickly. Fellowships often extend from several months to multiple years, providing deeper professional development through research, mentorship, and broader organizational involvement. The structured nature of fellowships usually includes additional training and networking opportunities, making them suitable for long-term career growth.
Skill Development Opportunities in Both Paths
Internships offer hands-on experience and practical skills in specific industry roles, enabling early career professionals to develop technical competencies and workplace etiquette. Fellowships emphasize advanced skill-building through research, mentorship, and specialized projects, fostering critical thinking and leadership abilities. Both paths enhance professional growth, but internships provide immediate application of skills while fellowships focus on deeper expertise and strategic development.
Financial Compensation: Internship vs Fellowship
Internships typically offer modest financial compensation or are unpaid, providing early career professionals with hands-on experience and skill development in exchange for limited wages or stipends. Fellowships often come with more substantial financial support, including competitive stipends or salaries, designed to enable fellows to engage in focused research or specialized training without financial strain. This distinction in compensation reflects the differing levels of responsibility, commitment, and professional advancement opportunities inherent in internships versus fellowships.
Networking Potential in Internships and Fellowships
Internships offer extensive networking opportunities through direct workplace interactions, mentorship, and exposure to industry professionals, fostering practical connections early in a career. Fellowships often provide specialized networking within academic or professional communities, emphasizing peer collaboration and expert engagement in a focused field. Both pathways enhance early career development, but internships typically deliver broader, hands-on networking access while fellowships cultivate niche, high-level relationships.
Impact on Career Trajectory
Internships provide hands-on experience and skill development that directly enhance early career opportunities and employability in competitive job markets. Fellowships often offer specialized research, professional networking, and mentorship, which can significantly influence long-term career progression and leadership roles. Choosing between internships and fellowships depends on immediate skill acquisition versus long-term career trajectory and industry exposure.
Industry Preferences for Internships and Fellowships
Internships are predominantly preferred by industries seeking practical, hands-on experience from early career professionals, especially in fields like technology, marketing, and finance. Fellowships tend to attract sectors such as academia, public policy, and healthcare, where specialized knowledge and research skills are prioritized. Companies often value internships for their short-term project contributions, while fellowships are favored for long-term strategic development and networking opportunities.
Choosing the Right Option for Early Career Success
Internships provide hands-on experience and practical skills in a specific industry, ideal for gaining immediate exposure and building a professional network. Fellowships focus on research, specialized training, and mentorship, offering deep expertise and leadership development in a particular field. Assess career goals, desired skill sets, and long-term aspirations to choose between internships and fellowships for early career success.
Related Important Terms
Micro-internships
Micro-internships offer short-term, project-based experiences ideal for early career development by providing practical skills and network opportunities without long-term commitment, contrasting with fellowships that typically involve deeper specialization and extended duration. These bite-sized internships enhance resume value and adaptability in competitive job markets, enabling swift skill acquisition and real-world exposure in diverse industries.
Fellowship-to-Hire Pathways
Fellowship-to-hire pathways offer structured, immersive experiences with a stronger emphasis on skill development, mentorship, and long-term career alignment compared to typical internships. Data shows fellows have a 30% higher conversion rate to full-time roles, making fellowships a strategic choice for early career professionals seeking enhanced job placement opportunities.
Experiential Fellowships
Experiential fellowships provide immersive, project-based learning opportunities that often include mentorship, offering deeper skill development compared to traditional internships. These fellowships emphasize real-world problem solving and leadership growth, making them valuable for early career professionals seeking hands-on experience and professional networking.
Remote-first Internships
Remote-first internships offer flexible, practical experiences that enhance early career development by providing access to global networks and diverse projects without geographical constraints. Unlike fellowships, which often emphasize research or specialized training, remote internships prioritize hands-on skills and real-world applications essential for building professional portfolios.
Skill-building Residencies
Internships provide hands-on experience and foundational skill-building opportunities essential for early career development, focusing on practical tasks within a professional environment. Fellowships, often longer and more specialized, combine advanced training with research or residencies that deepen expertise and professional networks in a targeted field.
Fellowship Rotations
Fellowship rotations offer structured, specialized training within multiple departments, enhancing practical expertise and interdisciplinary collaboration for early career development. This immersive experience contrasts with internships by providing deeper focus on advanced skills and professional growth in a specific field.
Project-based Internships
Project-based internships offer hands-on experience through real-world assignments that build practical skills and industry knowledge, making them ideal for early career development. Fellowships often focus on research or policy work with longer durations and structured mentorship, whereas project-based internships emphasize skill application and portfolio building.
Cohort-based Fellowships
Cohort-based fellowships offer structured, collaborative learning environments that enhance early career development through peer networking and mentorship, distinguishing them from traditional internships that often emphasize individual task completion. These fellowships provide targeted skill-building and industry-specific training, resulting in deeper professional growth and stronger career trajectories for participants.
Hybrid Internship-Fellowship Models
Hybrid Internship-Fellowship models combine hands-on project experience with mentorship and research opportunities, accelerating skill development and professional growth in early career stages. These programs offer structured work environments alongside academic enrichment, bridging practical industry exposure and advanced learning for more comprehensive career preparation.
Impact-driven Fellowships
Impact-driven fellowships offer early career professionals immersive, project-based experiences with strategic mentorship and networking opportunities, often emphasizing social change and innovation beyond traditional internship roles. These fellowships provide meaningful skill development and direct contributions to mission-oriented organizations, accelerating career growth and sector-specific impact more effectively than typical internships.
Internship vs Fellowship for early career development. Infographic
 hrdif.com
hrdif.com